Highly active
Human HDAC1 (HD1) was the first protein to be linked to histone deacetylase activity. It is homologous to the yeast protein Rpd31, a relationship which has since come to define the “class I HDACs”. HDAC1 promotes transcriptional repression by deacetylating lysine ε-amino groups in histone N-terminal tails, a function frequently carried out in association with multi-protein transcription repression complexes such as NuRD3, Sin34 and CoREST6. Ubiquitously expressed in human tissues HDAC1-containing complexes appear to contribute the greater part of (at least class I) deacetylase activity in HeLa nuclear extracts. Aside from its interaction with co-repressors, HDAC1 activity may be regulated by post-translation modifications such as phosphorylation9 and sumoylation or binding to the inhibitor maspin, a tumor-suppressive serpin homolog. Although originally described as a “histone deacetylase”, HDAC1 has been shown to catalyze the regulatory deacetylation of non-histone proteins, including p53. Overexpression of HDAC1 has been found in various cancer types. HDAC inhibitors (HDACi) have shown considerable promise as anti-cancer agents and HDACi compounds from multiple chemical classes are in stages of drug development ranging from preclinical to phase III trials.
Shipping: Available products typically ship within 24/48h, via priority shipping.
Do you need support? Contact Customer Service or Technical Support.
Online Account
Access or Create Your Account
Product Details
| Alternative Name |
Histone deacetylase 1 |
|---|---|
| Formulation |
Liquid. In 50mM TRIS, pH 8.0, 138mM sodium chloride and 10% glycerol. |
| Gene/Protein Identifier |
NM_004964 (RefSeq) |
| MW |
55 kDa |
| Purity Detail |
Partially purified by single-step affinity chromatography and gel filtration. |
| Source |
Produced in insect cells. HDAC1 from human cDNA (482 aa). Produced in a baculovirus expression system. |
| Specific Activity |
≥5 U/µg. One U=1 pmol/min at 37°C, 100µM, FLUOR DE LYS®-SIRT1 deacetylase substrate (Prod. No. BML-KI177). |
| UniProt ID |
Q13547 |
Handling & Storage
| Use/Stability |
The enzyme is stable on ice for the time typically required to set up an experiment (30-60 min.), but may lose activity with prolonged storage on ice. It is recommended that thawing and dilution of the enzyme be done within as short a time as possible before start of the assay. The remaining, unused, undiluted enzyme should be refrozen quickly by, for example, snap freezing in a dry/ice ethanol bath or liquid nitrogen. Freezing and storage of diluted enzyme is not recommended. |
|---|---|
| Long Term Storage |
-80°C |
| Shipping |
Dry Ice |
| Regulatory Status |
RUO – Research Use Only |
|---|
- Reprogramming of bacterial virulence by lysine acetylation: Lammers, M., Schmöker, O., et al.; Research Square , (2025)
- HDAC3 and HDAC8 PROTAC dual degrader reveals roles of histone acetylation in gene regulation: Xiao, Y., Hale, S., et al.; Cell Chem. Biol. 30, 1421 (2023), Abstract
- Novel hydroxamic acid derivative induces apoptosis and constrains autophagy in leukemic cells: M.A. Fischer, et al.; J. Adv. Res. , (2023), Abstract
- Design, Synthesis, and biological evaluation of HDAC6 inhibitors based on Cap modification strategy: X. Li, et al.; Bioorg. Chem. 125, 105874 (2022), Abstract
- Discovery of Novel Src Homology-2 Domain-Containing Phosphatase 2 and Histone Deacetylase Dual Inhibitors with Potent Antitumor Efficacy and Enhanced Antitumor Immunity: M. Liu, et al.; J. Med. Chem. 65, 12200 (2022), Abstract
- CaMKII exacerbates heart failure progression by activating class I HDACs: Zhang, M., Yang, X., et al.; J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 149, 73 (2020), Abstract
- Identification of novel multi-stage histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors that impair Schistosoma mansoni viability and egg production: A. Guidi, et al.; Parasit. Vectors 11, 668 (2018), Abstract
- Evaluation of WO2017018805: 1, 3, 4-oxadiazole sulfamide derivatives as selective HDAC6 inhibitors: Y.Y. Liang, et al.; Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 28, 647 (2018), Abstract
- Epigenetic regulation of HDAC1 SUMOylation as an endogenous neuroprotection against Aβ toxicity in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease: C.C. Tao, et al.; Cell Death Differ. 24, 597 (2017), Abstract — Full Text
- Reverse Biosynthesis: Generating Combinatorial Pools of Drug Leads From Enzyme-Mediated Fragmentation of Natural Products: T. Richardson-Sanchez, et al.; Chembiochem. 18, 368 (2017), Abstract
- Synthesis and evaluation of aliphatic-chain hydroxamates capped with osthole derivatives as histone deacetylase inhibitors: W.H. Huang, et al.; Eur. J. Med. Chem. 46, 4042 (2011), Abstract
- Class IIa histone deacetylases are hormone-activated regulators of FOXO and mammalian glucose homeostasis: M.M. Mihaylova, et al.; Cell 145, 607 (2011), Abstract — Full Text
