- Determination of 20S proteasome levels in biological samples (cell lysates, tissue extracts, plasma, serum)
- Comparison of 20S proteasome levels in plasma/serum samples associated with a particular disease/illness with samples from healthy controls
- Investigation of variation in 20S proteasome levels in abnormal cell lines/tissues
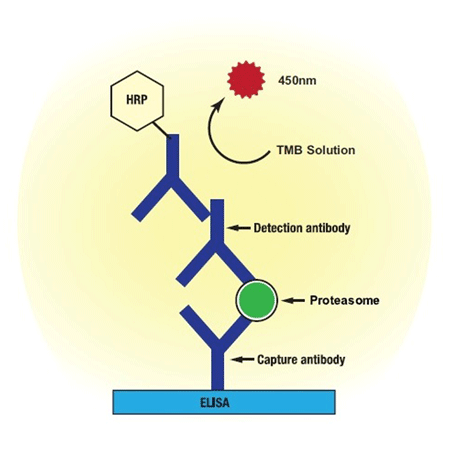
This kit provides the means to quantify 20S proteasome concentrations in biological samples using a sandwich ELISA technique, utilizing two 20S proteasome specific antibodies for capture and detection purposes together with a highly sensitive substrate. Sample 20S proteasome levels are determined by comparison to a 20S proteasome calibration curve produced in parallel. This kit provides sufficient material for 1×96 well plate set-up to be run.
Proteasomes are non-lysosomal proteolytic complexes localised primarily in the cytoplasm and in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. The 26S proteasome structure is composed of a 20S proteasome catalytic core complex and one or two 19S regulatory subcomplexes. The 20S core comprises two copies of 14 subunits (7 α-subunits and 7 β-subunits) arranged in a α7β7β7α7 cylindrical array. Varying catalytic subunit composition (β1, β1i; β2, β2i; β5, β5i) results in a variety of possible subtypes. The 19S regulatory subcomplexes, comprised of 6 ATPase and at least 10 non-ATPase subunits, specifically bind ubiquitinylated proteins and provide the 20S core with an ATP-ubiquitin–dependent proteolytic activity. The ubiquitin-proteasome system is the major non-lysosomal system for the degradation of short half-life proteins and peptides that are involved in basic cellular processes, such as cell-cycle regulation and apoptosis, transcriptional regulation, or antigen processing. Thus, protein degradation by the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway has a major regulatory function for proliferation activity and survival of both normal and malignant cells. The 20S proteasome has been detected in normal human blood plasma (known as circulating proteasome), possessing comparatively low specific activity and with a distinct pattern of subtypes. Proteasomes are often overexpressed in cancer cells; abnormally high expression of proteasomes having been found in human leukaemia cells, renal cancer cells and in breast cancer cell lines. In patients suffering from auto-immune diseases, malignant myelo-proliferative syndromes, multiple myeloma, acute and chronic lymphatic leukaemia, solid tumour, sepsis or trauma, the concentration of circulating proteasome has been found to be elevated, to correlate with the disease state, and may have prognostic significance. Proteasome levels have been measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) techniques in cell lysates, serum or plasma samples. This approach has been used to show that proteasome concentrations in peripheral blood are elevated in patients with certain types of malignant diseases, including multiple myeloma, suggesting that circulating proteasome levels may be correlated with tumour burden. The link between elevated circulating proteasome levels and disease activity has also been demonstrated in patients with systemic autoimmune diseases.
Shipping: Available products typically ship within 24/48h, via priority shipping.
Do you need support? Contact Customer Service or Technical Support.
Online Account
Access or Create Your Account
| Regulatory Status |
RUO – Research Use Only |
|---|
Last modified: May 29, 2024
 Lab Essentials
Lab Essentials AMPIVIEW® RNA probes
AMPIVIEW® RNA probes Enabling Your Projects
Enabling Your Projects  GMP Services
GMP Services Bulk Solutions
Bulk Solutions Research Travel Grant
Research Travel Grant Have You Published Using an Enzo Product?
Have You Published Using an Enzo Product?