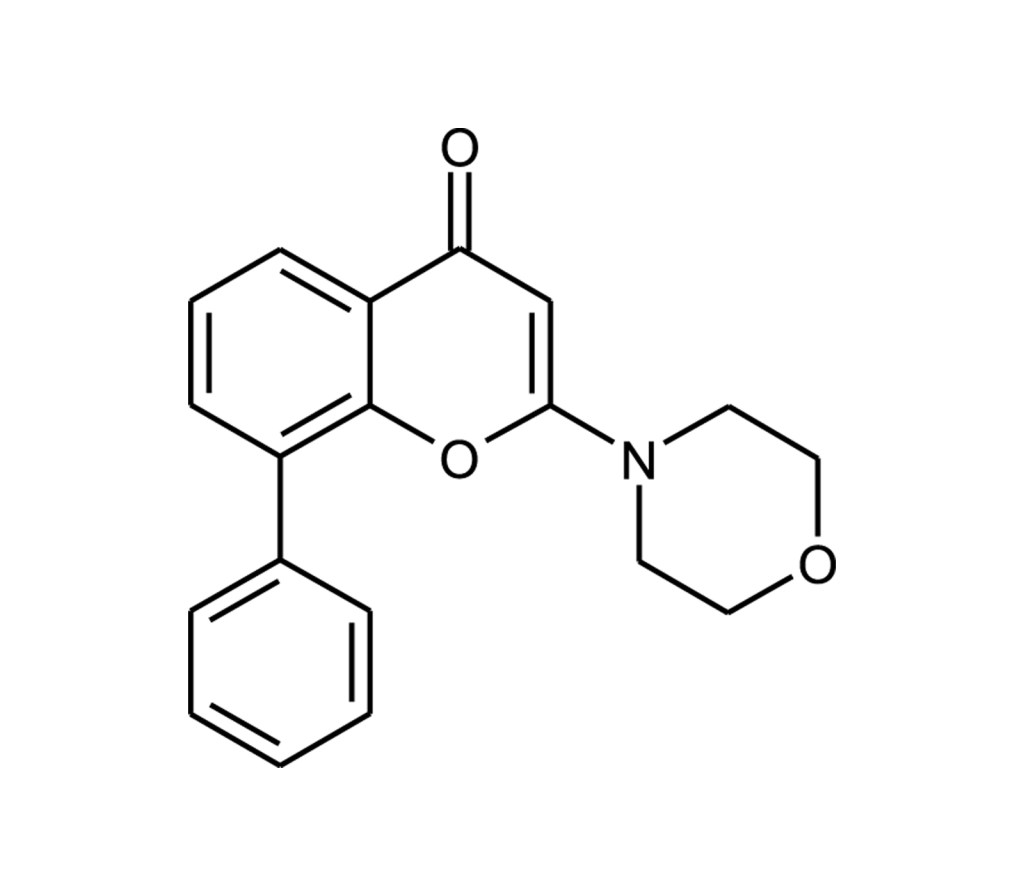
PI3 kinase inhibitor
Potent, cell permeable, inhibitor of PI(3)K (phosphoinositide 3-kinase) that acts on the ATP-binding site of the enzyme. Displays an IC50 of 1.4µM and inhibits all isoforms equally in in vitro assays using purified PI 3-kinase (p110α IC50=0.63µM). Inhibits Pim-1 kinase with IC50=4.0µM. Other kinases such as PKC, PKA, MAP kinase, S6 kinase, EGF receptor tyrosine kinase, c-src kinase, PI 4-kinase, diacylglycerol kinase or rabbit kidney ATPase are not inhibited at 50µM.
Induces apoptosis in many cell types by blocking the PI3-K/Akt anti-apoptotic pathway. Useful tool for identifying cellular events which are regulated by the PI3-K/Akt axis. Sensitizes tumor cells to drug-induced apoptosis independent of its PI3K inhibitory activity. Inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis in human colon cancer cells. Suppresses proliferation of mouse embryonic stem cells. Furthermore, inhibits autophagic sequestration in rat hepatocytes.
Shipping: Available products typically ship within 24/48h, via priority shipping.
Do you need support? Contact Customer Service or Technical Support.
