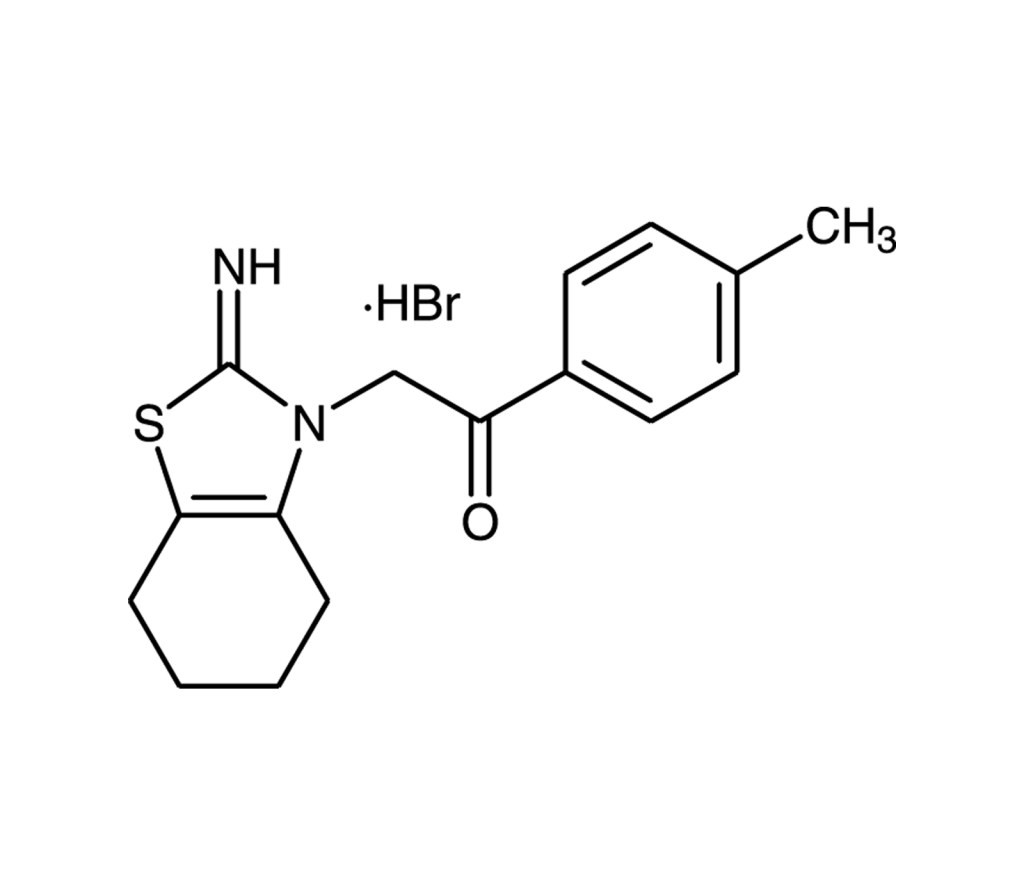
p53 inhibitor
Chemical inhibitor of p53 that protects mice from the side effects of cancer therapy. Reversibly blocks p53-dependent transcriptional activation and apoptosis. Protects against neuronal death in models of stroke and neurodegenerative disorders. Suppresses self-renewal of embryonic stem cells.
Shipping: Available products typically ship within 24/48h, via priority shipping.
Do you need support? Contact Customer Service or Technical Support.
Online Account
Access or Create Your Account
Product Details
| Alternative Name |
1-(4-Methylphenyl)-2-(4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-2-imino-3(2H)-benzothiazolyl)ethanone . HBr, PFT-α |
|---|---|
| Appearance |
White solid. |
| CAS |
63208-82-2 |
| Couple Target |
p53 |
| Couple Type |
Inhibitor |
| Formula |
C16H18N2OS . HBr |
| MW |
367.3 |
| Purity |
≥98% (TLC) |
| Solubility |
Soluble in DMSO (>25mg/ml) or methanol. |
Handling & Storage
| Use/Stability |
As indicated on product label or CoA when stored as recommended. Stable for at least 1 year after receipt when stored, as supplied, at -20°C. Stock solutions are stable for up to 3 months at -20°C. |
|---|---|
| Handling |
Protect from light. Keep under inert gas. Hygroscopic. |
| Long Term Storage |
-20°C |
| Shipping |
Ambient Temperature |
| Regulatory Status |
RUO – Research Use Only |
|---|
- Limb reduction in an Esco2 cohesinopathy mouse model is mediated by p53-dependent apoptosis and vascular disruption: A.S. Strasser, et l.; Nat. Commun. 15, 7154 (2024), Abstract
- Saturated Fatty Acids Promote GDF15 Expression in Human Macrophages through the PERK/eIF2/CHOP Signaling Pathway: L. L’homme, et al.; Nutrients 12, 3771 (2020), Abstract — Full Text
- A large shRNA library approach identifies lncRNA Ntep as an essential regulator of cell proliferation: Beermann, J., Kirste, D., et al.; Cell Death Differ. 25, 307 (2018), Abstract
- Acid ceramidase inhibition sensitizes human colon cancer cells to oxaliplatin through downregulation of transglutaminase 2 and β1 integrin/FAK−mediated signalling: M. Klobucar, et al.; Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 503, 843 (2018), Abstract
- Inhibition of the Cardiac Fibroblast-Enriched lncRNA Meg3 Prevents Cardiac Fibrosis and Diastolic Dysfunction: Piccoli, M. T., Gupta, S. K., et al.; Circ. Res. 121, 575 (2017), Abstract
- Reactivation of mutant p53 by capsaicin, the major constituent of peppers: Garufi, A., Pistritto, G., et al.; J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 35, 136 (2016), Abstract
- Murine Gammaherpesvirus 68 LANA and SOX Homologs Counteract ATM-Driven p53 Activity during Lytic Viral Replication: Sifford, J. M., Stahl, J. A., et al.; J. Virol. 90, 2571 (2015), Abstract
- Cisplatin-induced renal injury is independently mediated by OCT2 and p53: Sprowl, J. A., Lancaster, C. S., et al.; Clin. Cancer Res. 20, 4026 (2014), Abstract
- Dimethylfumarate attenuates restenosis after acute vascular injury by cell-specific and Nrf2-dependent mechanisms: Oh, C. J., Park, S., et al.; Redox Biol. 2, 855 (2014), Abstract
- Induction of p53-dependent p21 limits proliferative activity of rat hepatocytes in the presence of hepatocyte growth factor: Inoue, Y., Tomiya, T., et al.; PLoS One 8, e78346 (2013), Abstract
