Enhanced ligand that utilizes the proprietary Killer™ linker peptide that promotes stability.
- Increased stability
- Enhanced immune activation
KillerTRAIL™ (soluble) (human), (recombinant) is an enhanced ligand that utilizes the proprietary Killer™ linker peptide that promotes trimerization to form a more stable oligomer.
It has been well established that signals transmitted via TNF ligands and receptors are critical in mediating inflammation, cancer, and immunity. This has led to drug development aiming to either reduce or enhance receptor response. One limitation in this process is the inherent instability of recombinant ligands and their inability to effectively mimic the natural clustering of TNF receptors on the cell surface required for immune activation. Oligomerization of TNF ligands such as KillerTRAIL™ has been shown to improve stability and significantly enhance immune activation compared to recombinant ligands alone.
TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) is a protein ligand that induces the process of cell death called apoptosis.
Shipping: Available products typically ship within 24/48h, via priority shipping.
Do you need support? Contact Customer Service or Technical Support.
Online Account
Access or Create Your Account
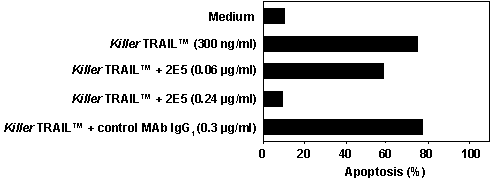
Figure: Specificity of KillerTRAIL™-induced apoptosis. Concentration dependent blocking of apoptosis induction of BJAB cells using MAb to TRAIL (human) (2E5) (Prod. No. ALX-804-296) reveals specificity of KillerTRAIL™-mediated killing.Method: Human BJAB cells were treated with KillerTRAIL™, Soluble (human) (recombinant) (at 300ng/ml) in the presence or absence of the indicated concentration of the MAb to TRAIL (human) (2E5) or a control IgG1 mouse monoclonal antibody. After 16 hours apoptosis was evaluated by forward/sideward scatter (FSC/SSC) combined with propidium iodide (PI) stain analysed by flow cytometry.”””,KillerTRAIL™ Protein (soluble) (human)
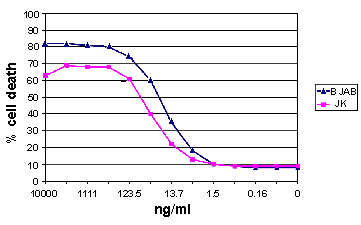
Figure: Apoptosis of TRAIL-sensitive cells. Concentration dependence of apoptosis induction in Jurkat and BJAB cells by KillerTRAIL™, Soluble (human) (recombinant) (Prod. No. ALX-201-073) reveals high activity even at concentrations of 10-100ng/ml.Method: 5×104 human Jurkat (JK) or BJAB cells were cultured in 100µl RPMI 1640 medium containing 10% fetal calf serum for 16 hours at 37°C in a 96-well plate in the presence of the indicated concentrations of KillerTRAIL™. Concentrations of KillerTRAIL™ required to induce apoptosis may vary depending on the cell type studied. Cell death was quantified by forward/sideward scatter (FSC/SSC) combined with propidium iodide (PI) staining analysed by flow cytometry.”””,KillerTRAIL™ Protein (soluble) (human)



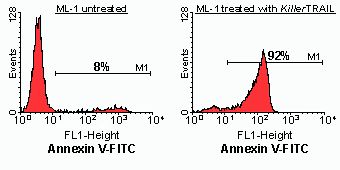
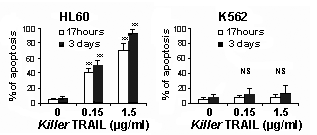
Product Details
| Alternative Name |
Apo-2L, TNFSF 10, CD253 |
|---|---|
| Biological Activity |
Induces apoptosis in a concentration range of 10-100ng/ml. |
| Endotoxin Content |
≤0.01 EU/μg purified protein (LAL test). |
| Formulation |
Liquid. HEPES, pH 7.4, sodium chloride, Tween 20, sucrose, azide free and 1mM DTT. |
| MW |
~24kDa (SDS-PAGE) |
| Purity |
≥99% (SDS-PAGE, MS analysis) |
| Purity Detail |
Affinity purified. Sterile filtered. |
| Reconstitution |
For a special storage and dilution buffer see KillerTRAIL™ Storage and Dilution Buffer (Prod. No. ALX-505-005). |
| Source |
Produced in E. coli. The extracellular domain of human TRAIL (aa 95-281) is fused at the N-terminus to a His-tag and a linker peptide. |
