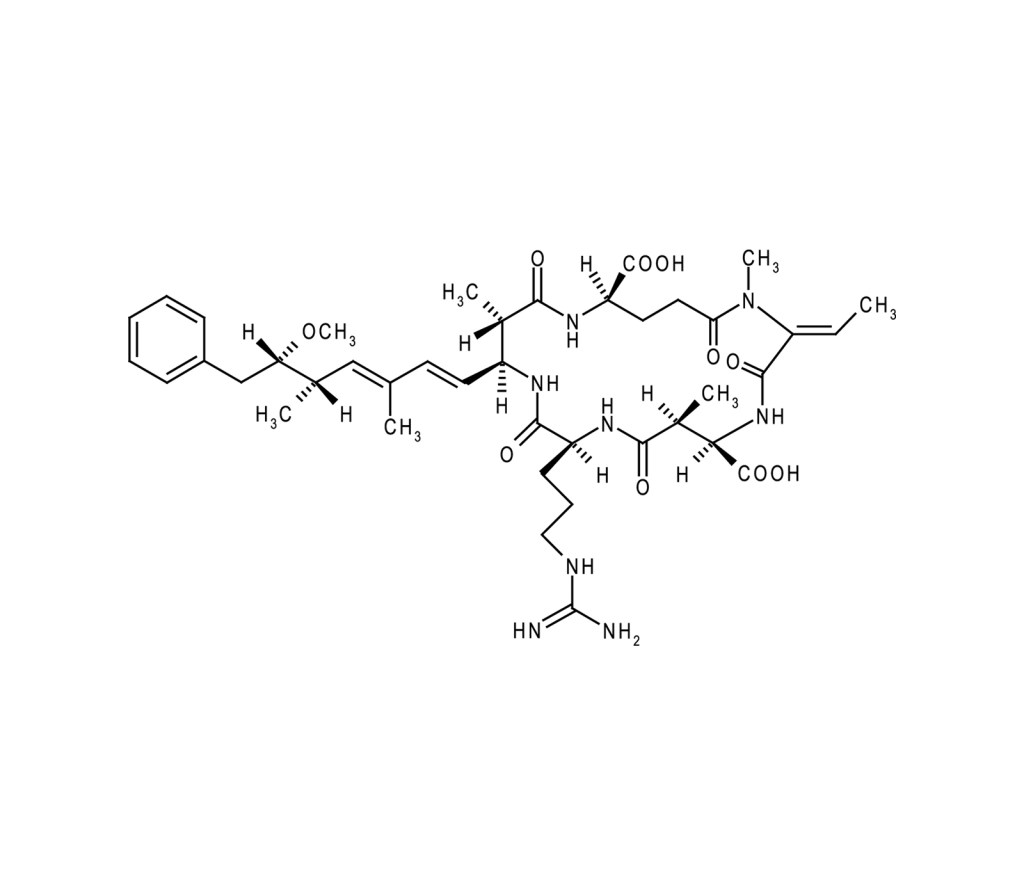
Inhibitor of PP1 and PP2A
- Hepatotoxin
- Potent inhibitor of PP1 and PP2A
- Useful for cytotoxicity and environmental studies
Nodularia spumigena is a cyanobacterium often found in drinking water in developing countries and capable of accumulating in fish and seafood. It produces nodularin, a genotoxic and hepatotoxic monocyclic pentapeptide. Nodularin inhibits protein phosphatase 1 (PP1) (IC50=1.8nM), protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) (IC50=0.026nM), and to a lesser extent protein phosphatase 2B (PP2B) (IC50=8.7µm). Nodularin is similar to microcystin-LR (Prod. No. ALX-350-012) but with increased water solubility. Nodularin is capable of inducing oxidative DNA damage by oxidation of purines as well as apoptosis in HepG2 cells.
May require a license for import, please contact us for more information.
Shipping: Available products typically ship within 24/48h, via priority shipping.
Do you need support? Contact Customer Service or Technical Support.
