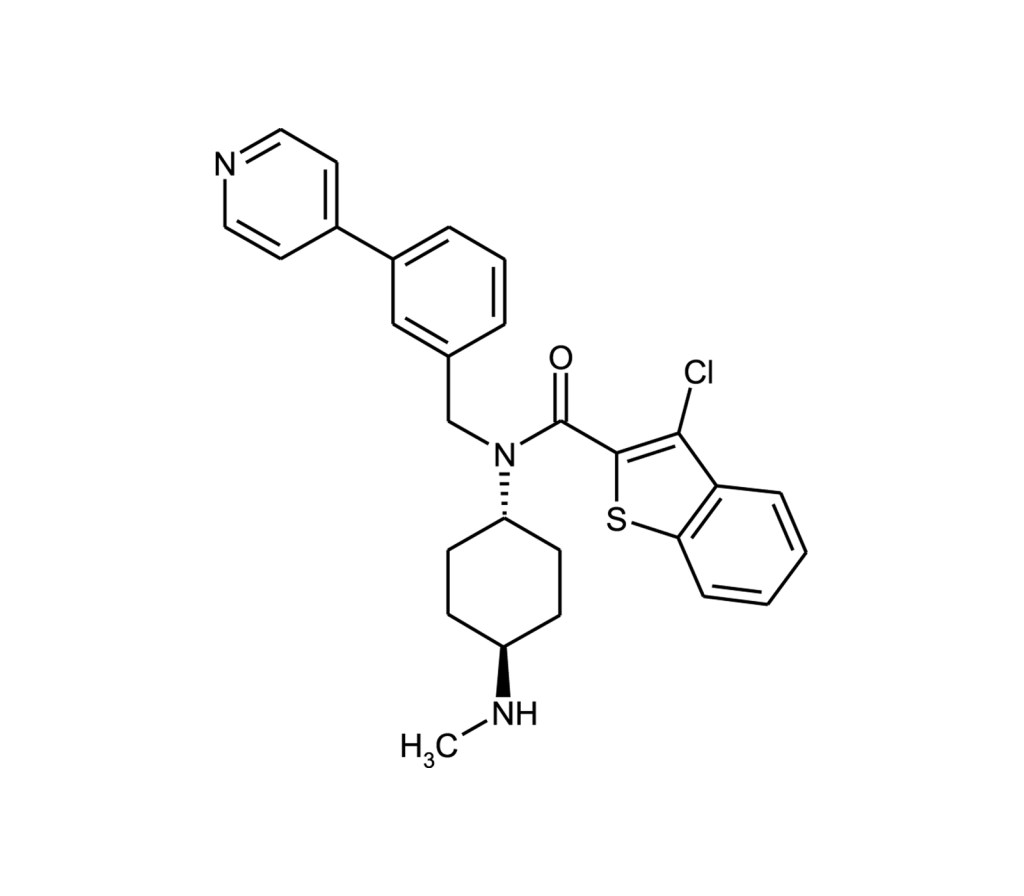
Smoothened agonist
- Potent Smoothened (Smo) receptor agonist
- Binds directly to Smo and antagonizes Cyclopamine
- Enhancer of neuronal differentiation of iPSCs into dopaminergic neurons
Smoothened (Smo) is a transmembrane receptor that relays the Hedgehog (Hh) signal and plays an essential role during embryonic development and tumorigenesis. SAG is a potent cell-permeable benzothiophene compound that modulates the coupling of Smo with its downstream effector by interacting with the Smo heptahelical domain (KD = 59 nM). SAG was shown to induce Hedgehog pathway activation independently of the Hh binding receptor Patched (Ptch) (EC50= ~3 nM in NIH 3T3-derived Shh-LIGHT2 cells) and counteract inhibition of Smo by Cyclopamine (Prod. No. BML-GR334). Smo is reported to act as an activator at low concentrations and as an inhibitor at very high concentrations.
Shipping: Available products typically ship within 24/48h, via priority shipping.
Do you need support? Contact Customer Service or Technical Support.