| Specific Activity |
ED50: 20ng/ml (BJAB cells) |
| Specificity |
Binds to human and mouse TRAIL receptors and osteoprotegerin (OPG). |
| UniProt ID |
P50591 |
Handling & Storage
| Use/Stability |
Stable for at least 12 months after receipt when stored at -80° C. |
|---|---|
| Handling |
Once thawed, prepare aliquots and store at -80°C (please note – to retain full activity the concentration of aliquots should be at least 0.1 mg/mL). Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. Keep vial closely capped before use, spin the tube at 5000 x g for 30 sec before use. |
| Long Term Storage |
-80°C |
| Shipping |
Dry Ice |
| Regulatory Status |
RUO – Research Use Only |
|---|
- Delivery of caspase inhibitors through GSDMD pores to inhibit pyroptosis: Groborz, K. M., Truong, M. E., et al.; bioRxiv , (2025)
- NF-κB/RelA controlled A20 limits TRAIL-induced apoptosis in pancreatic cancer: C. Geismann, et al.; Cell Death Dis. 14, 3 (2023), Abstract
- Negligible role of TRAIL death receptors in cell death upon endoplasmic reticulum stress in B-cell malignancies: F. Favaro, et al.; Oncogenes 12, 6 (2023), Abstract
- Exploiting the immunogenic potential of standard of care radiation or cisplatin therapy in preclinical models of HPV-associated malignancies: J.T. Kowalczyk, et al.; J. Immunother. Cancer 10, e005752 (2022), Abstract
- Ambivalent Effects of Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha on Apoptosis of Malignant and Normal Human Keratinocytes: G. Kokolakis, et al.; Skin Pharmacol. Physiol. 34, 94 (2021), Abstract — Full Text
- Selective HSP90β inhibition results in TNF and TRAIL mediated HIF1α degradation: Heck, A. L., Mishra, S., et al.; Immunobiology 226, 152070 (2021), Abstract
- Roles for ADAM17 in TNF-R1 Mediated Cell Death and Survival in Human U937 and Jurkat Cells: Fritsch, J., Frankenheim, J., et al.; Cells 10, (2021), Abstract
- Inhibition of ATM kinase upregulates levels of cell death induced by cannabidiol and γ-irradiation in human glioblastoma cells: Ivanov, V. N., Wu, J., et al.; Oncotarget 10, 825 (2019), Abstract
- The marine natural product Scalarin inhibits the receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) and autophagy in the PANC-1 and MIA PaCa-2 pancreatic cancer cell lines: E.A. Guzman, et al.; Invest. New Drugs 37, 262 (2019), Abstract
- Synthetic Lethal and Convergent Biological Effects of Cancer-Associated Spliceosomal Gene Mutations: Lee, S. C., North, K., et al.; Cancer Cell 34, 225 (2018), Abstract
- Anti-PD-L1/TGFβR2 (M7824) fusion protein induces immunogenic modulation of human urothelial carcinoma cell lines, rendering them more susceptible to immune-mediated recognition and lysis: I. Grenga, et al.; Urol. Oncol. 36, 9.30E+02 (2018), Abstract
- TRAIL/NF-κB/CX3CL1 Mediated Onco-Immuno Crosstalk Leading to TRAIL Resistance of Pancreatic Cancer Cell Lines: C. Geismann, et al.; Int. J. Mol. Sci. 19, E1661 (2018), Abstract — Full Text
- Loss of the Cyclin-Dependent Kinase Inhibitor 1 in the Context of Brachyury-Mediated Phenotypic Plasticity Drives Tumor Resistance to Immune Attack: D.H. Hamilton, et al.; Front. Oncol. 8, 143 (2018), Abstract — Full Text
- The combination of TRAIL and MG-132 induces apoptosis in both TRAIL-sensitive and TRAIL-resistant human follicular lymphoma cells: J. Adem, et al.; Leuk. Res. 66, 57 (2018), Abstract
- Pevonedistat, a Nedd8-activating enzyme inhibitor, sensitizes neoplastic B-cells to death receptor-mediated apoptosis: C. Paiva, et al.; Oncotarget 8, 21128 (2017), Abstract — Full Text
