The Hsp70 family of heat shock protiens contains multiple homologs ranging in size from 66-78 kDa, and are the eukaryotic equivalents of the bacterial DnaK. The most studied Hsp70 members include the cytosolic stress-induced Hsp70 (Hsp72), the constitutive cytosolic Hsc70 (Hsp73), and the ER-localized BiP (Grp78). Hsp70 family members contain highly conserved N-terminal ATP-ase and C-terminal protein binding domains. Binding of peptide to Hsp70 is assisted by Hsp40, and stimulates the inherent ATPase activity of Hsp70, facilitating ATP hydrolysis and enhanced peptide binding. Hsp70 nucleotide exchange and substrate binding coordinates the folding of newly synthesized proteins, the re-folding of misfolded or denatured proteins, coordinates trafficking of proteins across cellular membranes, inhibits protein aggregation, and targets the degradation of proteins via the proteasomal pathway.
Shipping: Available products typically ship within 24/48h, via priority shipping.
Do you need support? Contact Customer Service or Technical Support.
Online Account
Access or Create Your Account
This antibody is covered by our Worry-Free Guarantee.
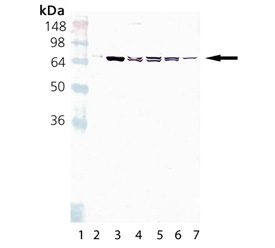
Western blot analysis of HSC70/HSP70 mAb (BB70) (Prod. No. ADI-SPA-822): Lane 1: MW marker, Lane 2:HSC70(HSP73) (Prod. No. ADI-SPP-751), Lane 3:HSP70(HSP72) (Prod. No. ADI-NSP-555), Lane 4:HeLa Cell Lysate (heat shocked)(Prod. No. ADI-LYC-HL101), Lane 5:PC-12 Cell Lysate (heat shocked)(Prod. No. ADI-LYC-PC101), Lane 6:RK-13 Cell Lysate (heat shocked), Lane 7: 3T3 Cell Lysate (heat shocked)(Prod. No. ADI-LYC-3T101)
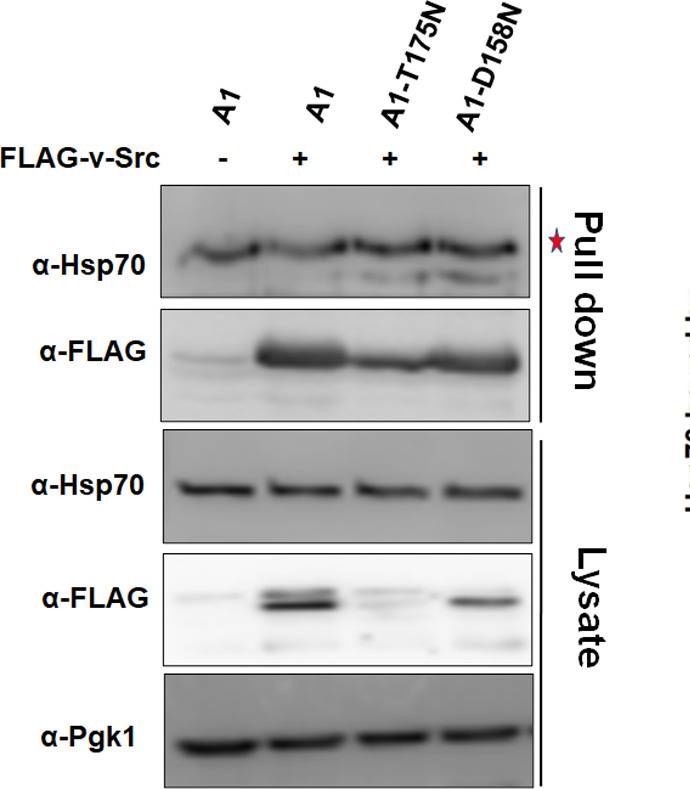
v-Src interaction with Ssa1-T175N and Ssa1-D158N is stronger than with Ssa1.The indicated strains were grown in selective SGal media for v-Src expression. The cellular lysate was incubated with anti-FLAG antibodies immobilized beads. The immunoprecipitated proteins were probed with indicated antibodies. The supernatant was used as a control to examine protein level in A1, A1-T175N and A1-D158N strains. Panel towards right depicts quantification of respective western blots. Star represents nonspecific band. Error bars represent standard error from 3 different biological replicates.
