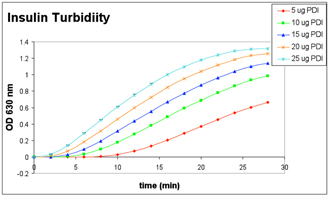
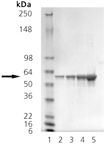
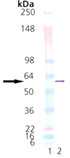
The mammalian protein disulfide-isomerase (PDI) family encompasses several highly divergent proteins involved in the processing and maturation of secretory proteins in the ER by catalyzing the rearrangement of disulfide bonds. PDI, an abundant protein of the ER (>400uM), contains a carboxy-terminal retention signal sequence, KDEL, similar to that of BiP and Grp94. The PDI proteins are characterized by the presence of one or more domains of ~95-110 amino acids related to the cytoplasmic protein thioredoxin. All but the PDI-D subfamily are composed entirely of repeats of such domains, with at least one domain containing – and one domain lacking – a redox-active Cys-X-X-Cys tetrapeptide. In addition to roles as redox catalysts and isomerases, PDI proteins perform such functions as peptide binding and cell adhesion, and may conduct chaperone activities1. Platelet surface thiols and disulfides play an important role in platelet responses. Catalytically active PDI resides on platelet surfaces where it mediates platelet aggregation and secretion by reducing disulfide bonds, thus exposing fibrinogen receptors in platelets.
Shipping: Available products typically ship within 24/48h, via priority shipping.
Do you need support? Contact Customer Service or Technical Support.
Online Account
Access or Create Your Account
| Regulatory Status |
RUO – Research Use Only |
|---|
Last modified: May 29, 2024
 Lab Essentials
Lab Essentials AMPIVIEW® RNA probes
AMPIVIEW® RNA probes Enabling Your Projects
Enabling Your Projects  GMP Services
GMP Services Bulk Solutions
Bulk Solutions Research Travel Grant
Research Travel Grant Have You Published Using an Enzo Product?
Have You Published Using an Enzo Product?