Online Account
Access or Create Your Account
Product Details
| Alternative Name |
3-chloro-N-[trans-4-(methylamino)cyclohexyl]-N-[[3-(4-pyridinyl)phenyl]methyl]-benzo[b]thiophene-2-carboxamide |
|---|---|
| Appearance |
Clear thin film (lyophilized). |
| CAS |
912545-86-9 |
| Couple Target |
Smoothened |
| Couple Type |
Activator, Ligand |
| Formula |
C28H28ClN3OS |
| Identity |
Identity determined by MS and NMR. |
| MW |
490.1 |
| Purity |
≥95% (HPLC) |
| Solubility |
Soluble in DMSO (10mg/ml), sparingly soluble in water (acidification with HCl increases water solubility). |
Handling & Storage
| Use/Stability |
As indicated on product label or CoA when stored as recommended. Stock solutions in DMSO are stable for at least 1 month when stored at -20°C. |
|---|---|
| Long Term Storage |
-20°C |
| Shipping |
Ambient Temperature |
| Regulatory Status |
RUO – Research Use Only |
|---|
- CETSA-MS unveils novel targets engaged by rigosertib to promote anti-tumor activity and inflammatory responses: Kechagioglou, P., Yurugi, H., et al.; iScience 28, 112748 (2025), Abstract
- Dual and opposing roles for the kinesin-2 motor, KIF17, in Hedgehog-dependent cerebellar development: Waas, B., Carpenter, B. S., et al.; Sci. Adv. 10, eade1650 (2024), Abstract
- Semaphorin Receptors Antagonize Wnt Signaling Through Beta-Catenin Degradation: Hoard, T. M., Liu, K., et al.; bioRxiv , (2024)
- CRX haploinsufficiency compromises photoreceptor precursor translocation and differentiation in human retinal organoids: D. Pan, et al.; Stem Cell Res. Ther. 14, 346 (2023), Abstract
- Generation of 3D lung organoids from human induced pluripotent stem cells for modeling of lung development and viral infection: Tiwari, S. K., Rana, T. M., et al.; Heliyon 9, e19601 (2023), Abstract
- Hedgehog-induced ciliary trafficking of kinesin-4 motor KIF7 requires intraflagellar transport but not KIF7’s microtubule binding: Y. Yue, et al.; Mol. Biol. Cell 33, br1 (2022), Abstract
- Mesenchymal-epithelial crosstalk shapes intestinal regionalisation via Wnt and Shh signalling: M. Maimets, et al.; Nat. Commun. 13, 715 (2022), Abstract
- Molecular basis underlying the ciliary defects caused by IFT52 variations found in skeletal ciliopathies: Y. Ishida, et al.; Mol. Biol. Cell 33, ar83 (2022), Abstract
- Hoxb1 regulates distinct signaling pathways in neuromesodermal and hindbrain progenitors to promote cell survival and specification: K. Pazur, et al.; Stem Cells 40, 175 (2022), Abstract
- Pituitary Lineage Differentiation from Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells in 2D and 3D Cultures: Y. Zhou, et al.; Stem Cells Dev. 31, 239 (2022), Abstract
- Plexins promote Hedgehog signaling through their cytoplasmic GAP activity: J.M. Pinskey, et al.; Elife 11, e74750 (2022), Abstract — Full Text
- Sequences in the stalk domain regulate autoinhibition and ciliary tip localization of the immotile kinesin-4 KIF7: T.L. Blasius, et al.; J. Cell Sci. 134, jcs258464 (2021), Abstract
- Human iPS cell derived RPE strips for secure delivery of graft cells at a target place with minimal surgical invasion.: Nishida, M., Tanaka, Y., et al.; Sci. Rep. 11, 21421 (2021), Abstract
- Taurine rescues mitochondria-related metabolic impairments in the patient-derived induced pluripotent stem cells and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in the retinal pigment epithelium: K. Homma, et al.; Redox Biol. 41, 101921 (2021), Abstract — Full Text
