Shipping: Available products typically ship within 24/48h, via priority shipping.
Do you need support? Contact Customer Service or Technical Support.
Online Account
Access or Create Your Account
Product Details
| Alternative Name |
Tumor necrosis factor-α, TNFSF 2 |
|---|---|
| Application Notes |
ELISA: binds to human TNF-R1 receptor. |
| Concentration |
1mg/ml after reconstitution. |
| Endotoxin Content |
<0.1EU/µg purified protein (LAL test; Associates of Cape Cod). |
| Formulation |
Lyophilized. Contains PBS. |
| Gene/Protein Identifier |
A002291 (UCSD Signaling Gateway ID) |
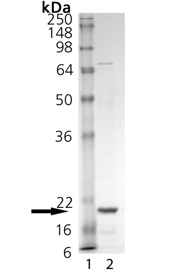
| MW |
~20kDa (SDS-PAGE). |
| Purity |
≥90% (SDS-PAGE) |
| Reconstitution |
Reconstitute with 50µl sterile water. Further dilutions should be made with medium containing 5% fetal calf serum. |
| Source |
Produced in E. coli. The extracellular domain of mouse TNF-α (tumor necrosis factor-α) (aa 77-235) is fused at the N-terminus to a linker peptide (8 aa) and a FLAG®-tag. |
| Specificity |
Binds to human, mouse and rat TNF-R1 and less efficiently to TNF-R2. In the presence of cross-linking enhancer (see Set Prod. No. ALX-850-061), TNF-α shows a significantly higher affinity for TNF-R2 than for TNF-R1, mimicking the characteristics of membrane-bound TNF-α. |
| Technical Info / Product Notes |
Historical lots have shown that it exerts its biological activity in a concentration range of 0.5-1ng/ml (WEHI 164 cells). FLAG is a registered trademark of Sigma-Aldrich Co. |
| UniProt ID |
P06804 |
Handling & Storage
| Use/Stability |
Stable for at least 6 months after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
|---|---|
| Handling |
Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. After reconstitution, prepare aliquots and store at -20°C. |
| Long Term Storage |
-20°C |
| Shipping |
Blue Ice |
| Regulatory Status |
RUO – Research Use Only |
|---|
- A RIPK1-specific PROTAC degrader achieves potent antitumor activity by enhancing immunogenic cell death: Mannion, J., Gifford, V., et al.; Immunity 57, 1514 (2024), Abstract
- ABIN1 (Q478) is Required to Prevent Hematopoietic Deficiencies through Regulating Type I IFNs Expression: Wu, X., Wang, Y., et al.; Adv. Sci. (Weinh.) 11, e2303555 (2024), Abstract
- Polarity protein AF6 functions as a modulator of necroptosis by regulating ubiquitination of RIPK1 in liver diseases: Xinyu, W., Qian, W., et al.; Cell Death Dis. 14, 673 (2023), Abstract
- Cleavage of cFLIP restrains cell death during viral infection and tissue injury and favors tissue repair: Martinez Lagunas, K., Savcigil, D. P., et al.; Sci. Adv. 9, eadg2829 (2023), Abstract
- Ubiquitin-binding domain in ABIN1 is critical for regulating cell death and inflammation during development: Li, M., Liu, Y., et al.; Cell Death Differ. 29, 2034 (2022), Abstract
- Synthesis of bioactive (1→6)-β-glucose branched poly-amido-saccharides that stimulate and induce M1 polarization in macrophages: Xiao, R., Zeng, J., et al.; Nat. Commun. 13, 4661 (2022), Abstract
- Bcl-3 promotes TNF-induced hepatocyte apoptosis by regulating the deubiquitination of RIP1: Hu, Y., Zhang, H., et al.; Cell Death Differ. 29, 1176 (2022), Abstract
- Tyrosine phosphorylation regulates RIPK1 activity to limit cell death and inflammation: Tu, H., Xiong, W., et al.; Nat. Commun. 13, 6603 (2022), Abstract
- RNPS1 inhibits excessive tumor necrosis factor/tumor necrosis factor receptor signaling to support hematopoiesis in mice: X. Zhong, et al.; PNAS 119, e2200128119 (2022), Abstract
- SMYD2 targets RIPK1 and restricts TNF-induced apoptosis and necroptosis to support colon tumor growth: Y.Q. Yu, et al.; Cell Death Dis. 13, 52 (2022), Abstract
- Simultaneous Inhibition of Three Major Cytokines and Its Therapeutic Effects: A Peptide-Based Novel Therapy against Endotoxemia in Mice: H.J. Shih, et al.; J. Pers. Med. 11, 436 (2021), Abstract
- Impaired RIPK1 ubiquitination sensitizes mice to TNF toxicity and inflammatory cell death: Kist, M., Komuves, L. G., et al.; Cell Death Differ. 28, 985 (2021), Abstract
- TAM Kinases Promote Necroptosis by Regulating Oligomerization of MLKL: Najafov, A., Mookhtiar, A. K., et al.; Mol. Cell 75, 457 (2019), Abstract
- Ubiquitination of RIPK1 suppresses programmed cell death by regulating RIPK1 kinase activation during embryogenesis: X. Zhang, et al.; Nat. Commun. 10, 4158 (2019), Abstract — Full Text
- K63-linked ubiquitination regulates RIPK1 kinase activity to prevent cell death during embryogenesis and inflammation: Y. Tang, et al.; Nat. Commun. 10, 4157 (2019), Abstract
- RIPK1 and Caspase-8 Ensure Chromosome Stability Independently of Their Role in Cell Death and Inflammation: G. Liccardi, et al.; Mol. Cell 73, 413 (2019), Abstract — Full Text
- Ubiquitin-Mediated Regulation of RIPK1 Kinase Activity Independent of IKK and MK2: A. Annibaldi, et al.; Mol. Cell 69, 566 (2018), Abstract — Full Text
- MK2 Phosphorylates RIPK1 to Prevent TNF-Induced Cell Death: I. Jaco, et al.; Mol. Cell 66, 698 (2017), Abstract — Full Text
- A novel TNFR1-triggered apoptosis pathway mediated by class IA PI3Ks in neutrophils: B. Geering, et al.; Blood 117, 5953 (2011), Application(s): Death assay on mouse neutrophils, Abstract — Full Text
- RasGAP-derived fragment N increases the resistance of beta cells towards apoptosis in NOD mice and delays the progression from mild to overt diabetes: N. Bulat, et al.; PLoS One 6, e22609 (2011), Abstract — Full Text
- Inhibition of interleukin 1 receptor/Toll-like receptor signaling through the alternatively spliced, short form of MyD88 is due to its failure to recruit IRAK-4: K. Burns, et al.; J. Exp. Med. 197, 263 (2003), Abstract — Full Text
- Conversion of membrane-bound Fas(CD95) ligand to its soluble form is associated with downregulation of its proapoptotic activity and loss of liver toxicity: P. Schneider, et al.; J. Exp. Med. 187, 1205 (1998), Abstract — Full Text
Last modified: May 29, 2024
Datasheet, Manuals, SDS & CofA
Manuals And Inserts
Certificate of Analysis
Please enter the lot number as featured on the product label
SDS
Enzo Life Science provides GHS Compliant SDS
If your language is not available please fill out the SDS request form
 Lab Essentials
Lab Essentials AMPIVIEW® RNA probes
AMPIVIEW® RNA probes Enabling Your Projects
Enabling Your Projects  GMP Services
GMP Services Bulk Solutions
Bulk Solutions Research Travel Grant
Research Travel Grant Have You Published Using an Enzo Product?
Have You Published Using an Enzo Product?