PP2A inhibitor
- Hepatotoxin
- Potent inhibitor of PP2A
- Cited in several water quality-related research articles
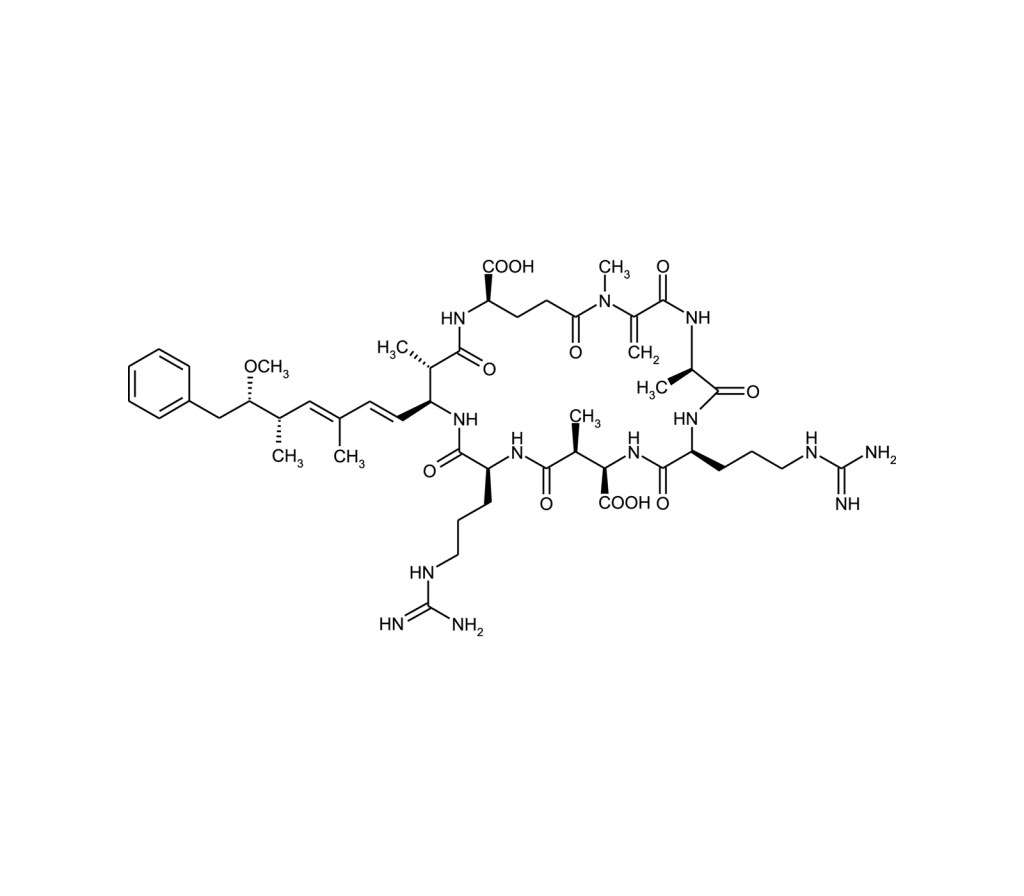
Microcystin-RR (MC-RR) is an Arg-Arg analog of Microcystin-LR (Prod. No. ALX-350-012). Although MC-RR was found to be up to 10-fold less toxic than MC-LR after intra-peritoneal injection in mice, it is both hepatotoxic and carcinogenic. It is a potent inhibitor of protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A).
May require a license for import, please contact us for more information.