- Balance between IL-3 and type Iinterferons and their interrelationship with FasL dictates lifespan and effector functions of human basophils: B.R. Hagmann, et al.; Clin. Exp. Allergy 47, 71 (2017), Abstract
- Role of CCL20 mediated immune cell recruitment in NF-κB mediated TRAIL resistance of pancreatic cancer: C. Geismann, et al.; Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 1864, 782 (2017), Abstract
- Regulation of human glioblastoma cell death by combined treatment of cannabidiol, γ-radiation and small molecule inhibitors of cell signaling pathways: Ivanov, V. N., Wu, J., et al.; Oncotarget 8, 74068 (2017), Abstract
- RIP1 has a role in CD40-mediated apoptosis in human follicular lymphoma cells: J. Adem, et al.; Immunobiology 222, 998 (2017), Abstract
- The SMAC mimetic BV6 induces cell death and sensitizes different cell lines to TNF-α and TRAIL-induced apoptosis: M. El-Mesery, et al.; Exp. Biol. Med. 241, 2015 (2016), Abstract
- TNF induced cleavage of HSP90 by cathepsin D potentiates apoptotic cell death: J. Fritsch, et al.; Oncotarget 7, 75774 (2016), Abstract — Full Text
- Programmable polyproteams built using twin peptide superglues: G. Veggiani, et al.; PNAS 113, 1202 (2016), Abstract — Full Text
- Differences and similarities in TRAIL-and tumor necrosis factor-mediated necroptotic signaling in cancer cells: J. Sosna, et al.; Mol. Cell. Biol. 36, 2626 (2016), Abstract
- Sensitization of Melanoma Cells for Death Ligand TRAIL Is Based on Cell Cycle Arrest, ROS Production, and Activation of Proapoptotic Bcl-2 Proteins: S.A. Quast, et al.; J. Invest. Dermatol. 135, 2794 (2015), Abstract
- Combinatorial treatment of CD95L and gemcitabine in pancreatic Cancer cells induces apoptotic and RIP1-mediated necroptotic cell death network: S. Pietkiewicz, et al.; Exp. Cell Res. 339, 1 (2015), Application(s): Apoptosis induced in pancreatic cancer cells , Abstract
- TRAF2 inhibits TRAIL- and CD95L-induced apoptosis and necroptosis: I. Karl, et al.; Cell Death Dis. 5, e1444 (2014), Application(s): Cell death induction in primary keratinocytes, HaCaT and HeLa cells, Abstract — Full Text
- Modulation of nuclear factor E2-related factor-2 (Nrf2) activation by the stress response gene immediate early response-3 (IER3) in colonic epithelial cells: a novel mechanism of cellular adaption to inflammatory stress: I. Stachel, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 289, 1917 (2014), Application(s): Apoptosis induced in human NCM460 colonocytes, Abstract — Full Text
- Intra- and interdimeric caspase-8 self-cleavage controls strength and timing of CD95-induced apoptosis: S.M. Kallenberger, et al.; Sci. Signal. 7, ra23 (2014), Abstract
- c-Rel is a critical mediator of NF-κB-dependent TRAIL resistance of pancreatic cancer cells: C. Geismann, et al.; Cell Death Dis. 5, e1455 (2014), Application(s): Apoptosis induced in human pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cells (PANC-1 and Patu8998t), Abstract — Full Text
- COX-2-independent effects of celecoxib sensitize lymphoma B cells to TRAIL-mediated apoptosis: A.S. Gallouet, et al.; Clin. Cancer Res. 20, 2663 (2014), Abstract
- A CD47-blocking TRAIL fusion protein with dual pro-phagocytic and pro-apoptotic anticancer activity: V.R. Wiersma, et al.; Br. J. Haematol. 164, 304 (2014), Abstract
- RAF inhibition overcomes resistance to TRAIL-induced apoptosis in melanoma cells: A. Berger, et al.; J. Invest. Dermatol. 134, 430 (2014), Abstract
