O-GlcNAcase inhibitor
- Highly pure O-GlcNAcase inhibitor
- Compound commonly used to induce diabetes in vivo
- Highly cited
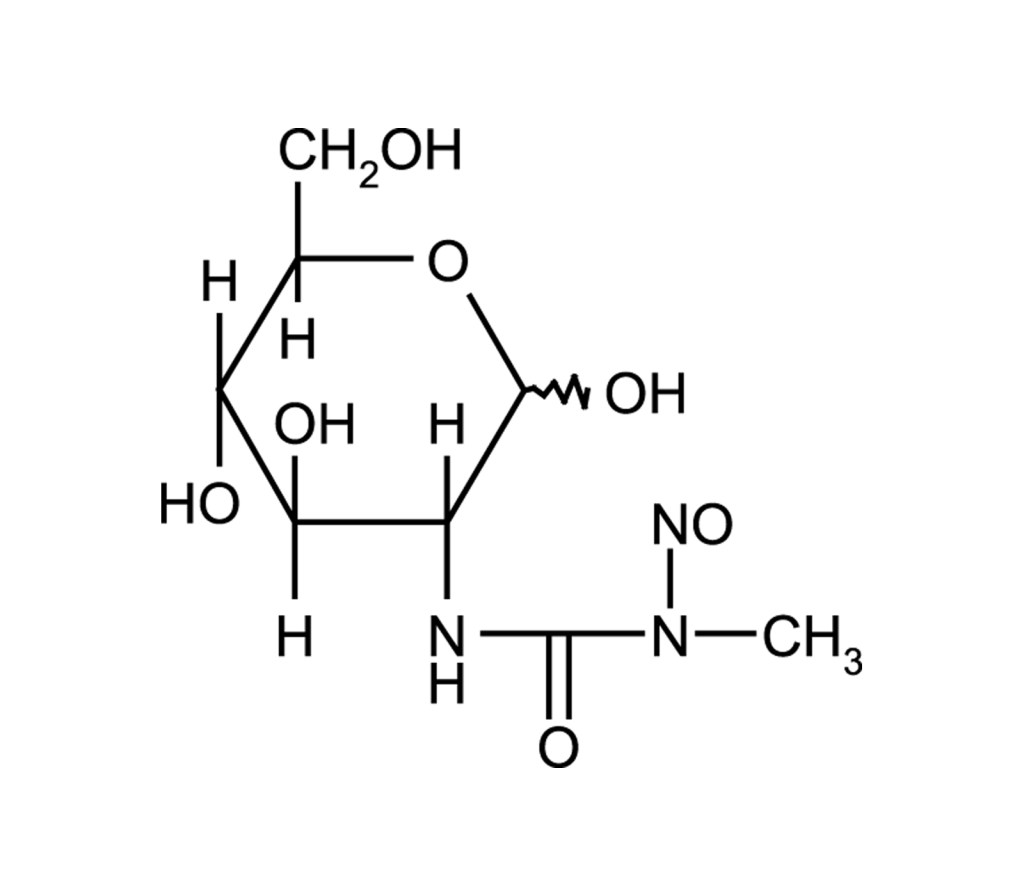
Streptozotocin (STZ) is a glucosamine-nitrosourea widely used as an inhibitor of O-GlcNAcase in b-cells to induce diabetes in rodents. Once entered inside b-cells via the glucose transporter GLUT2, STZ causes alkylation of DNA, activation of poly ADP-ribosylation, depletion of cellular ATP and NAD+, generation of superoxide radicals, and ultimately elimination of b-cells. STZ acts also as a nitric oxide (NO) donor and vasorelaxant capable of relaxing phenylephrine-contracted aortic rings at 10µM. STZ is a potent methylating agent for DNA.
Shipping: Available products typically ship within 24/48h, via priority shipping.
Do you need support? Contact Customer Service or Technical Support.