Cyanobacteria are photosynthetic prokaryotes mostly present in freshwater ecosystems. The increasingly frequent appearance of cyanobacteria blooms in lakes and rivers is linked to climate changes and human activities. Microcystins are a group of cyclic heptapeptide hepatotoxins produced by a number of cyanobacterial genera. The most notable of which, and namesake, is the widespread genus Microcystis. Structurally, all microcystins consist of the generalized structure cyclo(-D-Ala1-X2-D-MeAsp3-Y4-Adda5-D-Glu6-Mdha7-). X and Y are variable L-amino acids, D-MeAsp is D-erythro-β-methylaspartic acid and Mdha is N-methyldehydroalanine. Adda is the cyanobacteria unique C20 β-amino acid 3-amino-9-methoxy-2,6,8-trimethyl-10-phenyl-deca-4,6-dienoic acid. Substitutions of the variable L-amino acids at positions 2 and 4 give rise to at least 21 known primary microcystin analogs and alterations in the other constituent amino acids result in more than 90 reported mycrocystins to date.
Shipping: Available products typically ship within 24/48h, via priority shipping.
Do you need support? Contact Customer Service or Technical Support.
Online Account
Access or Create Your Account
Product Details
| Alternative Name |
MC-RR |
|---|---|
| Appearance |
Clear to whitish film adhered to inside of vial. |
| CAS |
111755-37-4 |
| Couple Target |
Serine/threonine-protein phosphatase |
| Couple Type |
Inhibitor |
| Formula |
C49H75N13O12 |
| Identity |
Identity determined by MS. |
| MW |
1038.2 |
| Purity |
≥95% (HPLC) |
| Solubility |
Soluble in 80% aqueous methanol. |
| Source |
Isolated from Microcystis aeruginosa. |
Handling & Storage
| Use/Stability |
As indicated on product label or CoA when stored as recommended. |
|---|---|
| Handling |
For maximum product recovery after thawing, centrifuge the vial before opening the cap. |
| Long Term Storage |
-20°C |
| Shipping |
Ambient Temperature |
| Regulatory Status |
RUO – Research Use Only |
|---|
- Identification of Serine-Containing Microcystins by UHPLC-MS/MS Using Thiol and Sulfoxide Derivatizations and Detection of Novel Neutral Losses: S.H. Premathilaka, et al.; Anal. Chem. 96, 775 (2024), Abstract
- Cyanotoxins Increase Cytotoxicity and Promote Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Progression by Enhancing Cell Steatosis: S. Niture, et al.; Toxins (Basel) 15, 411 (2023), Abstract
- Novel one-point calibration strategy for high-throughput quantitation of microcystins in freshwater using LC-MS/MS: H. Zhang, et al.; Sci. Total Environ. 858, 159345 (2023), Abstract
- Bioinspired polydopamine-mediated metal-organic framework click-grafting aptamers functionalized fabric for highly-specific recognition of microcystin-leucine arginine: Q. Xie, et al.; J. Chromatogr. A 1688, 463728 (2023), Abstract
- Adsorption behavior of polyamide microplastics as a vector of the cyanotoxin microcystin-LR in environmental freshwaters: N. Kim, et al.; J. Hazard. Mater. 446, 130683 (2023), Abstract
- A Feasibility Study into the Production of a Mussel Matrix Reference Material for the Cyanobacterial Toxins Microcystins and Nodularins: A.D. Turner, et al.; Toxins 15, 27 (2023), Abstract
- Identification of Novel Microcystins Using High-Resolution MS and MSn with Python Code: D. Baliu-Rodriguez, et al.; Environ. Sci. Technol. 56, 1652 (2022), Abstract
- Effect of cold food storage techniques on the contents of Microcystins and Cylindrospermopsin in leaves of spinach (Spinacia oleracea) and lettuce (Lactuca sativa): A.C. Rodríguez, et al.; Food Chem. Toxicol. 170, 113507 (2022), Abstract
- Confirmation Using Triple Quadrupole and High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry of a Fatal Canine Neurotoxicosis following Exposure to Anatoxins at an Inland Reservoir: A.D. Turner, et al.; Toxins 14, 804 (2022), Abstract