Image collected and cropped by CiteAb under a CC-BY license from the following publication: Ydj1 interaction at nucleotide-binding-domain of yeast Ssa1 impacts Hsp90 collaboration and client maturation. PLoS Genet (2022)
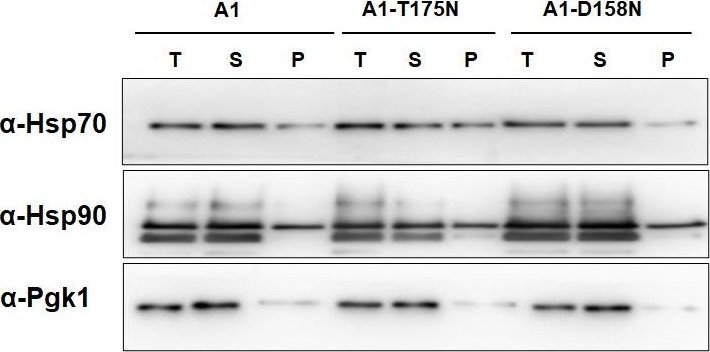
A1-T175N and A1-D158N show reduced v-Src kinase activity.(A) Indicated strains were grown in SGal liquid media for 6h. The whole cell lysate (T) was prepared, and fractionated into supernatant (S) and Pellet (P). All fractions were probed with anti-FLAG or anti-phosphotyrosine antibody. Panel towards right depicts quantification from immunoblots. (B) The Hsp70, Hsp90 or Pgk1 was probed with anti-Hsp70, anti-Hsp90 or anti-Pgk1 antibody respectively. Pgk1 is the loading control and is same for 2A and 2B. Error bars represent standard error from 3 different biological replicates.
Image collected and cropped by CiteAb under a CC-BY license from the following publication: Ydj1 interaction at nucleotide-binding-domain of yeast Ssa1 impacts Hsp90 collaboration and client maturation. PLoS Genet (2022)
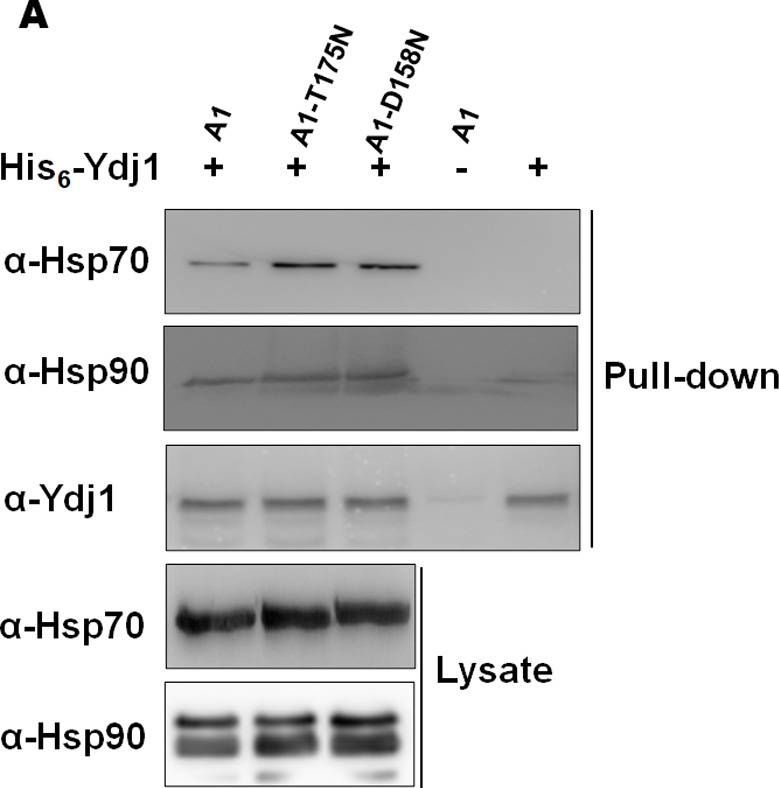
Hsp70 mutants show increased affinity to Ydj1.(A) Purified His6-Ydj1 was immobilized over Co2+-NTA beads and incubated with cellular lysate from indicated strains. The bound proteins were eluted and probed with anti-Hsp70, anti-Hsp90 and anti-Ydj1 antibodies. (B) BLI studies to monitor interaction between Ssa Hsp70 and Ydj1. Ydj1 (0.75μM) was immobilized over the biosensor surface, and Ssa Hsp70 (wt Ssa1 or its mutants) was used as analyte. The binding was monitored in the presence of ATP.