Online Account
Access or Create Your Account
Product Details
| Alternative Name |
Streptozocin, 2-Deoxy-2-(3-methyl-3-nitrosoureido)-D-glucopyranose, STZ |
|---|---|
| Appearance |
White to pale yellow crystalline solid. |
| CAS |
18883-66-4 |
| Couple Target |
O-GlcNAcase |
| Couple Type |
Inhibitor |
| Formula |
C8H15N3O7 |
| MI |
14: 8832 |
| MW |
265.2 |
| Purity |
≥97% (HPLC) |
| RTECS |
LZ5775000 |
| Solubility |
Soluble in 100% ethanol (200 proof at 0.92mg/ml) or water (nH2O at 102.8mg/ml). |
| Source |
Isolated from Streptomyces achromogenes. |
| Technical Info / Product Notes |
Solutions of Streptozotocin will spontaneously give off NO gas at room temperature. This NO release is slowed, but not completely stopped at -80°C, and the rate of NO release is also impacted by the solvent used (for example, dissolving Streptozotocin in buffers that contain sodium speeds up NO release). |
Handling & Storage
| Use/Stability |
As indicated on product label or CoA when stored as recommended. Because solutions of the compound spontaneously give off NO gas at room temperature, we recommend that solutions be made immediately before use. |
|---|---|
| Long Term Storage |
-20°C |
| Shipping |
Dry Ice |
| Regulatory Status |
RUO – Research Use Only |
|---|
- PET Imaging of Diabetes-Induced Alterations in Metabolism and Immune Activation: Lynch, S. E., Alsheikh, H. M., et al.; Mol. Imaging Biol. , (2025), Abstract
- Efficacy of a Novel Pleiotropic MMP-Inhibitor, CMC2.24, in a Long-Term Diabetes Rat Model with Severe Hyperglycemia-Induced Oral Bone Loss: H.D. Bhatt, et al.; J. Inflamm. Res. 16, 779 (2023), Abstract
- Pharmacokinetic assessment of cefpodoxime proxetil in diabetic rats: G. Mittal, et al.; J. Diabetes Metab. Disord. 22, 385 (2022), Abstract
- Post-stroke administration of L-4F promotes neurovascular and white matter remodeling in type-2 diabetic stroke mice: M. Zhou, et al.; Front. Neurol. 13, 863934 (2022), Abstract — Full Text
- Hirudo Lyophilized Powder Ameliorates Renal Injury in Diabetic Rats by Suppressing Oxidative Stress and Inflammation: F. Yang, et al.; Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2021, 6657673 (2021), Abstract — Full Text
- Normalizing glucose levels reconfigures the mammary tumor immune and metabolic microenvironment and decreases metastatic seeding: H.A.M. Alsheikh, et al.; Cancer Lett. 517, 24 (2021), Abstract
- Novologue Therapy Requires Heat Shock Protein 70 and Thioredoxin-Interacting Protein to Improve Mitochondrial Bioenergetics and Decrease Mitophagy in Diabetic Sensory Neurons: Y.A. Rodriguez, et al.; ACS Chem. Neurosci. 12, 3049 (2021), Abstract
- A Novel Modified-Curcumin Promotes Resolvin-Like Activity and Reduces Bone Loss in Diabetes-Induced Experimental Periodontitis: J. Deng, et al.; J. Inflamm. Res. 14, 5335 (2021), Abstract
- Carbohydrate response element‐binding protein regulates lipid metabolism via mTOR complex1 in diabetic nephropathy: N. Chen, et al.; J. Cell. Pysiol. 236, 625 (2021), Abstract
- C-myc upregulated by high glucose inhibits hacat differentiation by s100a6 transcriptional activation: J. Zhang, et al.; Front. Endocrinol. 12, 676403 (2021), Abstract — Full Text
- Modulation of Gut Microbiota Profile and Short-Chain Fatty Acids of Rats Fed with Taro Flour or Taro Starch: I. Surono, et al.; Int. J. Microbiol. 2020, 8893283 (2020), Abstract — Full Text
- Astragalus mongholicus Bunge and Panax notoginseng (Burkill) FH Chen formula for renal injury in diabetic nephropathy—in vivo and in vitro evidence: D. Wen, et al.; Front. Pharmacol. 11, 732 (2020), Abstract — Full Text