- A Summer of Cyanobacterial Blooms in Belgian Waterbodies: Microcystin Quantification and Molecular Characterizations: W.H.R. Van Hassel, et al.; Toxins 14, 61 (2022), Abstract
- Multiclass cyanotoxin analysis in reservoir waters: Tandem solid-phase extraction followed by zwitterionic hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry: M.M. Aparicio-Muriana, et al.; Talanta 237, 122929 (2022), Abstract
- Adsorption of cyanotoxins on polypropylene and polyethylene terephthalate: Microplastics as vector of eight microcystin analogues: D.S. Moura, et al.; Environ. Pollut. 303, 119135 (2022), Abstract
- Renoprotection of microcystin-RR in unilateral ureteral obstruction-induced renal fibrosis: targeting the PKM2-HIF-1α pathway: Y. Ren, et al.; Front. Pharmacol. 13, 830312 (2022), Abstract — Full Text
- Microcystin-LR exposure enhances toxin-degrading capacity and reduces metabolic diversity of sediment microbial communities: Q. Ding, et al.; Environ. Pollut. 311, 119947 (2022), Abstract
- Improving the Quantification of Cyanotoxins Using a Mass Balance-Based Effective Concentration-Equivalent Concentration Approach: A. Jia, et al.; Environ. Sci. Technol. 56, 14418 (2022), Abstract
- Degradation of Multiple Peptides by Microcystin-Degrader Paucibacter toxinivorans (2C20): A.A. Santos, et al.; Toxins (Basel) 13, 265 (2021), Abstract — Full Text
- Energy-effective elimination of harmful microcystins by a non-thermal plasma process: H. Kim, et al.; Chemosphere 284, 131338 (2021), Abstract
- Influence of refrigeration and freezing in Microcystins and Cylindrospermopsin concentrations on fish muscle of tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) and tench (Tinca tinca): L. Diez-Quijada, et al.; Food Chem. Toxicol. 158, 112673 (2021), Abstract
- Health risk assessment related to cyanotoxins exposure of a community living near Tri An Reservoir, Vietnam: T.A.D. Nguyen, et al.; Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 28, 56079 (2021), Abstract
- Development and field evaluation of the organic-diffusive gradients in thin-films (o-DGT) passive water sampler for microcystins: P. Wong, et al.; Chemosphere 287, 132079 (2021), Abstract
- Remediation Strategies to Control Toxic Cyanobacterial Blooms: Effects of Macrophyte Aqueous Extracts on Microcystis aeruginosa (Growth, Toxin Production and Oxidative Stress Response) and on Bacterial Ectoenzymatic Activities: Z. Tazart, et al.; Microorganisms 9, 1782 (2021), Abstract
- Selective interaction of microcystin congeners with zebrafish (Danio rerio) Oatp1d1 transporter: P. Marić, et al.; Chemosphere 283, 131155 (2021), Abstract
- An ELISA-based Method for Variant-independent Detection of Total 3 Microcystins and Nodularins via Multi-immunogen Approach: J. Liu, et al.; Environ. Sci. Technol. 55, 12984 (2021), Abstract
- Machine Learning Prediction of Cyanobacterial Toxin (Microcystin) Toxicodynamics in Humans: S. Altaner, et al.; ALTEX 37, 24 (2020), Abstract
- Exposure to aerosolized algal toxins in South Florida increases short- and long-term health risk in Drosophila model of aging: J. Hu, et al.; Toxins 12, 787 (2020), Abstract — Full Text
- Microcystins and Microcystis aeruginosa PCC7806 extracts modulate steroidogenesis differentially in the human H295R adrenal model: V. Mallia, et al.; PLoS One 15, 12 (2020), Abstract — Full Text
- Dhb Microcystins Discovered in USA Using an Online Concentration LC-MS/MS Platform: J.A. Birbeck, et al.; Toxins (Basel) 11, 653 (2019), Abstract — Full Text
