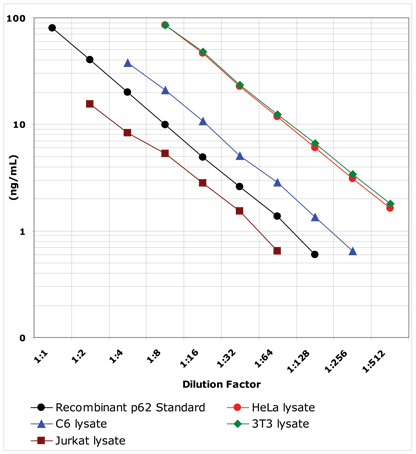
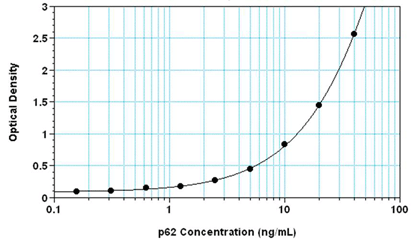
- Highly sensitive assay, measure as little as 100 pg/ml of p62
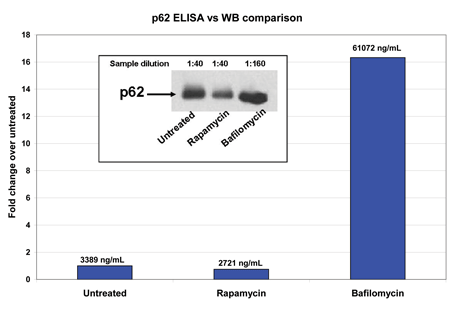
- Fully quantitative results surpass semi-quantitative Western blot analysis
- Higher throughput format, assay up to 40 samples in duplicate in just 3 hours
- Easy-to-use liquid color-coded reagents reduce errors
The p62 ELISA kit is a colorimetric, immunometric immunoassay kit with results in 3 hours.
The generic term ‘‘autophagy’’ comprises several processes by which the lysosome acquires cytosolic cargo, with three types of autophagy being discerned in the literature: (1) macroautophagy, characterized by the formation of a crescent-shaped structure (the phagophore) that expands to form the double-membrane autophagosome, capable of fusion with the lysosome; (2) microautophagy, in which lysosomes invaginate and directly sequester cytosolic components; and (3) chaperone-mediated autophagy (CMA), which involves translocation of unfolded proteins across the lysosomal membrane.
Upregulation of autophagy pathways occurs in response to extra- or intracellular stress and signals such as starvation, growth factor deprivation, ER stress and pathogen infection. Malfunction of these pathways is linked to various human pathologies including cancer, neurodegeneration and infectious diseases.
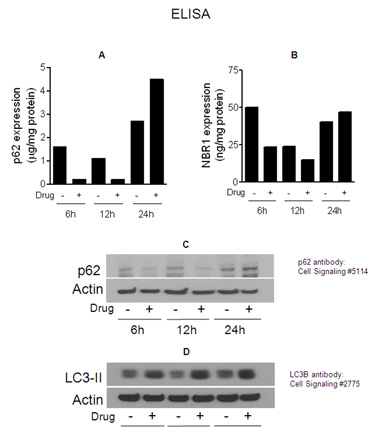
Selective macroautophagy describes the pathway of self-degradation of whole cellular components, protein aggregates or unusually long-lived proteins; in which double-membrane autophagosomes sequester organelles, ubiquitinylated proteins or ubiquitinylated protein aggregates and subsequently fuse with lysosomes for breakdown by resident hydrolases. Autophagic clearance of protein aggregates requires the ubiquitin-binding receptors p62 and NBR1.
The p62 protein, also known as sequestosome 1 (SQSTM1), has a dual functionality as both a scaffold protein and aiding in trafficking for protein degradation. It can polymerize and bind to NBR-1 via a PB1 (Phox and Bem1) domain, interact with ubiquitinated proteins linking them to the autophagic machinery via a UBA (ubiquitin-associated) domain and bind to the LC3II protein of the autophagy pathway through an LIR (LC3 interacting region) motif. p62 provides a key link between the ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS) and autophagy by facilitating autophagic degradation of ubiqutinated proteins, decreasing aggregation of misfolded and non-functional proteins within cells, resulting in enhanced cellular survival characteristics. Because p62 accumulates when autophagy is inhibited, and decreased levels can be observed when autophagy is induced, p62 may be used as a biomarker to study autophagic flux. Also, p62 has been implemented in neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s and in the skeletal disorder Paget’s disease of bone, establishing the p62 protein as a potential therapeutic target.
Shipping: Available products typically ship within 24/48h, via priority shipping.
Do you need support? Contact Customer Service or Technical Support.
Online Account
Access or Create Your Account
| Regulatory Status |
RUO – Research Use Only |
|---|
Last modified: May 29, 2024
 Lab Essentials
Lab Essentials AMPIVIEW® RNA probes
AMPIVIEW® RNA probes Enabling Your Projects
Enabling Your Projects  GMP Services
GMP Services Bulk Solutions
Bulk Solutions Research Travel Grant
Research Travel Grant Have You Published Using an Enzo Product?
Have You Published Using an Enzo Product?