- ROS-dependent phosphorylation of Bax by wortmannin sensitizes melanoma cells for TRAIL-induced apoptosis: S.A. Quast, et al.; Cell Death Dis. 10, e839 (2013), Abstract — Full Text
- Aurora and IKK kinases cooperatively interact to protect multiple myeloma cells from Apo2L/TRAIL: L. Mazzera, et al.; Blood 122, 2641 (2013), Application(s): TRAIL signaling analysis in multiple myeloma cells, Abstract
- CD40-directed scFv-TRAIL fusion proteins induce CD40-restricted tumor cell death and activate dendritic cells: M. El-Mesery, et al.; Cell Death Dis. 4, e916 (2013), Application(s): Stimulation of IL-8 production in HeLa and HeLa-CD40 transfected cells, Abstract
- High expression of crystallin αB represents an independent molecular marker for unfavourable ovarian cancer patient outcome and impairs TRAIL- and cisplatin-induced apoptosis in human ovarian cancer cells: J. Volkmann, et al.; Int. J. Cancer 132, 2820 (2013), Application(s): Apoptosis induced in human ovarian cancer cells (OV-MZ-6 and HEY), Abstract — Full Text
- Ubiquitination and degradation of the FADD adaptor protein regulate death receptor-mediated apoptosis and necroptosis: E.W. Lee, et al.; Nat. Commun. 3, 978 (2012), Abstract
- General Sensitization of Melanoma Cells for TRAIL-Induced Apoptosis by the Potassium Channel Inhibitor TRAM-34 Depends on Release of SMAC: S.A. Quest, et al.; Plos One 7, e39290 (2012), Abstract — Full Text
- Role of Apollon in Human Melanoma Resistance to Antitumor Agents That Activate the Intrinsic or the Extrinsic Apoptosis Pathways: E. Tassi, et al.; Clin. Cancer Res. 18, 3316 (2012), Application(s): Death induction of human melanoma cells, Abstract — Full Text
- Sensitization of melanoma cells for TRAIL-induced apoptosis by BMS-345541 correlates with altered phosphorylation and activation of Bax: A. Berger, et al.; Cell Death Dis. 4, e477 (2011), Abstract
- Inhibition of SREBP1 sensitizes cells to death ligands: Y. Eberhard, et al.; Oncotarget 2, 186 (2011), Abstract — Full Text
- Sensitization of melanoma cells for death ligand-induced apoptosis by an indirubin derivative–Enhancement of both extrinsic and intrinsic apoptosis pathways: A. Berger, et al.; Biochem. Pharmacol. 81, 71 (2011), Abstract
- Under HEMA conditions, self-replication of human erythroblasts is limited by autophagic death: G. Migliaccio, et al.; Blood Cells Mol. Dis. 47, 182 (2011), Abstract
- Efficient melanoma cell killing and reduced melanoma growth in mice by a selective replicating adenovirus armed with tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand: L.F. Fecker, et al.; Hum. Gene Ther. 22, 405 (2011), Abstract
- FOXO3A as a key molecule for all-trans retinoic acid-induced granulocytic differentiation and apoptosis in acute promyelocytic leukemia: Y. Sakoe, et al.; Blood 115, 3787 (2010), Application(s): Death induction of NB4 cells, Abstract — Full Text
- Lipopolysaccharide-induced expression of TRAIL promotes dendritic cell differentiation: Y.S. Cho, et al.; Immunology 130, 504 (2010), Abstract — Full Text
- Exploration of the lysis mechanisms of leukaemic blasts by chimaeric T-cells: D. Laurin, et al.; J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2010, 234540 (2010), Abstract — Full Text
- Enhanced death ligand-induced apoptosis in cutaneous SCC cells by treatment with diclofenac/hyaluronic acid correlates with downregulation of c-FLIP: L.F. Fecker, et al.; J. Invest. Dermatol. 130, 2098 (2010), Abstract
- Human CD34+ cells engineered to express membrane-bound tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand target both tumor cells and tumor vasculature: C. Lavazza, et al.; Blood 115, 2231 (2010), Application(s): Multiple myeloma killing studies in mice, Abstract — Full Text
