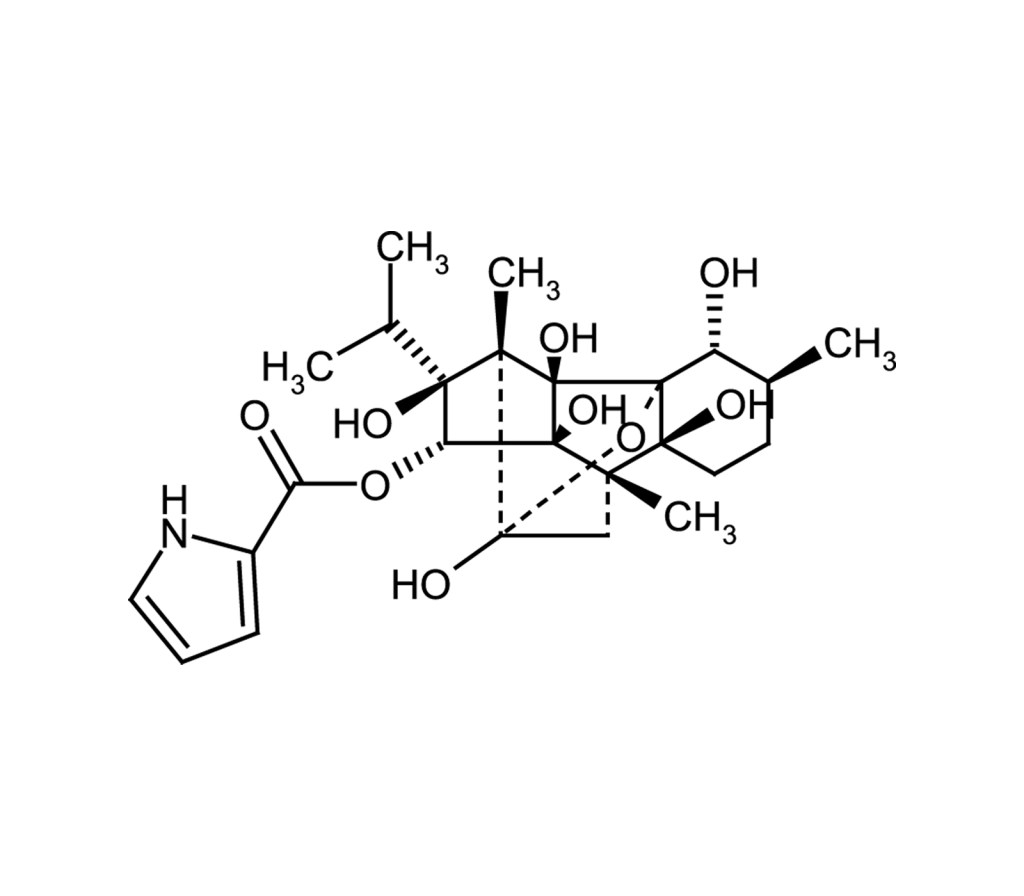
Ca2+ channel activator
Induces the release of intracellular Ca2+ . Ryanodine receptors mediate adenine nucleotide, Ca2+ and caffeine-sensitive release of Ca2+ from sarcoplasmic reticulum of cardiac and skeletal muscle and may also mediate intracellular Ca2+ release in neurons. Biphasic effect on sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium channels; Nanomolar levels open the channel and micromolar levels close it.
Shipping: Available products typically ship within 24/48h, via priority shipping.
Do you need support? Contact Customer Service or Technical Support.
Online Account
Access or Create Your Account
Product Details
| Appearance |
White to off-white solid. |
|---|---|
| CAS |
15662-33-6 |
| Couple Target |
Calcium channel |
| Couple Type |
Activator |
| Formula |
C25H35NO9 |
| MI |
14: 8307 |
| MW |
493.5 |
| Purity |
≥99% (HPLC) |
| RTECS |
VM4025000 |
| Solubility |
Soluble in methanol or DMSO (>29mg/ml), in 100% ethanol (16mg/ml); slightly soluble in water (warm). |
| Source |
Isolated from Ryania speciosa, Flacourtiaceae. |
Handling & Storage
| Use/Stability |
As indicated on product label or CoA when stored as recommended. |
|---|---|
| Handling |
Protect from light. |
| Long Term Storage |
-20°C |
| Shipping |
Ambient Temperature |
| Regulatory Status |
RUO – Research Use Only |
|---|
- Inactive ryanodine receptors sustain lysosomal availability for autophagy by promoting ER-lysosomal contact site formation: Vervliet, T., Loncke, J., et al.; Research Square , (2024)
- Imeglimin amplifies glucose-stimulated insulin release from diabetic islets via a distinct mechanism of action: Hallakou-Bozec, S., Kergoat, M., et al.; PLoS One 16, e0241651 (2021), Abstract
- MyoScreen, a High-Throughput Phenotypic Screening Platform Enabling Muscle Drug Discovery: Young, J., Margaron, Y., et al.; SLAS Discov. 23, 790 (2018), Abstract
- All three IP3 receptor isoforms generate Ca2+ puffs that display similar characteristics: Lock, J. T., Alzayady, K. J., et al.; Sci. Signal. 11, (2018), Abstract
- Increased calcium leak associated with reduced calsequestrin expression in hyperthyroid cardiomyocytes: D.R. de Alba-Aguayo, et al.; Cell Calcium 62, 29 (2017), Abstract
- Voltage Dependence of a Neuromodulator-Activated Ionic Current: Gray, M., Golowasch, J., et al.; eNeuro 3, (2016), Abstract
- Opposing roles of smooth muscle BK channels and ryanodine receptors in the regulation of nerve-evoked constriction of mesenteric resistance arteries: Krishnamoorthy, G., Sonkusare, S. K., et al.; Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 306, H981 (2014), Abstract
- Large-conductance voltage- and Ca2+-activated K+ channel regulation by protein kinase C in guinea pig urinary bladder smooth muscle: Hristov, K. L., Smith, A. C., et al.; Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 306, C460 (2014), Abstract
- Activation of muscarinic M3 receptors inhibits large-conductance voltage- and Ca2+-activated K+ channels in rat urinary bladder smooth muscle cells: Parajuli, S. P., Petkov, G. V., et al.; Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 305, C207 (2013), Abstract
- Selective inhibition of phosphodiesterase 1 relaxes urinary bladder smooth muscle: role for ryanodine receptor-mediated BK channel activation: W. Xin, et al.; Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 303, C1079 (2012), Application(s): ELISA analysis of guinea pig and human DSM cells, Abstract — Full Text