Online Account
Access or Create Your Account
Product Details
| Alternative Name |
2-(4-Morpholinyl)-8-phenyl-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one |
|---|---|
| Appearance |
White to pale yellow solid. |
| CAS |
154447-36-6 |
| Couple Target |
PI3 kinase, Pim |
| Couple Type |
Inhibitor |
| Formula |
C19H17NO3 |
| MW |
307.3 |
| Purity |
≥98% (HPLC) |
| Solubility |
Soluble in DMSO (25mg/ml, warm), 100% ethanol (25mg/ml, warm) or methanol. |
| Technical Info / Product Notes |
Replacement for ADI-HPK-106. |
Handling & Storage
| Use/Stability |
As indicated on product label or CoA when stored as recommended. Stable for at least 1 year after receipt when stored at -20°C. Stock solutions are stable for up to 3 months at -20°C. |
|---|---|
| Long Term Storage |
-20°C |
| Shipping |
Ambient Temperature |
| Regulatory Status |
RUO – Research Use Only |
|---|
- YAP Overexpression in Breast Cancer Cells Promotes Angiogenesis through Activating YAP Signaling in Vascular Endothelial Cells: Y. Yan, et al.; Anal. Cell. Pathol. (Amst.) 2022, 5942379 (2022), Abstract
- Acid sphingomyelinase promotes SGK1-dependent vascular calcification: T. Luong, et al.; Clin. Sci. 135, 515 (2021), Abstract — Full Text
- Carbon Monoxide Releasing Molecule-3 Enhances Heme Oxygenase-1 Induction via ROS-Dependent FoxO1 and Nrf2 in Brain Astrocytes: C. C. Lin, et al.; Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 5521196 (2021), Abstract
- Exendin-4, a glucagon-like peptide receptor agonist, facilitates osteoblast differentiation via connexin43: J. Chen, et al.; Endocrine 72, 672 (2021), Abstract
- LDOC1 Suppresses Microbe-Induced Production of IL-1β in Human Normal and Cancerous Oral Cells through the PI3K/Akt/GSK-3β Axis: C. Lee, et al.; Cancers (Basel) 12, 3148 (2020), Abstract — Full Text
- SGK1-dependent stimulation of vascular smooth muscle cell osteo-/chondrogenic transdifferentiation by interleukin-18: N. Schelski, et al.; Pflugers Arch. 471, 889 (2019), Abstract — Full Text
- Effect of selective serotonin (5-HT)2B receptor agonist BW723C86 on epidermal growth factor/transforming growth factor-α receptor tyrosine kinase and ribosomal p70 S6 kinase activities in primary cultures of adult rat hepatocytes: K. Naito, et al.; Biol. Pharm. Bull. 42, 631 (2019), Application(s): used w. adult rat liver hepatocytes, Abstract — Full Text
- Upregulation of microRNA‑300 induces the proliferation of liver cancer by downregulating transcription factor FOXO1: Chang, Y., Zhou, C., et al.; Oncol. Rep. 40, 3561 (2018), Abstract
- Intracellular formyl peptide receptor regulates naïve CD4 T cell migration: H.Y. Lee, et al.; Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 497, 226 (2018), Abstract
- CCL4 enhances preosteoclast migration and its receptor CCR5 downregulation by RANKL promotes osteoclastogenesis: D. Lee, et al.; Cell Death Dis. 9, 495 (2018), Abstract — Full Text
- Involvement of PI3K and PKA pathways in mouse tongue epithelial differentiation: J.K. Jung, et al.; Acta Histochem. 119, 92 (2017), Abstract
- 16-Hydroxycleroda-3, 13-dien-15, 16-olide inhibits the proliferation and induces mitochondrial-dependent apoptosis through Akt, mTOR, and MEK-ERK pathways in human renal carcinoma cells: C. Liu, et al.; Phytomedicine 36, 95 (2017), Abstract
- Anti-neoplastic drugs increase caveolin-1-dependent migration, invasion and metastasis of cancer cells: N.I. Díaz-Valdivia, et al.; Oncotarget 8, 111943 (2017), Abstract — Full Text
- Developing a Novel Embryo-Larval Zebrafish Xenograft Assay to Prioritize Human Glioblastoma Therapeutics: Wehmas, L. C., Tanguay, R. L., et al.; Zebrafish 13, 317 (2016), Abstract
- Boolean Modeling Reveals the Necessity of Transcriptional Regulation for Bistability in PC12 Cell Differentiation: Offermann, B., Knauer, S., et al.; Front. Genet. 7, 44 (2016), Abstract
- Avian leukosis virus subgroup J induces VEGF expression via NF-κB/PI3K-dependent IL-6 production: Gao, Y., Zhang, Y., et al.; Oncotarget 7, 80275 (2016), Application(s): In Vitro, Abstract
