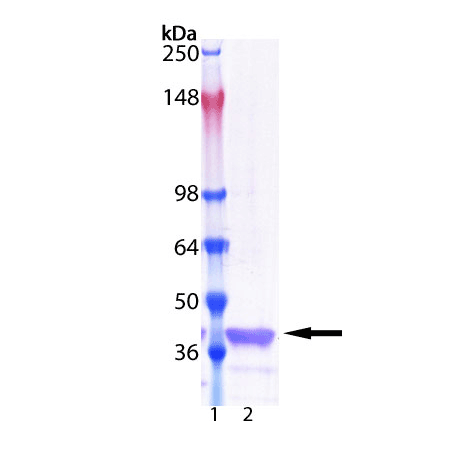
IκBa inhibits activation of the NF-κB pathway activation by associating with the major NF-κB heterodimeric complex p50/p65 and preventing its translocation from the cytoplasm into the nucleus, where it acts a transcription factor for genes involved in inflammation, autoimmune response, cell proliferation, and apoptosis. Inhibition of NF-κB pathway activation by IκBα is controlled by its sequential serine-phosphorylation, ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation. This process itself can be inhibited by SUMOylation of IκBα, providing an additional regulatory step for the activation of the NF-κB pathway.
Shipping: Available products typically ship within 24/48h, via priority shipping.
Do you need support? Contact Customer Service or Technical Support.
Online Account
Access or Create Your Account
| Regulatory Status |
RUO – Research Use Only |
|---|
Last modified: May 29, 2024
 Lab Essentials
Lab Essentials AMPIVIEW® RNA probes
AMPIVIEW® RNA probes Enabling Your Projects
Enabling Your Projects  GMP Services
GMP Services Bulk Solutions
Bulk Solutions Research Travel Grant
Research Travel Grant Have You Published Using an Enzo Product?
Have You Published Using an Enzo Product?