MDA5 is a highly conserved helicase whose ATPase activity can be stimulated by RNA and less potently by DNA. It contains two N-terminal CARD domains and a C-terminal helicase domain. The helicase domain, once freed from the CARD domains, then translocates from the cytoplasm to the nucleus where it acts on chromatin architecture. This could allow a more easy access of CAD, thereby accelerating the degradation of genomic DNA.
Shipping: Available products typically ship within 24/48h, via priority shipping.
Do you need support? Contact Customer Service or Technical Support.
Online Account
Access or Create Your Account
This antibody is covered by our Worry-Free Guarantee.
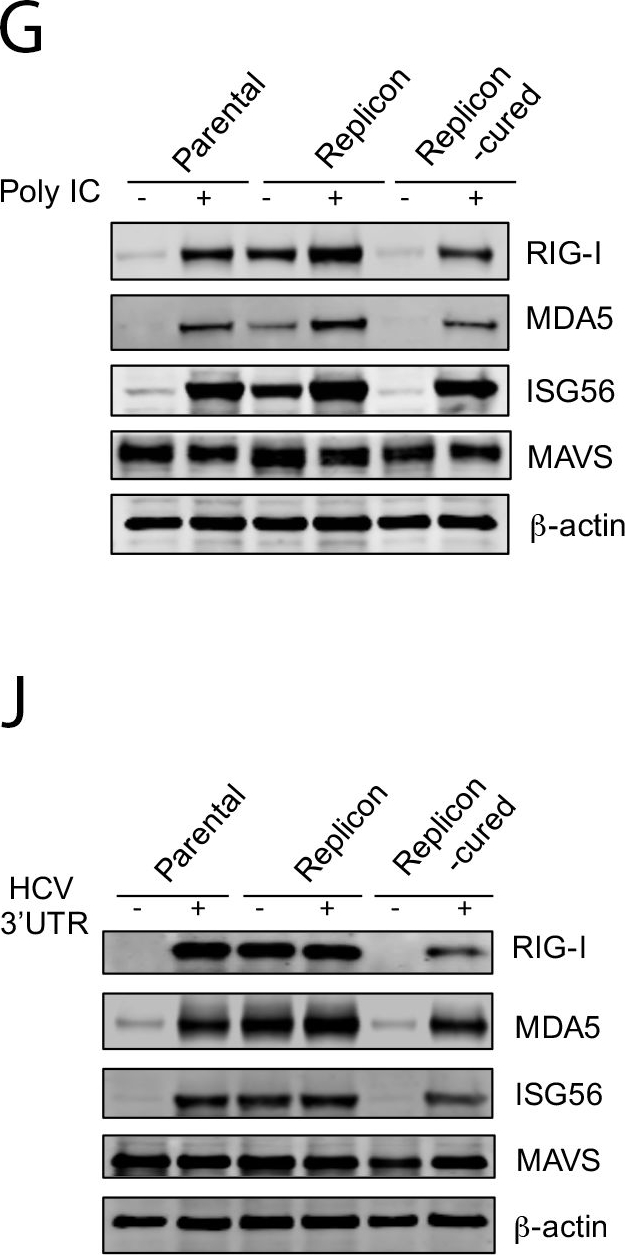
HEV does not target MAVS.(A) Confocal images showing MAVS and viral antigens in HepG2 cells infected with either HEV (top) or HAV (bottom). Cells were stained 5 days after infection with a rabbit anti-MAVS, chimpanzee 1313 serum (HEV), or a murine monoclonal antibody K24F2 (HAV). DAPI was used to stain the nuclei. Scale bar: 10 μm. (B) Confocal images showing the mitochondrial localization of MAVS in HepG2 cells with or without HEV replicon. MAVS was stained with a rabbit antibody against MAVS (green). Mitochondria was visualized with MitoTracker (red). Nuclei were stained with DAPI. Scale bar: 10 μm. (C) HepG2 cells with or without the HEV replicon were transfected with a MAVS-expressing plasmid along with a HAV 3ABC-expressing plasmid or an empty vector. The endogenous (closed arrowheads) and overexpressed MAVS (open arrowheads) were detected with a rabbit anti-MAVS antibody. Note that co-expression of HAV 3ABC led to the degradation of MAVS. (D) HepG2 cells with or without the HEV replicon were transfected with poly IC (6 μg/ml). After 6 h, cells were lysed and subjected to Western blot analysis using antibodies against MAVS and β-actin. Crude mitochondria were isolated and subjected to SDD-AGE for detection of MAVS polymer. (E-F) HepG2 cells with or without the HEV replicon were transfected with poly IC (6 μg/ml). After 6 h, intracellular IFN mRNA levels were measured by qRT-PCR (E) and supernatant IFN-λ concentration was measured by ELISA (F). In panel E, data are expressed as fold changes relative to mock transfected cells containing no replicon, and the results show the mean ± SEM of 2 independent experiments. (G) Immunoblots of endogenous RIG-I, MDA5, ISG56, MAVS, and β-actin in HepG2 cells, replicon cells or replicon-cured cells following poly IC transfection (1.5 μg/ml, 12 h). (H-I) HepG2 cells with or without the HEV replicon were transfected with the hepatitis C virus (HCV) 3’UTR RNA. After 6 h, intracellular IFN mRNA levels were measured by qRT-PCR (H), and concentrations of supernatant IFN-λ were measured by ELISA (I). The results show the mean ± SEM of 2 independent experiments. (J) Immunoblots of endogenous RIG-I, MDA5, ISG56, MAVS, and β-actin in HepG2 cells with or without the replicon before or after HCV 3’UTR RNA transfection (3.6 μg/ml, 14 h).