Online Account
Access or Create Your Account
Product Details
| Appearance |
Dry residue containing traces of monobasic potassium phosphate. |
|---|---|
| CAS |
118399-22-7 |
| Couple Target |
Serine/threonine-protein phosphatase |
| Couple Type |
Inhibitor |
| Formula |
C41H60N8O10 |
| Identity |
Identity determined by MS. |
| MW |
825.0 |
| Purity |
≥95% (HPLC) |
| RTECS |
GU2294250 |
| Solubility |
Soluble in methanol:water (1:1). |
| Source |
Isolated from Nodularia spumigena. |
Handling & Storage
| Use/Stability |
As indicated on product label or CoA when stored as recommended. |
|---|---|
| Long Term Storage |
-20°C |
| Shipping |
Ambient Temperature |
| Regulatory Status |
RUO – Research Use Only |
|---|
- Phosphorylation by JNK switches BRD4 functions: Devaiah, B. N., Singh, A. K., et al.; Mol. Cell 84, 4282 (2024), Abstract
- Cyanotoxins Increase Cytotoxicity and Promote Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Progression by Enhancing Cell Steatosis: S. Niture, et al.; Toxins (Basel) 15, 411 (2023), Abstract
- Toxicological response of Pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei to a hazardous cyanotoxin nodularin exposure: Y. Duan, et al.; Environ. Pollut. 318, 120950 (2023), Abstract
- A Feasibility Study into the Production of a Mussel Matrix Reference Material for the Cyanobacterial Toxins Microcystins and Nodularins: A.D. Turner, et al.; Toxins 15, 27 (2023), Abstract
- Multiclass cyanotoxin analysis in reservoir waters: Tandem solid-phase extraction followed by zwitterionic hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry: M.M. Aparicio-Muriana, et al.; Talanta 237, 122929 (2022), Abstract
- LC-MS/MS Validation and Quantification of Cyanotoxins in Algal Food Supplements from the Belgium Market and Their Molecular Origins: W.H.R. Van Hassel, et al.; Toxins 14, 513 (2022), Abstract
- Confirmation Using Triple Quadrupole and High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry of a Fatal Canine Neurotoxicosis following Exposure to Anatoxins at an Inland Reservoir: A.D. Turner, et al.; Toxins 14, 804 (2022), Abstract
- Lateral flow immunoassay (LFIA) for the detection of lethal amatoxins from mushrooms: C.S. Beyer, et al.; PLoS One 15, E0231781 (2020), Abstract — Full Text
- Phosphorylated Lamin A/C in the nuclear interior binds active enhancers associated with abnormal transcription in progeria: K. Ikegami, et al.; Dev. Cell 52, 699 (2020), Abstract — Full Text
- Uptake and accumulation of Microcystin-LR based on exposure through drinking water: An animal model assessing the human health risk: B. Greer, et al.; Sci. Rep. 8, 4913 (2018), Abstract — Full Text
- A new conjugation method used for the development of an immunoassay for the detection of amanitin, a deadly mushroom toxin: C.S. Beyer, et al.; Toxins 10, 265 (2018), Abstract — Full Text
- Simple, high efficiency detection of microcystins and nodularin-R in water by fluorescence polarization immunoassay: H. Zhang, et al.; Anal. Chim. Acta 992, 119 (2017), Abstract
- Comparative effects of nodularin and microcystin-LR in zebrafish: 2. Uptake and molecular effects in eleuthero-embryos and adult liver with focus on endoplasmic reticulum stress: S. Faltermann, et al.; Aquat. Toxicol. 171, 77 (2016), Application(s): Induced ER-stress and TNFα in liver organ cultures of zebrafish, Abstract
- Comparative effects of nodularin and microcystin-LR in zebrafish: 1. Uptake by organic anion transporting polypeptide Oatp1d1 (Slco1d1): S. Faltermann, et al.; Aquat. Toxicol. 171, 69 (2016), Application(s): Cellular uptake and immunoblotting, Abstract
- Nodularin induces tumor necrosis factor-alpha and mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK) and leads to induction of endoplasmic reticulum stress: N. Meili, et al.; Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 300, 25 (2016), Application(s): Cell culture, Abstract
- Rapid and Sensitive Analysis of Microcystins using Ionic Liquid-based in situ Dispersive Liquid-Liquid Microextraction: H. Yu, et al.; J. Chromatogr. A 1406, 10 (2015), Application(s): Cell Culture, Abstract
- Effect of light intensity on the relative dominance of toxigenic and nontoxigenic strains of Microcystis aeruginosa: Leblanc Renaud, S., Pick, F. R., et al.; Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 77, 7016 (2011), Abstract