- Involvement of ryanodine receptors in neurotrophin-induced hippocampal synaptic plasticity and spatial memory formation: T. Adasme, et al.; PNAS U.S.A. 108, 3029 (2011), Abstract — Full Text
- I(f) and SR Ca(2+) release both contribute to pacemaker activity in canine sinoatrial node cells: Gao, Z., Chen, B., et al.; J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 49, 33 (2010), Abstract
- The interaction of ryanoids with individual ryanodine receptor channels: A. J. Williams and B. Tanna; Biol. Res. 37, 527 (2004), Abstract
- The pharmacology of ryanodine and related compounds: J. L. Sutko, et al.; Pharmacol. Rev. 49, 53 (1997), Abstract
- The ryanodine receptor/Ca2+ release channel: P.S. McPherson & K.P. Campbell; J. Biol. Chem. 268, 13765 (1993), Abstract
- Cyclic ADP-ribose: a new way to control calcium: A. Galione; Science 259, 325 (1993), Abstract
- Ryanodine as a functional probe of the skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ release channel: G. Meissner & A. el-Hashem; Mol. Cell. Biochem. 114, 119 (1992), Abstract
- The brain ryanodine receptor: a caffeine-sensitive calcium release channel: P.S. McPherson et al.; Neuron 7, 17 (1991), Abstract
- Depolarization promotes caffeine induced [3H]-noradrenaline release in calcium-free solution from peripheral sympathetic nerves: P.T. Toth et al.; Cell. Calcium 11, 557 (1990), Abstract
- Rapid kinetic analysis of the calcium-release channels of skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum: the effect of inhibitors: G. Calviello & M. Chiesi; Biochemistry 28, 1301 (1989), Abstract
- Structural aspects of ryanodine action and selectivity: A.L. Waterhouse, et al.; J. Med. Chem. 30, 710 (1987), Abstract
- Rapid flow chemical quench studies of calcium release from isolated sarcoplasmic reticulum: N. Ikemoto et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 260, 14096 (1985), Abstract
- The calcium-ryanodine receptor complex of skeletal and cardiac muscle: I.N. Pessah, et al.; BBRC 128, 449 (1985), Abstract
- Mechanism of action of ryanodine on cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum: J.J. Feher & G.B. Lipford; Biochim. Biophys. Acta 813, 77 (1985), Abstract
- Ryanodine: a modifier of sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium release in striated muscle: J.L. Sutko, et al.; Fed. Prod. 44, 2984 (1985), Abstract
- Ryanodine modification of cardiac muscle responses to potassium-free solutions. Evidence for inhibition of sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium release: J.L. Sutko & J.L. Kenyon; J. Gen. Physiol. 82, 385 (1983), Abstract
- The pharmacology of ryanodine: D.J. Jenden & A.S. Fairhurst; Pharmacol. Rev. 21, 1 (1969), (Review), Abstract
Last modified: May 29, 2024
Datasheet, Manuals, SDS & CofA
Manuals And Inserts
Certificate of Analysis
Please enter the lot number as featured on the product label
SDS
Enzo Life Science provides GHS Compliant SDS
If your language is not available please fill out the SDS request form
 Lab Essentials
Lab Essentials AMPIVIEW® RNA probes
AMPIVIEW® RNA probes Enabling Your Projects
Enabling Your Projects  GMP Services
GMP Services Bulk Solutions
Bulk Solutions Research Travel Grant
Research Travel Grant Have You Published Using an Enzo Product?
Have You Published Using an Enzo Product?