- Effect of functional food ingredients on gut microbiota in a rodent diabetes model: I.S. Surono, et al.; Nutr. Metab. 17, 77 (2020), Abstract — Full Text
- Tanshinone IIA ameliorates streptozotocin-induced diabetic nephropathy, partly by attenuating PERK pathway-induced fibrosis: S. Xu, et al.; Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 14, 5773 (2020), Abstract — Full Text
- 1-Palmitoyl-2-Linoleoyl-3-Acetyl-rac-Glycerol Attenuates Streptozotocin-Induced Pancreatic Beta Cell Damage by Promoting Glucose Transporter 2 Endocytosis: J. Kim, et al.; Mol. Cell. Biol. 39, e00157-19 (2019), Abstract — Full Text
- The effect of moderate endurance training on gastrocnemius retinol-binding protein 4 and insulin resistance in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats: M.R. Yousefi & H. TaheriChadorneshin; Interv. Med. Appl. Sci. 10, 59 (2018), Abstract — Full Text
- Aloe vera gel improves behavioral deficits and oxidative status in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats: S.R.F. Tabatabaei, et al.; Biomed. Pharmacother. 96, 279 (2017), Abstract
- Extravascular modified lipoproteins: a role in the propagation of diabetic retinopathy in a mouse model of type 1 diabetes: J. Yu, et al.; Diabetologia 59, 2026 (2016), Application(s): Plasma lipoproteins permeation, Abstract — Full Text
- Simvastatin enhances the hippocampal klotho in a rat model of streptozotocin-induced cognitive decline: S. Adeli, et al.; Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 72, 87 (2016), Application(s): Drug administration to rats, Abstract
- Elevation of cortical C26:0 due to the decline of peroxisomal β-oxidation potentiates amyloid β generation and spatial memory deficits via oxidative stress in diabetic rats: Y. Shi, et al.; Neuroscience 315, 125 (2015), Application(s): Intraperitoneally injected into rats, Abstract
- Characterization of Insulin-Secreting Porcine Bone Marrow Stromal Cells Ex Vivo and Autologous Cell Therapy In Vivo.: H.V. Do, et al.; Cell Transplant. 24, 1205 (2015), Abstract
- Finasteride reduces microvessel density and expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in renal tissue of diabetic rats: H. Tian, et al.; Am. J. Med. Sci. 349, 516 (2015), Abstract
- A Lipidomic Screen of Hyperglycemia-Treated Human Retinal Endothelial Cells Links Lipid Metabolites of 12/15-Lipoxygenase to Microvascular Dysfunction during Diabetic Retinopathy via NADPH Oxidase: A.S. Ibrahim, et al.; J. Lipid Res. 56, 599 (2015), Application(s): Injection, Abstract — Full Text
- Antihyperglycemic and antihyperlipidemic effects of hydroalcoholic extract of Securigera securidaca seeds in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats: Z. Rajaei, et al.; Adv. Biomed. Res. 4, 33 (2015), Application(s): Injection, Full Text
- Effects of Hydroalcoholic Extract of Watercress (Nasturtium Officinale) Leaves on Serum Glucose and Lipid Levels in Diabetic Rats: M.A. Hadjzadeh, et al.; Indian J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 59, 223 (2015), Application(s): Injection into rat, Abstract — Full Text
- Early Systemic Microvascular Damage in Pigs with Atherogenic Diabetes Mellitus Coincides with Renal Angiopoietin Dysbalance: M. Khairoun, et al.; PLoS One 10, e0121555 (2015), Application(s): Slow intravenous injection into pigs, Abstract — Full Text
- Pigment epithelium-derived factor inhibits retinal microvascular dysfunction induced by 12/15-lipoxygenase-derived eicosanoids: A.S. Ibrahim, et al.; Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1851, 290 (2015), Application(s): Injection, Abstract