Image collected and cropped by CiteAb under a CC-BY license from the following publication: Ydj1 interaction at nucleotide-binding-domain of yeast Ssa1 impacts Hsp90 collaboration and client maturation. PLoS Genet (2022)




Product Details
| Alternative Name |
Heat shock protein 70, Hsc70, Hsp73 |
|---|---|
| Application |
IHC, IP, WB |
| Application Notes |
Detects a band of ~72kDa by Western blot. |
| Clone |
BB70 |
| Formulation |
Liquid. In PBS, pH 7.2, containing 50% glycerol and 0.09% sodium azide. |
| GenBank ID |
J02579 |
| Host |
Mouse |
| Immunogen |
Chicken Hsp70/Hsp90 complex. |
| Isotype |
IgG2a |
| Purity Detail |
Protein G affinity purified. |
| Recommendation Dilutions/Conditions |
Western Blot (1:1,000, colorimetric)Suggested dilutions/conditions may not be available for all applications.Optimal conditions must be determined individually for each application. |
| Source |
Purified from mouse ascites. |
| Species Reactivity |
Drosophila, Housefly, Human, Mouse, Rabbit, Rat, Sponge, Yeast |
| UniProt ID |
P08106 |
| Worry-free Guarantee |
This antibody is covered by our Worry-Free Guarantee. |
Handling & Storage
| Handling |
Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
|---|---|
| Long Term Storage |
-20°C |
| Shipping |
Blue Ice |
| Regulatory Status |
RUO – Research Use Only |
|---|
- Total propagation of yeast prion conformers in ssz1∆ upf1∆ Hsp104T160M triple mutants: ; Curr. Genet. 71, 8 (2025), Abstract
- Kinesin-1 mediates proper ER folding of the CaV1.2 channel and maintains mouse glucose homeostasis: Tanaka, Y., Farkhondeh, A., et al.; EMBO Rep. 25, 4777 (2024), Abstract
- Lack of Hikeshi activates HSF1 activity under normal conditions and disturbs the heat-shock response: S. Kose, et al.; Life Sci. Alliance 5, e202101241 (2022), Abstract
- Ydj1 interaction at nucleotide-binding-domain of yeast Ssa1 impacts Hsp90 collaboration and client maturation.: Gaur, D., Kumar, N., et al.; PLoS Genet. 18, e1010442 (2022), Application(s): WB / Reactant(s): Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Abstract
- Tah1, A Key Component of R2TP Complex that Regulates Assembly of snoRNP, is Involved in De Novo Generation and Maintenance of Yeast Prion [URE3]: A. Puri, et al.; J. Mol. Biol. 433, 166976 (2021), Abstract
- Modulation of Expression of PVYNTN RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase (NIb) and Heat Shock Cognate Host Protein HSC70 in Susceptible and Hypersensitive Potato Cultivars: E. Koziel, et al.; Vaccines (Basel) 9, 1254 (2021), Abstract
- The Hsp70-Bag3 complex modulates the phosphorylation and nuclear translocation of Hippo pathway protein Yap: Baldan, S., Meriin, A. B., et al.; J. Cell Sci. 134, (2021), Abstract
- The Yeast Hsp70 Cochaperone Ydj1 Regulates Functional Distinction of Ssa Hsp70s in the Hsp90 Chaperoning Pathway: Gaur, D., Singh, P., et al.; Genetics 215, 683 (2020), Abstract
- Proteomic analysis of circulating extracellular vesicles identifies potential markers of breast cancer progression, recurrence, and response.: Gutman, M., Halperin, S., et al.; Sci. Adv. 6, (2020), Application(s): WB / Reactant(s): Human, Abstract
- An advanced cell cycle tag toolbox reveals principles underlying temporal control of structure-selective nucleases.: Bittmann, J., Grigaitis, R., et al.; Elife 9, (2020), Application(s): WB / Reactant(s): Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Abstract
- Forms and abundance of chaperone proteins influence yeast prion variant competition: Yu, C. I., King, C. Y., et al.; Mol. Microbiol. 111, 798 (2019), Abstract
- Global analysis of polysome-associated mRNA in vesicular stomatitis virus infected cells.: Neidermyer, W. J., Whelan, S. P. J., et al.; PLoS Pathog. 15, e1007875 (2019), Application(s): IP / Reactant(s): Human, Abstract
- Modulation of Protein Quality Control and Proteasome to Autophagy Switch in Immortalized Myoblasts from Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Patients: M. Wattin, et al.; Int. J. Mol. Sci. 19, 178 (2018), Application(s): Western Blot, Abstract — Full Text
- The cellular stress response of the scleractinian coral Goniopora columna during the progression of the black band disease: D. Seveso, et al.; Cell Stress Chaperones 22, 225 (2017), Application(s): Western Blot, Abstract — Full Text
- ER stress causes widespread protein aggregation and prion formation.: Grant, C. M., Kritsiligkou, P., et al.; J. Cell Biol. 216, 2295 (2017), Application(s): WB / Reactant(s): Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Abstract
