Enhanced ligand with improved stability providing significantly enhanced immune activation.
- Increased stability
- Enhanced immune activation
SUPERKILLERTRAIL® (soluble) (human), (recombinant) is an enhanced ligand that utilizes the Killer™ linker peptide mutated to increase disulfide-mediated cross-linking to form a more stable oligomer.
It has been well established that signals transmitted via TNF ligands and receptors are critical in mediating inflammation, cancer, and immunity. This has led to drug development aiming to either reduce or enhance receptor response. One limitation in this process is the inherent instability of recombinant ligands and their inability to effectively mimic the natural clustering of TNF receptors on the cell surface required for immune activation. Oligomerization of TNF ligands such as SUPERKILLERTRAIL® has been shown to improve stability and significantly enhance immune activation compared to recombinant ligands alone.
TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) is a protein ligand that induces the process of cell death called apoptosis.
Shipping: Available products typically ship within 24/48h, via priority shipping.
Do you need support? Contact Customer Service or Technical Support.
Online Account
Access or Create Your Account
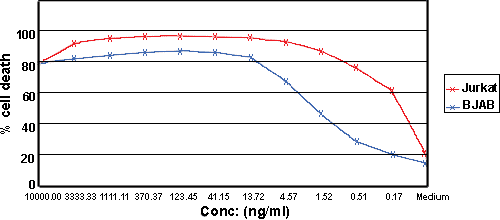
Figure: Apoptosis of TRAIL-sensitive cells. Apoptosis induction in BJAB cells by SUPERKILLERTRAIL®, Soluble (human) (rec.) reveals killing activity at concentrations of 10-15ng/ml, on Jurkat cells even as low as 1-10ng/ml. Method: 5×104 human BJAB cells were cultured in 50µl RPMI 1640 medium containing 10% fetal calf serum for 18 hours at 37°C in a 96-well plate in the presence of the indicated concentrations of SUPERKILLERTRAIL®, Soluble (human) (rec.). Concentrations of SUPERKILLERTRAIL®, Soluble (human) (rec.) required to induce apoptosis may vary depending on the cell type studied. Cell death was quantified by forward/sideward scatter (FSC/SSC) combined with propidium iodide (PI) staining analyzed by flow cytometry.
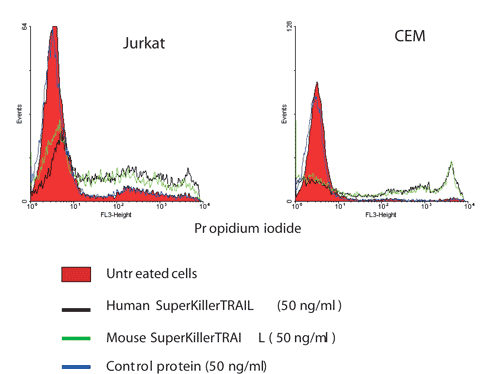
Figure: Comparison of pro-apoptotic activities of human and mouse SUPERKILLERTRAIL®, Soluble (human) (rec.) on human tumor cell lines Jurkat and CEM.Method: Cells were treated with mouse and human SUPERKILLERTRAIL®, Soluble (human) (rec.) (CC-mutant) (50ng/ml) for 14 hours, stained with propidium iodide and analyzed by flow cytometry.