- On the chemistry, toxicology and genetics of the cyanobacterial toxins, microcystin, nodularin, saxitoxin and cylindrospermopsin: L. Pearson, et al.; Mar. Drugs 8, 1650 (2010), Abstract — Full Text
- Nodularin-induced genotoxicity following oxidative DNA damage and aneuploidy in HepG2 cells: A. Lankoff, et al.; Toxicol. Lett. 164, 239 (2006), Abstract
- Genotoxic potential of Microcystin-LR and nodularin in vitro in primary cultured rat hepatocytes and in vivo in rat liver: N. Bouaicha, et al.; Environ. Toxicol. 20, 341 (2005), Abstract
- Bacterial degradation of microcystins and nodularin: S. Imanishi, et al.; Chem. Res. Toxicol. 18, 591 (2005), Abstract
- Study on the distribution of nodularin in tissues and cell level in mice: Z. Zhang, et al.; Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi 36, 100 (2002), Abstract
- The microcystins and nodularins: cyclic polypeptide inhibitors of PP1 and PP2A: B.M. Gulledgea, et al.; Curr. Med. Chem. 9, 1991 (2002), Abstract
- Influence of microcystin-YR and nodularin on the activity of some proteolytic enzymes in mouse liver: A. Lankoff & A. Kolataj; Toxicon 39, 419 (2001), Abstract
- Nodularin-Har: a new nodularin from Nodularia: K. Saito, et al; J. Nat. Prod. 64, 139 (2001), Abstract
- Detection of nodularin in flounders and cod from the Baltic Sea: V. Sipia, et al.; Environ. Toxicol. 16, 121 (2001), Abstract
- Isolation and detection of microcystins and nodularins, cyanobacterial peptide hepatotoxins: J. Meriluoto, et al.; Methods Mol. Biol. 145, 65 (2000), Abstract
- Degradation of the cyanobacterial hepatotoxin, nodularin, under light and dark conditions: H. Twist & G.A. Codd; FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 151, 83 (1997), Abstract
- Cyanobacterial nodularin is a potent inhibitor of type 1 and type 2A protein phosphatases: R.E. Honkanen, et al.; Mol. Pharmacol. 40, 577 (1991), Abstract
- Internal surface reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatographic separation of the cyanobacterial peptide toxins microcystin-LA, -LR, -YR, -RR and nodularin: J.A. Meriluoto, et al.; J. Chromatogr. 509, 390 (1990), Abstract
- In vitro and in vivo effects of protein phosphatase inhibitors, microcystins and nodularin, on mouse skin and fibroblasts: R. Matsushima, et al.; BBRC 171, 867 (1990), Abstract
- Rapid purification of the peptide toxins microcystin-LR and nodularin: C. Martin, et al.; FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 56, 1 (1990), Abstract
- Inhibition of protein phosphatases by microcystins and nodularin associated with hepatotoxicity: S. Yoshizawa, et al.; J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 116, 609 (1990), Abstract
- Toxicity and partial structure of a hepatotoxic peptide produced by the cyanobacterium Nodularia spumigena Mertens emend. L575 from New Zealand: W.W. Carmichael, et al.; Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 54, 2257 (1988), Abstract
- Nodularin, microcystin and the configuration of Adda: K.L. Rinehart, et al.; JACS 110, 8557 (1988)
Related Products
| Alternative Name | MC-LR |
|---|---|
| CAS | 101043-37-2 |
| Couple Type | Inhibitor |
| Purity | ≥95% (HPLC) |
| Alternative Name | MC-RR |
|---|---|
| CAS | 111755-37-4 |
| Couple Type | Inhibitor |
| Purity | ≥95% (HPLC) |
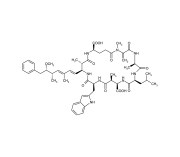
| Alternative Name | MC-LW |
|---|---|
| CAS | 157622-02-1 |
| Couple Type | Inhibitor |
| Purity | ≥95% (HPLC) |
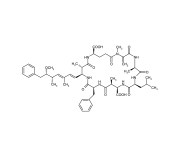
| Alternative Name | MC-LF |
|---|---|
| CAS | 154037-70-4 |
| Couple Type | Inhibitor |
| Purity | ≥95% (HPLC) |
Last modified: May 29, 2024
Datasheet, Manuals, SDS & CofA
Manuals And Inserts
Certificate of Analysis
Please enter the lot number as featured on the product label
SDS
Enzo Life Science provides GHS Compliant SDS
If your language is not available please fill out the SDS request form
 Lab Essentials
Lab Essentials AMPIVIEW® RNA probes
AMPIVIEW® RNA probes Enabling Your Projects
Enabling Your Projects  GMP Services
GMP Services Bulk Solutions
Bulk Solutions Research Travel Grant
Research Travel Grant Have You Published Using an Enzo Product?
Have You Published Using an Enzo Product?