- Small molecule inhibition of phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-triphosphate (PIP3) binding to pleckstrin homology domains: B. Miao, et al.; PNAS 107, 20126 (2010), Application(s): Death induction of sensitized U87MG cells, Abstract — Full Text
- Resistance of cutaneous anaplastic large-cell lymphoma cells to apoptosis by death ligands is enhanced by CD30-mediated overexpression of c-FLIP: F.K. Braun, et al.; J. Invest. Dermatol. 130, 826 (2010), Abstract
- HYD1-induced increase in reactive oxygen species leads to autophagy and necrotic cell death in multiple myeloma cells: R.R. Nair, et al.; Mol. Cancer Ther. 8, 2441 (2009), Application(s): Death induction of H929 cells, Abstract — Full Text
- IFN-α-Induced Apoptosis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Involves Promyelocytic Leukemia Protein and TRAIL Independently of p53: K. Herzer, et al.; Cancer Res. 69, 855 (2009), Application(s): Death induction of Hep3B, Huh7, Huh6, HepG2 and Chang cells, Abstract — Full Text
- PRMT5, a Novel TRAIL Receptor-Binding Protein, Inhibits TRAIL-Induced Apoptosis via Nuclear Factor-κB Activation: H. Tanaka, et al.; Mol. Cancer Res. 7, 557 (2009), Application(s): Death induction of HeLa, A549, HCT116 and HT1080 cells, Abstract — Full Text
- Caspase-8 Cleaves Histone Deacetylase 7 and Abolishes Its Transcription Repressor Function: F.L. Scott, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 283, 19499 (2008), Application(s): Death induction of HEK293 cells, Abstract — Full Text
- Topoisomerase I Requirement for Death Receptor-induced Apoptotic Nuclear Fission: O. Sordet, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 283, 23200 (2008), Application(s): Death induction of HCT116 and Jurkat cells, Abstract — Full Text
- Resistance of melanoma cells to TRAIL does not result from upregulation of antiapoptotic proteins by NF-kappaB but is related to downregulation of initiator caspases and DR4: B.M. Kurbanov, et al.; Oncogene 26, 3364 (2007), Abstract
- Blockade of death receptor-mediated pathways early in the signaling cascade coincides with distinct apoptosis resistance in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma cells: F.K. Braun, et al.; J. Invest. Dermatol. 127, 2425 (2007), Abstract
- TRAIL promotes metastasis of human pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: A. Trauzold, et al.; Oncogene 25, 7434 (2006), Abstract — Full Text
- Inorganic selenium sensitizes prostate cancer cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis through superoxide/p53/Bax-mediated activation of mitochondrial pathway: H. Hu, et al.; Mol. Cancer Ther. 5, 1873 (2006), Application(s): Death induction and sensitation analysis of LNCaP and DU145 cells, Abstract — Full Text
- Increased death receptor resistance and FLIPshort expression in polycythemia vera erythroid precursor cells: A. Zeuner, et al.; Blood 107, 3495 (2006), Application(s): Death induction of human erythroblasts, Abstract — Full Text
- Chronic lymphocytic leukemic cells exhibit apoptotic signaling via TRAIL-R1: M. MacFarlane, et al.; Cell Death Differ. 12, 773 (2005), Abstract
- Efficient TRAIL-R1/DR4-mediated apoptosis in melanoma cells by tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL): Kurbanov, B. M., Geilen, C. C., et al.; J. Invest. Dermatol. 125, 1010 (2005), Abstract
