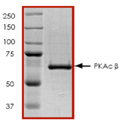
PKA belongs to the cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA) family. PKA isoforms type I and II include respective dimeric R subunits RI and RII which each produce two subunits designated RI-α, RI-β, RII-α, and RII-β. The catalytic subunit also consists of more than one gene product. Researchers cloned mammalian catalytic subunit C-α, C-β, and C-γ cDNAs. The catalytic subunit C-β belongs to the Ser/Thr protein kinase family. Activated by cAMP, PKA C-β resides in the cytoplasm (inactive holoenzyme and monomeric catalytic subunit), and translocates into the nucleus (monomeric catalytic subunit). A number of inactive tetrameric holoenzymes result from the combination of homo- or heterodimers of the different regulatory subunits associated with the two catalytic subunits. cAMP causes the dissociation of the inactive holoenzyme into a dimer of regulatory subunits bound to four cAMP and two free monomeric catalytic subunits. PKA C-β acts as a p75 neurotrophin receptor (NTR)-interacting protein, which phosphorylates p75 (NTR) at Ser304.
Shipping: Available products typically ship within 24/48h, via priority shipping.
Do you need support? Contact Customer Service or Technical Support.
Online Account
Access or Create Your Account
| Regulatory Status |
RUO – Research Use Only |
|---|
Last modified: October 9, 2025
 Lab Essentials
Lab Essentials AMPIVIEW® RNA probes
AMPIVIEW® RNA probes Enabling Your Projects
Enabling Your Projects  GMP Services
GMP Services Bulk Solutions
Bulk Solutions Research Travel Grant
Research Travel Grant Have You Published Using an Enzo Product?
Have You Published Using an Enzo Product?