- Ribonuclease 5 facilitates corneal endothelial wound healing via activation of PI3-kinase/Akt pathway.: Kim, K. W., Park, S. H., et al.; Sci. Rep. 6, 31162 (2016), Abstract
- AMPK activates LXRα and ABCA1 expression in human macrophages: M. Kemmerer, et al.; Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 16, 30154 (2016), Application(s): Cell culture using human monocytic cells, Abstract
- Co-treatment of LY294002 or MK-2206 with AZD5363 Attenuates AZD5363-induced Increase in the Level of Phosphorylated AKT: A.R. Choi, et al.; Anticancer Res. 36, 5849 (2016), Application(s): Cell treatment, MK-2206 cells, Abstract — Full Text
- Corticotropin-Releasing Hormone (CRH) Promotes Macrophage Foam Cell Formation via Reduced Expression of ATP Binding Cassette Transporter-1 (ABCA1): W. Cho, et al.; PLoS One 10, e0130587 (2015), Application(s): Cell Culture, Abstract — Full Text
- Yersinia entry into host cells requires Rab5-dependent dephosphorylation of PI(4,5)P₂ and membrane scission: H. Sarantis, et al.; Cell Host Microbe 11, 117 (2015), Application(s): COS cells treatment, Abstract — Full Text
- Antigen receptor-mediated depletion of FOXP3 in induced regulatory T-lymphocytes via PTPN2 and FOXO1: E. Bothur, et al.; Nat. Commun. 6, 8576 (2015), Application(s): Cell preparation and in vitro stimulation, Abstract — Full Text
- Autophagy positively regulates DNA damage recognition by nucleotide excision repair: Qiang, L., Zhao, B., et al.; Autophagy 12, 357 (2015), Abstract
- Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Induce Lipoxygenase-mediated Apoptosis and Necrosis in Human Neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y Cells: J.H. Kim, et al.; Neurochem. Int. 90, 204 (2015), Application(s): Cell Culture, Abstract
- Acidic preconditioning improves the proangiogenic responses of endothelial colony forming cells: H.A. Mena, et al.; Angiogenesis 17, 867 (2014), Abstract
- Insulin suppresses IKs (KCNQ1/KCNE1) currents, which require β-subunit KCNE1: M. Wu, et al.; Pflugers Arch. 466, 937 (2014), Abstract
- Lack of Liver X Receptors Leads to Cell Proliferation in a Model of Mouse Dorsal Prostate Epithelial Cell: J. Dufour, et al.; PLoS One 8, e58876 (2013), Abstract — Full Text
- Piperine, a dietary phytochemical, inhibits angiogenesis: Doucette, C. D., Hilchie, A. L., et al.; J. Nutr. Biochem. 24, 231 (2013), Abstract
- Novel insulin sensitizer modulates nutrient sensing pathways and maintains β-cell phenotype in human islets: N. Rohatgi, et al.; PloS One 8, e62012 (2013), Application(s): WB, PCR, IHC, Abstract — Full Text
- Reverse engineering a hierarchical regulatory network downstream of oncogenic KRAS: Stelniec-Klotz, I., Legewie, S., et al.; Mol. Syst. Biol. 8, 601 (2012), Abstract
- Induction of interleukin-10 is dependent on p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway in macrophages infected with porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus: Hou, J., Wang, L., et al.; Virol. J. 9, 165 (2012), Abstract
- Fyn is induced by Ras/PI3K/Akt signaling and is required for enhanced invasion/migration: V. Yadav; Mol. Carcinog. 50, 346 (2011), Application(s): WB, PCR, Abstract — Full Text
- Arf6-dependent intracellular trafficking of Pasteurella multocida toxin and pH-dependent translocation from late endosomes: Repella, T. L., Ho, M., et al.; Toxins (Basel) 3, 218 (2011), Abstract
- mRNA degradation plays a significant role in the program of gene expression regulated by phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling: J.R. Graham, et al.; Mol. Cell. Biol. 30, 5295 (2010), Application(s): WB, PCR, Abstract — Full Text
- Early activation of the beta-catenin pathway in osteocytes is mediated by nitric oxide, phosphatidyl inositol-3 kinase/Akt, and focal adhesion kinase: A. Santos, et al.; Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 391, 364 (2010), Application(s): WB, PCR, PFF, Abstract
- Sevoflurane postconditioning prevents activation of caspase 3 and 9 through antiapoptotic signaling after myocardial ischemia-reperfusion: Y. Inamura, et al.; J. Anesth. 24, 215 (2010), Application(s): WB, Abstract