- Telomerase-Dependent Virotherapy Overcomes Resistance of Hepatocellular Carcinomas against Chemotherapy and Tumor Necrosis Factor-Related Apoptosis-Inducing Ligand by Elimination of Mcl-1: T. Wirth, et al.; Cancer Res. 65, 7393 (2005), Application(s): Death induction of sensitized Huh7 and Hep3B cells and Hep3B-derived s.c. tumor xenografts in mice, Abstract — Full Text
- HPC1/RNASEL Mediates Apoptosis of Prostate Cancer Cells Treated with 2′,5′-Oligoadenylates, Topoisomerase I Inhibitors, and Tumor Necrosis Factor-Related Apoptosis-Inducing Ligand: K. Malathi, et al.; Cancer Res. 64, 9144 (2004), Application(s): Death induction of prostate epithelial cells, DU145 and PC3 cells, Abstract — Full Text
- Autocrine Secretion of Fas Ligand Shields Tumor Cells from Fas-Mediated Killing by Cytotoxic Lymphocytes: K. Hallermalm, et al.; Cancer Res. 64, 6775 (2004), Application(s): Death induction of Jurkat cells and death induction trials with OCM1 and OCM8 cells, Abstract — Full Text
- TRAIL and its receptors in the colonic epithelium: a putative role in the defense of viral infections: J. Sträter, et. al.; Gastroenterology 122, 659 (2002), Abstract
- TRAIL (Apo2L) suppresses growth of primary human leukemia and myelodysplasia progenitors: M. Plasilova, et al.; Leukemia 16, 67 (2002), Abstract — Full Text
- The Human Papillomavirus Type 16 E5 Protein Impairs TRAIL- and FasL-Mediated Apoptosis in HaCaT Cells by Different Mechanisms: K. Kabsch & A. Alonso; J. Virol. 76, 12162 (2002), Application(s): Death induction of HaCaT and A31 cells, Abstract — Full Text
- The anti-apoptotic protein BAG-3 is overexpressed in pancreatic cancer and induced by heat stress in pancreatic cancer cell lines: Q. Liao, et al.; FEBS Lett. 503, 151 (2001), Abstract
Related Products
SUPERKILLERTRAIL® Protein (soluble) (human), (recombinant)
ALX-201-115
Enhanced ligand with improved stability providing significantly enhanced immune activation.

| Alternative Name | TNFSF 10, Apo-2L, CD253 |
|---|---|
| Purity | ≥98% (SDS-PAGE). MS analysis, <1% impurity (mainly Hsp70 protein from E. coli) |
| Source | Produced in E. coli. The extracellular domain of human TRAIL (aa 95-281) is fused at the N-terminus to a His-tag and a linker peptide. The active multimeric conformation is stabilized by an inserted mutation allowing an additional CC-bridge. |
MEGACD40L® Protein (soluble) (human), (recombinant)
ALX-522-110
High activity, high purity CD40L protein for co-stimulatory activation of an immune response

| Alternative Name | CD40L:ACRP30headless, CD154:ACRP30headless, TNFSF 5:ACRP30headless, gp39:ACRP30headless |
|---|---|
| Purity | ≥90% (SDS-PAGE) |
| Source | Produced in CHO cells. The extracellular domain of human CD40L (CD154) (aa 116-261) is fused at the N-terminus to mouse ACRP30headless (aa 18-111) and a FLAG®-tag. |

| Alternative Name | Apo-2L, TNFSF 10, CD253 |
|---|---|
| Application | Flow Cytometry, FUNC |
| Host | Mouse |
| Isotype | IgG1 |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
Last modified: May 29, 2024
Datasheet, Manuals, SDS & CofA
Manuals And Inserts
Certificate of Analysis
Please enter the lot number as featured on the product label
SDS
Enzo Life Science provides GHS Compliant SDS
If your language is not available please fill out the SDS request form
 Lab Essentials
Lab Essentials AMPIVIEW® RNA probes
AMPIVIEW® RNA probes Enabling Your Projects
Enabling Your Projects  GMP Services
GMP Services Bulk Solutions
Bulk Solutions Research Travel Grant
Research Travel Grant Have You Published Using an Enzo Product?
Have You Published Using an Enzo Product?