Product Details
| Alternative Name |
TNFSF 10, Apo-2L, CD253 |
|---|---|
| Biological Activity |
Induces apoptosis at concentrations of >5ng/ml. Note: Does not require a cross-linking enhancer for its potent biological activity. Shows superior activity on human cell lines that require extensive cross-linking of TRAIL-Rs for killing (e.g. Jurkat). |
| Concentration |
0.5mg/ml |
| Endotoxin Content |
<0.01EU/µg purified protein (LAL test). |
| Formulation |
Liquid. HEPES, pH 7.4, sodium chloride, Tween 20, sucrose, azide free and 1mM DTT. |
| MW |
~26kDa |
| Purity |
≥98% (SDS-PAGE). MS analysis, <1% impurity (mainly Hsp70 protein from E. coli) |
| Purity Detail |
Affinity purified. Sterile filtered. |
| Source |
Produced in E. coli. The extracellular domain of human TRAIL (aa 95-281) is fused at the N-terminus to a His-tag and a linker peptide. The active multimeric conformation is stabilized by an inserted mutation allowing an additional CC-bridge. |
| Specificity |
Binds to human TRAIL receptors. |
| Technical Info / Product Notes |
Click here for an example of SUPERKILLERTRAIL® used by Eidgenössische Technische Hochschule (ETH) Zürich. |
| UniProt ID |
P50591 |
Handling & Storage
| Use/Stability |
Once thawed it is recommended to prepare appropriate aliquots and to store them at -80°C. In order to retain full activity aliquote concentration must be at least 0.1mg/ml; prepare 20µl aliquots and store at -80°C. Working dilution: 2-100ng/ml. Recommended: Prod. No. ALX-505-005, special storage and dilution buffer. |
|---|---|
| Handling |
Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Long Term Storage |
-80°C |
| Shipping |
Dry Ice |
| Regulatory Status |
RUO – Research Use Only |
|---|
- Novel meriolin derivatives activate the mitochondrial apoptosis pathway in the presence of antiapoptotic Bcl-2: L. Schmitt, et al.; Cell Death Discov. 10, 125 (2024), Abstract
- TRAIL receptors promote constitutive and inducible IL-8 secretion in non-small cell lung carcinoma: F. Favaro, et al.; Cell Death Dis. 13, 1046 (2022), Abstract
- Cytoplasmic mRNA decay represses RNA polymerase II transcription during early apoptosis: Duncan-Lewis, C., Hartenian, E., et al.; Elife 10, (2021), Abstract
- Impact of Staphylococcus aureus Small Colony Variants on Human Lung Epithelial Cells with Subsequent Influenza Virus Infection: J.J. Wilden, et al.; Microorganisms 8, 12 (2020), Abstract — Full Text
- Ferroptosis occurs through an osmotic mechanism and propagates independently of cell rupture: Riegman, M., Sagie, L., et al.; Nat. Cell Biol. 22, 1042 (2020), Abstract
- Mathematical Modeling Highlights the Complex Role of AKT in TRAIL-Induced Apoptosis of Colorectal Carcinoma Cells: Anderson, M. W., Moss, J. J., et al.; iScience 12, 182 (2019), Abstract
- Mitochondrial origins of fractional control in regulated cell death: L.C. Santos, et al.; Nat. Commun. 10, 1313 (2019), Abstract — Full Text
- Loss of the Cyclin-Dependent Kinase Inhibitor 1 in the Context of Brachyury-Mediated Phenotypic Plasticity Drives Tumor Resistance to Immune Attack: D.H. Hamilton, et al.; Front. Oncol. 8, 143 (2018), Abstract — Full Text
- Acquired Resistance of ER-Positive Breast Cancer to Endocrine Treatment Confers an Adaptive Sensitivity to TRAIL through Posttranslational Downregulation of c-FLIP: L. Piggott, et al.; Clin. Cancer Res. 24, 2452 (2018), Abstract
- PNPT1 Release from Mitochondria during Apoptosis Triggers Decay of Poly(A) RNAs: X. Liu, et al.; Cell 174, 187 (2018), Abstract
- N-glycosylation of mouse TRAIL-R restrains TRAIL-induced apoptosis: Y. Estornes, et al.; Cell Death Dis. 9, 494 (2018), Abstract — Full Text