Image collected and cropped by CiteAb under a CC-BY license from the following publication: Hepatitis E virus persists in the presence of a type III interferon response. PLoS Pathog (2017)

Product Details
| Alternative Name |
Helicard, Melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5, Interferon-induced helicase C domain-containing protein 1, RH116, CADM-140 autoantigen, RIG-I-like receptor 2, RLR-2 |
|---|---|
| Application |
IP, WB |
| Formulation |
Liquid. In PBS containing 0.02% sodium azide. |
| Host |
Rabbit |
| Immunogen |
Recombinant human MDA5 (melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5) (aa 78-555). |
| Purity Detail |
Epitope-affinity purified. |
| Recommendation Dilutions/Conditions |
Immunoprecipitation (1:100)Western Blot (1:1,000)Suggested dilutions/conditions may not be available for all applications.Optimal conditions must be determined individually for each application. |
| Source |
Purified from rabbit serum. |
| Species Reactivity |
Human |
| UniProt ID |
Q9BYX4 |
| Worry-free Guarantee |
This antibody is covered by our Worry-Free Guarantee. |
Handling & Storage
| Use/Stability |
Stable for at least 1 year after receipt when stored as recommended. |
|---|---|
| Handling |
Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Short Term Storage |
+4°C |
| Long Term Storage |
-20°C |
| Shipping |
Blue Ice |
| Regulatory Status |
RUO – Research Use Only |
|---|
- Palbociclib and dsRNA sensor co-operate to enhance anti-cancer effects through ER stress and modulation of immune evasion.: Roulstone, V., Kyula-Currie, J., et al.; Nat. Commun. 16, 4855 (2025), Abstract
- Immune-epithelial cell cross-talk enhances antiviral responsiveness to SARS-CoV-2 in children.: Gonçalves Magalhães, V., Lukassen, S., et al.; EMBO Rep. 24, e57912 (2023), Application(s): WB, Abstract
- Prolonged Primary Rhinovirus Infection of Human Nasal Epithelial Cells Diminishes the Viral Load of Secondary Influenza H3N2 Infection via the Antiviral State Mediated by RIG-I and Interferon-Stimulated Genes.: Ong, H. H., Liu, J., et al.; Cells 12, (2023), Application(s): WB, Abstract
- Identification of interferon-stimulated genes with modulated expression during hepatitis E virus infection in pig liver tissues and human HepaRG cells.: Meyer, L., Duquénois, I., et al.; Front. Immunol. 14, 1291186 (2023), Application(s): WB, Abstract
- CDK4/6 inhibition and dsRNA sensor agonism co-operate to enhance anti-cancer effects through ER stress and immune modulation of tumour cells: Roulstone, V., Kyula, J., et al.; bioRxiv , (2022), Reactant(s): Mouse
- Cooperative effects of RIG-I-like receptor signaling and IRF1 on DNA damage-induced cell death.: Magalhães, V. G., Binder, M., et al.; Cell Death Dis. 13, 364 (2022), Application(s): WB / Reactant(s): Human, Abstract
- MDA5 Governs the Innate Immune Response to SARS-CoV-2 in Lung Epithelial Cells: X. Yin, et al.; Cell Rep. 32, 108628 (2021), Application(s): Western Blot, Abstract — Full Text
- Cooperative Effects of RIG-I-like Receptor Signaling and IRF1 on DNA Damage-Induced Cell Death: Binder, M., Wüst, S., et al.; bioRxiv , (2021), Application(s): WB / Reactant(s): Human
- Structural analysis of RIG-I-like receptors reveals ancient rules of engagement between diverse RNA helicases and TRIM ubiquitin ligases.: Young, J. M., Zhu, Z., et al.; Mol. Cell 81, 599 (2021), Application(s): WB / Reactant(s): Human, Abstract
- ADAR and hnRNPC deficiency synergize in activating endogenous dsRNA-induced type I IFN responses.: Modrusan, Z., Yeo, G. W., et al.; J. Exp. Med. 218, (2021), Application(s): WB / Reactant(s): Human, Abstract
- Structural analysis of RIG-I-like receptors reveals ancient rules of engagement between diverse RNA helicases and TRIM ubiquitin ligases: Kato, K., Ahmad, S., et al.; bioRxiv , (2020)
- DHX15 Is a Coreceptor for RLR Signaling That Promotes Antiviral Defense Against RNA Virus Infection: S. Pattabhi, et al.; J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 39, 331 (2019), Abstract
- Basal expression of interferon regulatory factor 1 drives intrinsic hepatocyte resistance to multiple RNA viruses: Yamane, D., Feng, H., et al.; Nat. Microbiol. 4, 1096 (2019), Abstract