- Simple, high efficiency detection of microcystins and nodularin-R in water by fluorescence polarization immunoassay: H. Zhang, et al.; Anal. Chim. Acta 992, 119 (2017), Abstract
- Are We Underestimating Benthic Cyanotoxins? Extensive Sampling Results from Spain: E. A. Cantoral Uriza, et al.; Toxins (Basel) 9, 385 (2017), Abstract — Full Text
- Hepatotoxic Microcystin Removal Using Pumice Embedded Monolithic Composite Cryogel as an Alternative Water Treatment Method: F. Gurbuz, et al.; Water Res. 90, 337 (2016), Application(s): Injection, Abstract
- Effect of chlorination on the protein phosphatase inhibition activity for several microcystins: H. Mash, et al.; Water Res. 95, 230 (2016), Abstract
- Microcystin-RR exposure results in growth impairment by disrupting thyroid endocrine in zebrafish larvae: L. Xie, et al.; Aquat. Toxicol. 164, 16 (2015), Application(s): Cell Culture, Abstract
- Rapid and Sensitive Analysis of Microcystins using Ionic Liquid-based in situ Dispersive Liquid-Liquid Microextraction: H. Yu, et al.; J. Chromatogr. A 1406, 10 (2015), Application(s): Cell Culture, Abstract
- Similar uptake profiles of microcystin-LR and-RR in an in vitro human intestinal model: P. Zeller, et al.; Toxicology 290, 7 (2011), Abstract
- The apoptotic effect of oral administration of microcystin-RR on mice liver: P. Huang, et al.; Environ. Toxicol. 26, 443 (2010), Abstract
- Microcystin-RR-induced accumulation of reactive oxygen species and alteration of antioxidant systems in tobacco BY-2 cells: L. Yin, et al.; Toxicon. 46, 507 (2005), Abstract
- Physiological and biochemical analyses of microcystin-RR toxicity to the cyanobacterium Synechococcus elongatus: Z.Q. Hu, et al.; Environ. Toxicol. 19, 571 (2004), Abstract
- Determination of some physicochemical parameters of microcystins (cyanobacterial toxins) and trace level analysis in environmental samples using liquid chromatography: C. Rivasseau, et al.; J. Chromatogr. A 799, 155 (1998), Abstract
- Extraction and high-performance liquid chromatographic method for the determination of microcystins in raw and treated waters: L.A. Lawton, et al.; Analyst 119, 1525 (1994), Abstract
- Inhibition of protein phosphatases activates glucose-6-phosphatase in isolated rat hepatocytes: S. Claeyssens, et al.; FEBS Lett. 315, 7 (1993), Abstract
- Toxicity and toxins of natural blooms and isolated strains of Microcystis spp. (Cyanobacteria) and improved procedure for purification of cultures: M. Shirai, et al.; Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 57, 1241 (1991), Abstract
- The structure of a cyclic peptide toxin, cyanogenosin-RR from Microcystis aeruginosa: P. Painuly, et al.; THL 29, 11 (1988)
Related Products
| Alternative Name | MC-LR |
|---|---|
| CAS | 101043-37-2 |
| Couple Type | Inhibitor |
| Purity | ≥95% (HPLC) |
| Alternative Name | MC-YR |
|---|---|
| CAS | 101064-48-6 |
| Couple Type | Inhibitor |
| Purity | ≥95% (HPLC) |
| Alternative Name | MC-LW |
|---|---|
| CAS | 157622-02-1 |
| Couple Type | Inhibitor |
| Purity | ≥95% (HPLC) |
| Alternative Name | MC-LF |
|---|---|
| CAS | 154037-70-4 |
| Couple Type | Inhibitor |
| Purity | ≥95% (HPLC) |
Last modified: May 29, 2024
Datasheet, Manuals, SDS & CofA
Manuals And Inserts
Certificate of Analysis
Please enter the lot number as featured on the product label
SDS
Enzo Life Science provides GHS Compliant SDS
If your language is not available please fill out the SDS request form
 Lab Essentials
Lab Essentials AMPIVIEW® RNA probes
AMPIVIEW® RNA probes Enabling Your Projects
Enabling Your Projects  GMP Services
GMP Services Bulk Solutions
Bulk Solutions Research Travel Grant
Research Travel Grant Have You Published Using an Enzo Product?
Have You Published Using an Enzo Product?