- Staphylococcus aureus triggers a shift from influenza virus-induced apoptosis to necrotic cell death: A. van Krüchten, et al.; FASEB J. 32, 2779 (2018), Abstract — Full Text
- Corrected and Republished from: The COP9 Signalosome Interactswith and Regulates Interferon Regulatory Factor 5 Protein Stability: J. Korczeniewska, et al.; Mol. Cell. Biol. 38, e00493-17 (2018), Application(s):THP-1 cells, Abstract — Full Text
- Quinacrine mediated sensitization of glioblastoma (GBM) cells to TRAIL through MMP‐sensitive PEG hydrogel carriers: P. Erkoc, et al.; Macromol. Biosci. 17, 1600267 (2017), Abstract
- Synergistic induction of apoptosis by a polo-like kinase 1 inhibitor and microtubule-interfering drugs in Ewing sarcoma cells: L.M. Weiss, et al.; Int. J. Cancer 138, 497 (2016), Abstract
- Synthetic ligands of death receptor 5 display a cell-selective agonistic effect at different oligomerization levels: J. Beyrath, et al.; Oncotarget 7, 64942 (2016), Abstract — Full Text
- CRISPR library designer (CLD): software for multispecies design of single guide RNA libraries: F. Heigwer, et al.; Genome Biol. 17, 55 (2016), Abstract — Full Text
- Cytoplasmic levels of cFLIP determine a broad susceptibility of breast cancer stem/progenitor-like cells to TRAIL: R. French, et al.; Mol. Cancer. 14, 209 (2015), Application(s): Death induction of human breast cancer cells, Abstract — Full Text
- The cellular apoptosis susceptibility protein (CAS) promotes TRAIL-induced apoptosis and cell proliferation: P. Monian, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 91, 127 (2015), Application(s): Western blot, Abstract — Full Text
- pERK 1/2 inhibit Caspase-8 induced apoptosis in cancer cells by phosphorylating it in a cell cycle specific manner: R. Mandal, et al.; Mol. Oncol. 8, 232 (2014), Application(s): Analysis of human breast and ovarian cancer cells by WB, Abstract
- Gingerol sensitizes TRAIL-induced apoptotic cell death of glioblastoma cells: D.H. Lee, et al.; Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 279, 253 (2014), Abstract — Full Text
- Sulforaphane and TRAIL induce a synergistic elimination of advanced prostate cancer stem-like cells: S. Labsch, et al.; Int. J. Oncol. 44, 1470 (2014), Abstract — Full Text
- Survivin Inhibitor YM-155 Sensitizes Tumor Necrosis Factor – Related Apoptosis-Inducing Ligand-Resistant Glioma Cells to Apoptosis through Mcl-1 Downregulation and by Engaging the Mitochondrial Death Pathway: D.R. Premkumar, et al.; J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 346, 201 (2013), Application(s): Death induction of sensitized U373 and LNZ308 glioma cells, Abstract
- hnRNP K suppresses apoptosis independent of p53 status by maintaining high levels of endogenous caspase inhibitors: Z. Xiao, et al.; Carcinogenesis 34, 1458 (2013), Application(s): Death induction of hepatocellular carcinoma cells, Abstract
- TRAIL+ Human Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells Kill Tumor Cells In Vitro: Mechanisms of Imiquimod- and IFN-α-Mediated Antitumor Reactivity: M.L. Kalb, et al.; J. Immunol. 188, 1583 (2012), Application(s): Death induction of SKMel2, WM793 and Jurkat cells , Abstract — Full Text
- Isolation of a TRAIL Antagonist from the Serum of HIV-infected Patients: D.J. Schnepple, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 286, 35742 (2011), Application(s): Death induction of peripheral blood lymphocytes, Jurkat and HeLa cells, Abstract — Full Text
- Intrinsic Anticancer Drug Resistance of Malignant Melanoma Cells Is Abrogated by IFN-β and Valproic Acid: W.P. Roos, et al.; Cancer Res. 71, 4150 (2011), Application(s): Death induction of D05, A375, and D14 cells, Abstract — Full Text