- The 14-3-3η chaperone protein promotes antiviral innate immunity via facilitating MDA5 oligomerization and intracellular redistribution: J.P. Lin, et al.; PLoS Pathog. 15, e1007582 (2019), Application(s): WB / Reactant(s) Human, Abstract
- Inhibition of Japanese encephalitis virus infection by the host zinc-finger antiviral protein: H.P. Chiu, et al.; PLoS Pathog. 14, e1007166 (2018), Application(s): WB / Reactant(s) Human, Abstract — Full Text
- Hepatitis E virus persists in the presence of a type III interferon response: X. Yin, et al.; PLoS Pathog. 13, e1006417 (2017), Application(s): WB / Reactant(s) Human, Abstract — Full Text
- Disruption of MDA5-Mediated Innate Immune Responses by the 3C Proteins of Coxsackievirus A16, Coxsackievirus A6, and Enterovirus D68: Y. Rui, et al.; J. Virol. 91, e00546-17 (2017), Abstract — Full Text
- Silencing of retrotransposons by SETDB1 inhibits the interferon response in acute myeloid leukemia: T.L. Cuellar, et al.; J. Cell Biol. 216, 3535 (2017), Application(s): WB / Reactant(s) Human, Abstract — Full Text
- Association of a Network of Interferon-Stimulated Genes with a Locus Encoding a Negative Regulator of Non-conventional IKK Kinases and IFNB1: S. Jeidane, et al.; Cell Rep. 17, 425 (2016), Application(s): Western Immunoblot Analyses, Abstract — Full Text
- ATP hydrolysis by the viral RNA sensor RIG-I prevents unintentional recognition of self-RNA: C. Lässig, et al.; eLife 4, e10859 (2015), Application(s): Sense RNA from a broad range of viruses, dependent signaling, Abstract — Full Text
- Paramyxovirus V proteins interact with the RNA Helicase LGP2 to inhibit RIG-I-dependent interferon induction.: Childs, K., Randall, R., et al.; J. Virol. 86, 3411 (2012), Application(s): WB, Abstract
- The C proteins of human parainfluenza virus type 1 limit double-stranded RNA accumulation that would otherwise trigger activation of MDA5 and protein kinase R.: Akira, S., Boonyaratanakornkit, J., et al.; J. Virol. 85, 1495 (2011), Application(s): WB / Reactant(s): Human, Abstract
- The antiviral adaptor proteins Cardif and Trif are processed and inactivated by caspases: M. Rebsamen, et al.; Cell Death Differ. 15, 1804 (2008), Abstract
- Activation of an immunoregulatory and antiviral gene expression program in poly(I:C)-transfected human neutrophils: N. Tamassia, et al.; J. Immunol. 181, 6563 (2008), Abstract
- Distinct RIG-I and MDA5 signaling by RNA viruses in innate immunity: Y.M. Loo, et al.; J. Virol. 82, 335 (2008), Abstract
Related Products

| Alternative Name | Helicard, Melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5, Interferon-induced helicase C domain-containing protein 1, RH116, CADM-140 autoantigen, RIG-I-like receptor 2, RLR-2 |
|---|---|
| Application | ELISA, IP, WB |
| Host | Mouse |
| Isotype | IgG1 |
| Species Reactivity | Human |

| Alternative Name | Helicard, Melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5, Interferon-induced helicase C domain-containing protein 1, RH116, CADM-140 autoantigen, RIG-I-like receptor 2, RLR-2 |
|---|---|
| Application | ELISA, WB |
| Host | Mouse |
| Isotype | IgG1 |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |

| Alternative Name | Helicard, Melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5, Interferon-induced helicase C domain-containing protein 1, RH116, CADM-140 autoantigen, RIG-I-like receptor 2, RLR-2 |
|---|---|
| Application | ELISA, IF, IHC (PS), WB |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
Last modified: May 29, 2024
Datasheet, Manuals, SDS & CofA
Manuals And Inserts
Certificate of Analysis
Please enter the lot number as featured on the product label
SDS
Enzo Life Science provides GHS Compliant SDS
If your language is not available please fill out the SDS request form
 Lab Essentials
Lab Essentials AMPIVIEW® RNA probes
AMPIVIEW® RNA probes Enabling Your Projects
Enabling Your Projects  GMP Services
GMP Services Bulk Solutions
Bulk Solutions Research Travel Grant
Research Travel Grant Have You Published Using an Enzo Product?
Have You Published Using an Enzo Product?