- Cooperation of the IFT-A complex with the IFT-B complex is required for ciliary retrograde protein trafficking and GPCR import: T. Kobayashi, et al.; Mol. Biol. Cell 32, 45 (2021), Abstract — Full Text
- Directed induction of retinal organoids from human pluripotent stem cells: X. Zhang, et al.; J. Vis. Exp. , (2021), Abstract
- CCRK/CDK20 regulates ciliary retrograde protein trafficking via interacting with BROMI/TBC1D32: T. Noguchi, et al.; PLoS One 16, e0258497 (2021), Abstract
- Mice lacking DYRK2 exhibit congenital malformations with lung hypoplasia and altered Foxf1 expression gradient: S. Yogosawa, et al.; Commun. Biol. 4, 1204 (2021), Abstract
- CEP120-mediated KIAA0753 recruitment onto centrioles is required for timely neuronal differentiation and germinal zone exit in the developing cerebellum: C.H. Chang, et al.; Genes Dev. 35, 1445 (2021), Abstract
- Thyroid hormone-induced expression of Foxl1 in subepithelial fibroblasts correlates with adult stem cell development during Xenopus intestinal remodeling: T. Hasebe, et al.; Sci. Rep. 10, 20715 (2020), Abstract — Full Text
- Transient primary cilia mediate robust hedgehog pathway-dependent cell cycle control: E.K. Ho, et al.; Curr. Biol. 30, 2829 (2020), Abstract — Full Text
- The excretory/secretory Products of Fifth-Stage Larval Angiostrongylus Cantonensis Induces Autophagy via the Sonic Hedgehog Pathway in Mouse Brain Astrocytes: K. Chen, et al.; PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 14, e0008290 (2020), Abstract — Full Text
- Single-cell transcriptomics of Parkinson’s disease human in vitro models reveals dopamine neuron-specific stress responses: H.J.R. Fernandes, et al.; Cell Rep. 33, 108263 (2020), Abstract
- Patient-specific retinal organoids recapitulate disease features of late-onset retinitis pigmentosa: M.L. Gao, et al.; Front. Cell. Dev. Biol. 8, 128 (2020), Abstract — Full Text
- Near-atomic structures of the BBSome reveal a novel mechanism for transition zone crossing: Bahl, K., Yang, S., et al.; bioRxiv , (2020)
- Generation of lung organoids from human pluripotent stem cells in vitro: Miller, A. J., Dye, B. R., et al.; Nat. Protoc. 14, 518 (2019), Abstract
- Atoh1 Controls Primary Cilia Formation to Allow for SHH-Triggered Granule Neuron Progenitor Proliferation: Chang, C. H., Zanini, M., et al.; Dev. Cell 48, 184 (2019), Abstract
- Acute Inhibition of Heterotrimeric Kinesin-2 Function Reveals Mechanisms of Intraflagellar Transport in Mammalian Cilia: Engelke, M. F., Waas, B., et al.; Curr. Biol. 29, 1137 (2019), Abstract
- Neurite Collapse and Altered ER Ca2+ Control in Human Parkinson Disease Patient iPSC-Derived Neurons with LRRK2 G2019S Mutation.: Korecka, J. A., Talbot, S., et al.; Stem Cell Reports 12, 29 (2019), Abstract
- Felodipine induces autophagy in mouse brains with pharmacokinetics amenable to repurposing: F.H. Soddiqi, et al.; Nat. Commun. 10, 1817 (2019), Abstract — Full Text
- A novel Cep120-dependent mechanism inhibits centriole maturation in quiescent cells: E. Betleja, et al.; Elife 7, e35439 (2018), Abstract — Full Text
- BBSome trains remove activated GPCRs from cilia by enabling passage through the transition zone: F. Ye, et al.; J. Cell Biol. 217, 1847 (2018), Abstract — Full Text
- Characterization of Primary Cilia in Normal Fallopian Tube Epithelium and Serous Tubal Intraepithelial Carcinoma: Abdelhamed, Z. A., Ryan, T. A., et al.; Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 28, 1535 (2018), Abstract