- IGF1 activates cell cycle arrest following irradiation by reducing binding of ΔNp63 to the p21 promoter: Mitchell, G. C., Fillinger, J. L., et al.; Cell Death Dis. 1, e50 (2011), Abstract
- Molecular mechanisms of nutlin-induced apoptosis in multiple myeloma: evidence for p53-transcription-dependent and -independent pathways: Saha, M. N., Jiang, H., et al.; Cancer Biol. Ther. 10, 567 (2010), Abstract
- Functional p53 signaling in Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus lymphomas: implications for therapy: Petre, C. E., Sin, S. H., et al.; J. Virol. 81, 1912 (2007), Abstract
- Silibinin activates p53-caspase 2 pathway and causes caspase-mediated cleavage of Cip1/p21 in apoptosis induction in bladder transitional-cell papilloma RT4 cells: evidence for a regulatory loop between p53 and caspase 2: Tyagi, A., Singh, R. P., et al.; Carcinogenesis 27, 2269 (2006), Abstract
- Pifithrin-alpha inhibits p53 signaling after interaction of the tumor suppressor protein with hsp90 and its nuclear translocation: P.J. Murphy, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 279, 30195 (2004), Abstract
- Transcription factor AP-2alpha triggers apoptosis in cardiac myocytes: F.U. Muller, et al.; Cell Death Differ. 11, 485 (2004), Abstract
- Inactivation of p21WAF1 sensitizes cells to apoptosis via an increase of both p14ARF and p53 levels and an alteration of the Bax/Bcl-2 ratio: D. Javelaud & F. Besancon; J. Biol. Chem. 277, 37949 (2002), Abstract — Full Text
- Wild-type and mutated presenilins 2 trigger p53-dependent apoptosis and down-regulate presenilin 1 expression in HEK293 human cells and in murine neurons: C. Alves da Costa, et al.; PNAS 99, 4043 (2002), Abstract
- Neurons are protected from excitotoxic death by p53 antisense oligonucleotides delivered in anionic liposomes: A. Lakkaraju, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 276, 32000 (2001), Abstract — Full Text
- Suppression of p53: a new approach to overcome side effects of antitumor therapy: E.A. Komarova & A.V. Gudkov; Biochemistry (Mosc) 65, 41 (2000), (Review), Abstract — Full Text
Related Products
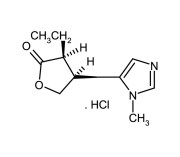
| CAS | 38966-21-1 |
|---|---|
| Couple Type | Inhibitor |
| Purity | ≥98% (TLC) |
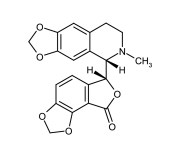
| Alternative Name | D-Bicuculline |
|---|---|
| CAS | 485-49-4 |
| Couple Type | Inhibitor, Ligand |
| Purity | ≥98% (HPLC) |
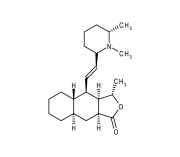
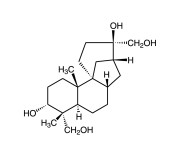
| Alternative Name | (3S,3aR,4R,4aS,8aR,9aS)-4-[(1E)-2-[(2R,6S)-1,6-Dimethyl-2-piperdinyl]ethenyl]decahydro-3-methyl-naphtho[2,3-c]furan-1(3H)-one |
|---|---|
| CAS | 6879-74-9 |
| Couple Type | Inhibitor |
| Purity | ≥98% |
Last modified: May 29, 2024
Datasheet, Manuals, SDS & CofA
Manuals And Inserts
Certificate of Analysis
Please enter the lot number as featured on the product label
SDS
Enzo Life Science provides GHS Compliant SDS
If your language is not available please fill out the SDS request form
 Lab Essentials
Lab Essentials AMPIVIEW® RNA probes
AMPIVIEW® RNA probes Enabling Your Projects
Enabling Your Projects  GMP Services
GMP Services Bulk Solutions
Bulk Solutions Research Travel Grant
Research Travel Grant Have You Published Using an Enzo Product?
Have You Published Using an Enzo Product?