- Bortezomib Sensitizes Malignant Human Glioma Cells to TRAIL, Mediated by Inhibition of the NF-κB Signaling Pathway: E.P. Jane, et al.; Mol. Cancer Ther. 10, 198 (2011), Application(s): Death induction on a panel of 8 glioma cell lines, Abstract — Full Text
- Sulforaphane targets pancreatic tumor-initiating cells by NF-{kappa}B-induced anti-apoptotic signaling: G. Kallifatidis, et al.; Gut 58, 949 (2009), Abstract
- Hepatitis C Virus Infection Sensitizes Human Hepatocytes to TRAIL-Induced Apoptosis in a Caspase 9-Dependent Manner: L. Lan, et al.; J. Immunol. 181, 4926 (2008), Application(s): Death induction of primary human hepatocytes and Huh7.5 cells, Abstract — Full Text
- CD73 Participates in Cellular Multiresistance Program and Protects against TRAIL-Induced Apoptosis: A. Mikhailov, et al.; J. Immunol. 181, 464 (2008), Application(s): Death induction of Jurkat cells, Abstract — Full Text
- Resistance to FasL and tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-mediated apoptosis in Sézary syndrome T-cells associated with impaired death receptor and FLICE-inhibitory protein expression: E. Contassot, et al.; Blood 111, 4780 (2008), Application(s): Death induction of CTCL cell lines, SzS and HD cells, Abstract — Full Text
- Fas Receptor Clustering and Involvement of the Death Receptor Pathway in Rituximab-Mediated Apoptosis with Concomitant Sensitization of Lymphoma B Cells to Fas-Induced Apoptosis: A.J. Stel, et al.; J. Immunol. 178, 2287 (2007), Application(s): Death induction of Ramos cells , Abstract — Full Text
- Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Protease Cleaves Procaspase 8 In Vivo: Z. Nie, et al.; J. Virol. 81, 6947 (2007), Application(s): Death induction of Jurkat cells, Abstract — Full Text
- Coxsackievirus Protein 2BC Blocks Host Cell Apoptosis by Inhibiting Caspase-3: M.A. Salako, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 281, 16296 (2006), Application(s): Death induction of HeLa cells, Abstract — Full Text
- Synthetic lethal targeting of MYC by activation of the DR5 death receptor pathway: Y. Wang, et al.; Cancer Cell 5, 501 (2004), Abstract
- IFNα-stimulated neutrophils and monocytes release a soluble form of TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL/Apo-2 ligand) displaying apoptotic activity on leukemic cells: C. Tecchio, et al.; Blood 103, 3837 (2004), Application(s): Death induction of human neutrophils , Abstract — Full Text
Related Products
KillerTRAIL™ Protein (soluble) (human), (recombinant)
ALX-201-073
Enhanced ligand that utilizes the proprietary Killer™ linker peptide that promotes stability.

| Alternative Name | Apo-2L, TNFSF 10, CD253 |
|---|---|
| Purity | ≥99% (SDS-PAGE, MS analysis) |
| Source | Produced in E. coli. The extracellular domain of human TRAIL (aa 95-281) is fused at the N-terminus to a His-tag and a linker peptide. |

| Alternative Name | Apo-2L, TNFSF 10, CD253 |
|---|---|
| Purity | ≥98% (SDS-PAGE) |
| Source | Produced in E. coli. The extracellular domain of human TRAIL (aa 95-281) is fused at the N-terminus to a His-tag and a linker peptide. |
Last modified: May 29, 2024
Datasheet, Manuals, SDS & CofA
Manuals And Inserts
Certificate of Analysis
Please enter the lot number as featured on the product label
SDS
Enzo Life Science provides GHS Compliant SDS
If your language is not available please fill out the SDS request form
 Lab Essentials
Lab Essentials AMPIVIEW® RNA probes
AMPIVIEW® RNA probes Enabling Your Projects
Enabling Your Projects  GMP Services
GMP Services Bulk Solutions
Bulk Solutions Research Travel Grant
Research Travel Grant Have You Published Using an Enzo Product?
Have You Published Using an Enzo Product?