- Antiglycation and Hypolipidemic Effects of Polyphenols from Zingiber officinale Roscoe (Zingiberaceae) in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats: M.I. Kazeem, et al.; Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 14, 55 (2015), Application(s): Injection, Full Text
- Streptozotocin induces G2 arrest in skeletal muscle myoblasts and impairs muscle growth in vivo: A.P. Johnston, et al.; Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 292, C1033 (2007), Abstract
- Genotoxicity of streptozotocin: A.D. Bolzan & M.S. Bianchi; Mutat. Res. 512, 121 (2002), (Review), Abstract
- The mechanism of alloxan and streptozotocin action in B cells of the rat pancreas: T. Szkudelski; Physiol. Res. 50, 537 (2001), (Review), Abstract
- N-monomethyl-arginine and nicotinamide prevent streptozotocin-induced double strand DNA break formation in pancreatic rat islets: F.J. Bedoya, et al.; Experientia 52, 344 (1996), Abstract
- Nitric oxide generation during cellular metabolization of the diabetogenic N-methyl-N-nitroso-urea streptozotozin contributes to islet cell DNA damage: K.-D. Kroncke, et al.; Biol. Chem. Hoppe Seyler 376, 179 (1995), Abstract
- Nitric oxide generation from streptozotocin: N.S. Kwon, et al.; FASEB J. 8, 529 (1994), Abstract
- Biochemical evidence for nitric oxide formation from streptozotocin in isolated pancreatic islets: J. Turk, et al.; BBRC 197, 1458 (1993), Abstract
- NO- and NO2-carrying molecules potentiate photorelaxation in rat trachea and aorta: K.C. Chang, et al.; BBRC 191, 509 (1993), Abstract
- Streptozotocin: a nitric oxide carrying molecule and its effect on vasodilation: G. Thomas & P. Ramwell; Eur. J. Pharmacol. 161, 279 (1989), Abstract
- Mouse models of insulin dependent diabetes: low-dose streptozocin-induced diabetes and nonobese diabetic (NOD) mice: H. Kolb; Diabetes Metab. Rev. 3, 751 (1987), Abstract
- Alkylation of DNA in rat tissues following administration of streptozotocin: R.A. Bennett & A.E. Pegg; Cancer Res. 41, 2786 (1981), Abstract
- The structure of streptozotocin: R.R. Herr, et al.; JACS 89, 4808 (1967), Abstract
- Studies on the diabetogenic action of streptozotocin: N. Rakieten, et al.; Cancer Chemother. Rep. 29, 91 (1963)
Related Products
AMP’D® GLP-1 ELISA kit
ENZ-KIT104
Ultra-sensitive AMP’D® GLP-1 ELISA kit enabling the ability to use less sample to detect levels of human Glucagon-like peptide 1 (7-36) amide, a potent promoter of insulin secretion, a major incretin hormone, and therapeutic for type 2 diabetes.

| Application | Colorimetric detection, ELISA |
|---|---|
| Assay Time | 3 hours |
| Sensitivity | 5.5 pg/ml (range 7.8-250 pg/ml) |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
Insulin ELISA kit
ENZ-KIT141
Highly sensitive Insulin ELISA kit enabling detection of insulin in serum, plasma, tissue culture media in just 3 hours.

| Application | Colorimetric detection, ELISA |
|---|---|
| Assay Time | 3 hours |
| Sensitivity | 15.5 pg/ml (15.6-500 pg/ml) |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Porcine |
Last modified: May 29, 2024
Datasheet, Manuals, SDS & CofA
Manuals And Inserts
Certificate of Analysis
Please enter the lot number as featured on the product label
SDS
Enzo Life Science provides GHS Compliant SDS
If your language is not available please fill out the SDS request form
 Lab Essentials
Lab Essentials AMPIVIEW® RNA probes
AMPIVIEW® RNA probes Enabling Your Projects
Enabling Your Projects  GMP Services
GMP Services Bulk Solutions
Bulk Solutions Research Travel Grant
Research Travel Grant Have You Published Using an Enzo Product?
Have You Published Using an Enzo Product?