- A double hit to kill tumor and endothelial cells by TRAIL and antiangiogenic 3TSR: Ren, B., Song, K., et al.; Cancer Res. 69, 3856 (2009), Abstract
- Identification and characterization of NVP-BEZ235, a new orally available dual phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor with potent in vivo antitumor activity: Maira, S. M., Stauffer, F., et al.; Mol. Cancer Ther. 7, 1851 (2008), Abstract
- Inhibition of N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)retinamide-induced autophagy at a lower dose enhances cell death in malignant glioma cells: Tiwari, M., Bajpai, V. K., et al.; Carcinogenesis 29, 600 (2008), Abstract
- Muscle-specific overexpression of the type 1 IGF receptor results in myoblast-independent muscle hypertrophy via PI3K, and not calcineurin, signaling: Quinn, L. S., Anderson, B. G., et al.; Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 293, E1538 (2007), Abstract
- Synthesis and biological evaluation of sulfonylhydrazone-substituted imidazo[1,2-a]pyridines as novel PI3 kinase p110alpha inhibitors: M. Hayakawa, et al.; Bioorg. Med. Chem. 15, 5837 (2007), Abstract
- The small GTPase R-Ras regulates organization of actin and drives membrane protrusions through the activity of PLCepsilon: Ada-Nguema, A. S., Xenias, H., et al.; J. Cell Sci. 119, 1307 (2006), Abstract
- LY294002 and LY303511 Sensitize Tumor Cells to Drug-Induced Apoptosis via Intracellular Hydrogen Peroxide Production Independent of the Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase-Akt Pathway: T.W. Poh and S. Pervaiz; Cancer Res. 65, 6264 (2005), Abstract
- Pim-1 Ligand-bound Structures Reveal the Mechanism of Serine/Threonine Kinase Inhibition by LY294002: M.D. Jacobs, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 280, 13728 (2005), Abstract
- NS398 reduces hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1alpha and HIF-1 activity: multiple-level effects involving cyclooxygenase-2 dependent and independent mechanisms: Zhong, H., Willard, M., et al.; Int. J. Cancer 112, 585 (2004), Abstract
- Up-regulation of c-jun mRNA in cardiac myocytes requires the extracellular signal-regulated kinase cascade, but c-Jun N-terminal kinases are required for efficient up-regulation of c-Jun protein: Clerk, A., Kemp, T. J., et al.; Biochem. J. 368, 101 (2002), Abstract
- Reduction of Abeta accumulation in the Tg2576 animal model of Alzheimer’s disease after oral administration of the phosphatidyl-inositol kinase inhibitor wortmannin: Haugabook, S. J., Le, T., et al.; FASEB J. 15, 16 (2001), Abstract
- Phosphoinositide 3-kinase inhibition spares actin assembly in activating platelets but reverses platelet aggregation: T.J. Kovacsovics, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 270, 11358 (1995), Abstract — Full Text
- Investigation of neutrophil signal transduction using a specific inhibitor of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase: C.J. Vlahos, et al.; J. Immunol. 154, 2413 (1995), Abstract
- Requirement for phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase in the prevention of apoptosis by nerve growth factor: R. Yao & G.M. Cooper; Science 267, 2003 (1995), Abstract
Related Products
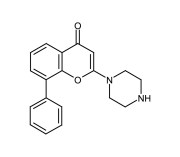
| Alternative Name | 2-(4-Piperazinyl)-8-phenyl-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one |
|---|---|
| CAS | 154447-38-8 |
| Purity | ≥95% (HPLC) |
Last modified: May 29, 2024
Datasheet, Manuals, SDS & CofA
Manuals And Inserts
Certificate of Analysis
Please enter the lot number as featured on the product label
SDS
Enzo Life Science provides GHS Compliant SDS
If your language is not available please fill out the SDS request form
 Lab Essentials
Lab Essentials AMPIVIEW® RNA probes
AMPIVIEW® RNA probes Enabling Your Projects
Enabling Your Projects  GMP Services
GMP Services Bulk Solutions
Bulk Solutions Research Travel Grant
Research Travel Grant Have You Published Using an Enzo Product?
Have You Published Using an Enzo Product?