- Dynamic remodeling of membrane composition drives cell cycle through primary cilia excision: S.C. Phua, et al.; Cell 148, 264 (2017), Abstract — Full Text
- Sonic Hedgehog Activates Phospholipase A2 to Enhance Smoothened Ciliary Translocation: Arensdorf, A. M., Dillard, M. E., et al.; Cell Rep. 19, 2074 (2017), Abstract
- Extra-mitochondrial prosurvival BCL-2 proteins regulate gene transcription by inhibiting the SUFU tumour suppressor.: X. Wu, et al.; Nat. Cell Biol. 19, 1226 (2017), Abstract — Full Text
- Generation of Xeno-Free, cGMP-Compliant Patient-Specific iPSCs from Skin Biopsy.: L.A. Wiley, et al.; Curr. Protoc. Stem Cell Biol. 42, 4A.12.1 (2017), Abstract — Full Text
- Human iPSC-Derived Neural Progenitors Are an Effective Drug Discovery Model for Neurological mtDNA Disorders: Lorenz, C., Lesimple, P., et al.; Cell Stem Cell 20, 659 (2017), Abstract
- Maml1 acts cooperatively with Gli proteins to regulate sonic hedgehog signaling pathway: R. Quaranta, et al.; Cell Death Dis. 7, e2942 (2017), Abstract — Full Text
- Ciliary Entry of the Hedgehog Transcriptional Activator Gli2 Is Mediated by the Nuclear Import Machinery but Differs from Nuclear Transport in Being Imp-α/β1-Independent: Torrado, B., Graña, M., et al.; PLoS One 11, e0162033 (2016), Abstract
- cGMP production of patient-specific iPSCs and photoreceptor precursor cells to treat retinal degenerative blindness: L.A. Wiley, et al.; Sci. Rep. 6, 30742 (2016), Abstract — Full Text
- Functional anterior pituitary generated in self-organizing culture of human embryonic stem cells: C. Ozone, et al.; Nat. Commun. 7, Article number 10351 (2016), Application(s): Cell culture, Abstract
- Sequential Differentiation of Embryonic Stem Cells into Neural Epithelial-Like Stem Cells and Oligodendrocyte Progenitor Cells: J. Bian, et al.; PLoS One 11, e0155227 (2016), Application(s): Cell culture, Abstract — Full Text
- Identification and Correction of Mechanisms Underlying Inherited Blindness in Human iPSC-Derived Optic Cups: D.A. Parfitt, et al.; Cell Stem Cell 18, 769 (2016), Application(s): Cell culture, Abstract
- Modeling amyotrophic lateral sclerosis in pure human iPSc-derived motor neurons isolated by a novel FACS double selection technique: D. Toli, et al.; Neurobiol. Dis. 82, 269 (2015), Application(s): Cell Culture, Abstract
- Asymmetric cell division of granule neuron progenitors in the external granule layer of the mouse cerebellum: P. Haldipur, et al.; Biol. Open 4, 865 (2015), Abstract — Full Text
- A central region of Gli2 regulates its localization to the primary cilium and transcriptional activity: Santos, N., Reiter, J. F., et al.; J. Cell Sci. 127, 1500 (2014), Abstract
- Simultaneous measurement of smoothened entry into and exit from the primary cilium: Kim, J., Hsia, E. Y., et al.; PLoS One 9, e104070 (2014), Abstract
- An assay for clogging the ciliary pore complex distinguishes mechanisms of cytosolic and membrane protein entry: Takao, D., Dishinger, J. F., et al.; Curr. Biol. 24, 2288 (2014), Abstract
- Hedgehog signaling in human medullary thyroid carcinoma: a novel signaling pathway: Bohinc, B., Michelotti, G., et al.; Thyroid 23, 1119 (2013), Abstract
- Histone acetyltransferase PCAF is required for Hedgehog-Gli-dependent transcription and cancer cell proliferation: Malatesta, M., Steinhauer, C., et al.; Cancer Res. 73, 6323 (2013), Abstract