- Differential expression patterns among heat-shock protein genes and thermal responses in the whitefly Bemisia tabaci(MEAM 1): F. Diaz, et al.; J. Therm. Biol. 52, 199 (2015), Application(s): Western Blot, Abstract
- Identification and quantitative analysis of cellular proteins affected by treatment with withaferin A using A SILAC-based proteomics approach: M. Narayan, et al.; J. Ethnopharmacol. 8741, 30149 (2015), Application(s): Western Blot, Abstract
- HSP90 inhibitor-SN-38 conjugate strategy for targeted delivery of topoisomerase I inhibitor to tumors: D.A. Proia, et al.; Mol. Cancer Ther. 14, 2422 (2015), Application(s): Immunoblotting , Abstract — Full Text
- Prion-like transmission of neuronal huntingtin aggregates to phagocytic glia in the Drosophila brain: M. M. Pearce, et al.; Nat. Commun. 6, 6768 (2015), Application(s): Immunofluorescence / Reactant(s): Drosophila melanogaster, Abstract
- Activation of p107 by fibroblast growth factor, which is essential for chondrocyte cell cycle exit, is mediated by the protein phosphatase 2A/B55α holoenzyme: Kurimchak, A., Haines, D. S., et al.; Mol. Cell. Biol. 33, 3330 (2013), Abstract
- Hsp90 orchestrates transcriptional regulation by Hsf1 and cell wall remodelling by MAPK signalling during thermal adaptation in a pathogenic yeast.: Brown, A. J., Cowen, L. E., et al.; PLoS Pathog. 8, e1003069 (2012), Application(s): WB, Abstract
- Uptake of the antifungal cationic peptide Histatin 5 by Candida albicans Ssa2p requires binding to non-conventional sites within the ATPase domain: M. Edgerton, et al.; Mol. Microbiol. 70, 1246 (2008), Application(s): WB using yeast cell lysates, Abstract
- The Expression of Tubulin Polymerization Promoting Protein TPPP/p25α is Developmentally Regulated in Cultured Rat Brain Oligodendrocytes and Affected by Proteolytic Stress: C. Richter-Landsberg, et al.; Glia 56, 1736 (2008), Application(s): WB, IF using rat tissue, Abstract
- Phosphoglucose isomerase genotype affects running speed and heat shockprotein expression after exposure to extreme temperatures in a montanewillow beetle: N. Rank, et al.; J. Exp. Biol. 210, 750 (2007), Application(s): WB using insect cell lysates, Abstract
- Developmental and hyperthermia-induced expression of the heat shockproteins HSP60 and HSP70 in tissues of the housefly Musca domestica:An in vitro study: P. Tiwari, et al.; Genet. Mol. Biol. 30, 159 (2007), Application(s): WB, IHC using housefly tissue, Abstract
- Co-translational folding of caspase-activated DNase with Hsp70, Hsp40, and inhibitor of caspase-activated DNase: S. Nagata, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 277, 3364 (2002), Application(s): IP using rabbit samples, Abstract
- Tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 is an ATPase regulated by silencer of death domain: E.M. Eddy, et al.; Mol. Cell. Biol. 22, 2536 (2002), Application(s): WB using mouse samples, Abstract
- Modulation of Drosophila heat shock transcription factor activity by the molecular chaperone DROJ1: C. Wu, et al.; EMBO J. 20, 499 (2001), Application(s): WB using drosophila samples, Abstract
- Regional distribution of Hsp70 in the CNS of young and old food-restricted rats following hyperthermia: P.A. Mason, et al.; Brain Res. Bull. 55, 367 (2001), Application(s): WB using rat samples, Abstract
- Identification of genes that modify ataxin-1-induced neurodegeneration: J. Botas, et al.; Nature 408, 101 (2000), Application(s): IHC using drosophila samples, Abstract
- Repression of heat shock transcription factor HSF1 activation by HSP90 (HSP90 complex) that forms a stress-sensitive complex with HSF1: R. Voellmy, et al.; Cell 94, 471 (1998), Application(s): WB, IP using human samples, Abstract
Related Products
HSP70/HSP72 (human), (recombinant)
ADI-NSP-555
A molecular chaperone that assists in the folding of emerging polypeptides and the refolding of denatured proteins.

| Alternative Name | Heat shock protein 70, HspA1A, HspA1B |
|---|---|
| Purity | ≥95% (SDS-PAGE; Western blot) |
| Source | Produced in E. coli. |

| Application | ELISA, WB |
|---|---|
| Host | Goat |
| Species Reactivity | Mouse |
Last modified: May 29, 2024
Datasheet, Manuals, SDS & CofA
Manuals And Inserts
Certificate of Analysis
Please enter the lot number as featured on the product label
SDS
Enzo Life Science provides GHS Compliant SDS
If your language is not available please fill out the SDS request form
 Lab Essentials
Lab Essentials AMPIVIEW® RNA probes
AMPIVIEW® RNA probes Enabling Your Projects
Enabling Your Projects  GMP Services
GMP Services Bulk Solutions
Bulk Solutions Research Travel Grant
Research Travel Grant Have You Published Using an Enzo Product?
Have You Published Using an Enzo Product?