- Hedgehog-responsive mesenchymal clusters direct patterning and emergence of intestinal villi: Walton, K. D., Kolterud, A., et al.; PNAS 109, 15817 (2012), Abstract
- Small molecules greatly improve conversion of human-induced pluripotent stem cells to the neuronal lineage: Mak, S. K., Huang, Y. A., et al.; Stem Cells Int. 2012, 140427 (2012), Abstract
- Subregional specification of embryonic stem cell-derived ventral telencephalic tissues by timed and combinatory treatment with extrinsic signals: T. Danjo, et al.; J. Neurosci. 31, 1919 (2011), Abstract
- Hedgehog signaling regulates size of the dorsal aortae and density of the plexus during avian vascular development: Moran, C. M., Salanga, M. C., et al.; Dev. Dyn. 240, 1354 (2011), Abstract
- Identification of a suppressive mechanism for Hedgehog signaling through a novel interaction of Gli with 14-3-3: Y. Asoaka, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 285, 4185 (2010), Abstract — Full Text
- Wnt signaling stimulates transcriptional outcome of the Hedgehog pathway by stabilizing GLI1 mRNA: F.K. Noubissi, et al.; Cancer Res. 69, 8572 (2009), Abstract — Full Text
- Smoothened Signal Transduction is Promoted by G-Protein Coupled Receptor Kinase 2: A.R. Meloni et al.; Mol Cell Biol. 26, 7550 (2006), Abstract
- Oxysterols stimulate Sonic hedgehog signal transduction and proliferation of medulloblastoma cells: R.B. Corcoran and M.P. Scott; PNAS 103, 8408 (2006), Abstract — Full Text
- Activity-dependent internalization of smoothened mediated by beta-arrestin 2 and GRK2: W. Chen, et al.; Science 306, 2257 (2004), Abstract
- Small-molecule modulators of Hedgehog signaling: identification and characterization of Smoothened agonists and antagonists: M. Frank-Kamenetsky, et al.; J. Biol. 1, 10 (2002), Abstract — Full Text
- Small molecule modulation of Smoothened activity: J.K. Chen, et al.; PNAS 99, 14071 (2002), Abstract — Full Text
Related Products
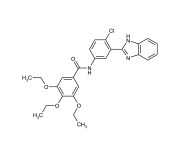
| Alternative Name | N-[3-(1H-Benzimidazol-2-yl)-4-chlorophenyl]-3,4,5-triethoxybenzamide |
|---|---|
| CAS | 329196-48-7 |
| Couple Type | Inhibitor |
| Purity | ≥95% |
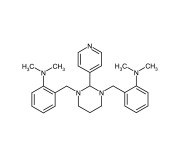
| Alternative Name | NSC 136476, 2,2’-[[Dihydro-2-(4-pyridinyl)-1,3(2H,4H)-pyrimidinediyl]bis(methylene)]bis[N,N-dimethyl]-benzenamine |
|---|---|
| CAS | 500579-04-4 |
| Couple Type | Inhibitor |
| Purity | ≥95% (HPLC) |
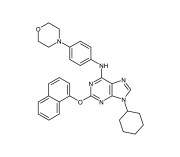
| Alternative Name | 2-(1-Naphthoxy)-6-(4-morpholinoanilino)-9-cyclohexylpurine |
|---|---|
| CAS | 483367-10-8 |
| Couple Type | Activator |
| Purity | ≥98% (HPLC) |
| Alternative Name | Shh signaling antagonist V, (E)-N-(4-benzylpiperazin-1-yl)-1-(3,5-dimethyl-1-phenylpyrazol-4-yl)methanimine |
|---|---|
| CAS | 304909-07-7 |
| Couple Type | Inhibitor |
| Purity | ≥99% (HPLC) |
Last modified: May 29, 2024
Datasheet, Manuals, SDS & CofA
Manuals And Inserts
Certificate of Analysis
Please enter the lot number as featured on the product label
SDS
Enzo Life Science provides GHS Compliant SDS
If your language is not available please fill out the SDS request form
 Lab Essentials
Lab Essentials AMPIVIEW® RNA probes
AMPIVIEW® RNA probes Enabling Your Projects
Enabling Your Projects  GMP Services
GMP Services Bulk Solutions
Bulk Solutions Research Travel Grant
Research Travel Grant Have You Published Using an Enzo Product?
Have You Published Using an Enzo Product?