- Endogenous inhibition of histone deacetylase 1 by tumor-suppressive maspin: X. Li et al.; Cancer Res. 66, 9323 (2006), Abstract
- Histone deacetylase 3 (HDAC3) and other class I HDACs regulate colon cell maturation and p21 expression and are deregulated in human colon cancer: A. J. Wilson et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 281, 13548 (2006), Abstract
- Acetylation and deacetylation of non-histone proteins: M. A. Glozak et al.; Gene 363, 15 (2005), Abstract
- Quantitation of HDAC1 mRNA expression in invasive carcinoma of the breast*: Z. Zhang et al.; Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 94, 11 (2005), Abstract
- Upregulation and nuclear recruitment of HDAC1 in hormone refractory prostate cancer: K. Halkidou; Prostate 59, 177 (2004), Abstract
- Histone deacetylases (HDACs): characterization of the classical HDAC family: A. J. de Ruijter et al.; Biochem. J. 370, 737 (2003), Abstract
- SUMO-1 modification of histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) modulates its biological activities: G. David et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 277, 23658 (2002), Abstract
- CoREST is an integral component of the CoREST- human histone deacetylase complex: A. You et al.; PNAS 98, 1454 (2001), Abstract
- Stable histone deacetylase complexes distinguished by the presence of SANT domain proteins CoREST/kiaa0071 and Mta-L1: G. W. Humphrey et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 276, 6817 (2001), Abstract
- Histone deacetylase 1 phosphorylation promotes enzymatic activity and complex formation: M. K. Pflum et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 276, 47733 (2001), Abstract
- Expression profile of histone deacetylase 1 in gastric cancer tissues: J. H. Choi et al.; Jpn. J. Cancer Res. 92, 1300 (2001), Abstract
- Histone deacetylases specifically down-regulate p53-dependent gene activation: L. J. Juan et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 275, 20436 (2000), Abstract
- Deacetylation of p53 modulates its effect on cell growth and apoptosis: J. Luo et al.; Nature 408, 377 (2000), Abstract
- Three proteins define a class of human histone deacetylases related to yeast Hda1p: C. M. Grozinger et al.; PNAS 96, 4868 (1999), Abstract
- Analysis of the NuRD subunits reveals a histone deacetylase core complex and a connection with DNA methylation: Y. Zhang et al.; Genes Dev. 13, 1924 (1999), Abstract
- Isolation and characterization of cDNAs corresponding to an additional member of the human histone deacetylase gene family: W. M. Yang et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 272, 44 (1997), Abstract
- Histone deacetylases associated with the mSin3 corepressor mediate mad transcriptional repression: C. D. Laherty et al.; Cell 89, 349 (1997), Abstract
- A mammalian histone deacetylase related to the yeast transcriptional regulator Rpd3p: J. Taunton et al.; Science 272, 408 (1996), Abstract
Related Products

| Application | Activity assay, Cell-based assays, Fluorescent detection, HTS |
|---|
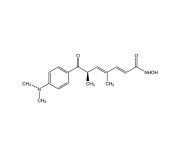
| Alternative Name | [R-(E,E)]-7-[4-(Dimethylamino)phenyl]-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethyl-7-oxo-2,4-heptadienamide |
|---|---|
| CAS | 58880-19-6 |
| Couple Type | Inhibitor |
| Purity | ≥98% (HPLC) |
Last modified: May 29, 2024
Datasheet, Manuals, SDS & CofA
Manuals And Inserts
Specific Protocol
Assay of HDAC1 (Prod. No. BML-SE456) with FLUOR DE LYS®-SIRT1 substrate (Prod. No. BML-KI177) & FLUOR DE LYS® Developer II (Prod. No. BML-KI176)
Components of Assay:
HDAC Assay Buffer II (Prod. No. BML-KI422)*
(50 mM Tris/Cl, pH 8.0, 137 mM NaCl, 2.7 mM KCl, 1 mM MgCl2, 1 mg/ml BSA (fatty acid free BSA, e.g. Sigma catalog # A3803))
HDAC1 (Prod. No. BML-SE456)*
Dilute to enough HDAC1 to 0.1 µg/µl with HDAC Assay Buffer II (Prod. No. BML-KI422) to provide 5 µl per well. Keep on ice until use.
FLUOR DE LYS®-SIRT1 substrate (Prod. No. BML-KI177)*
Thaw quickly and keep on ice. Dilute 5 mM stock in HDAC Assay Buffer II.
2x Substrate Solution
Prepare a 2x substrate solution by diluting the 5 mM FLUOR DE LYS®-SIRT1 substrate (Prod. No. BML-KI177) in HDAC Assay Buffer II (BML-KI422). Each assay well will require 25 µl (see below). For example, prepare 1 ml of 20 µM substrate (for final 10 µM) by mixing 4 µl of 5 mM FLUOR DE LYS®-SIRT1 substrate (Prod. No. BML-KI177) and 996 µl HDAC Assay Buffer II (Prod. No. BML-KI422). Warm to 37°C before use. (NOTE: HDAC1's Km for FLUOR DE LYS- SIRT1 substrate (Prod. No. BML-KI177) is ~20 µM. Therefore, a reasonable substrate concentration for inhibitor screening would be 10-20 µM FLUOR DE LYS®-SIRT1 (Prod. No. BML-KI177), while 100 or 200 µM would be more suitable for a specific activity measurement at a saturating substrate concentration.)
Trichostatin A (Prod. No. BML-GR309; HDAC Inhibitor)
Prepare a 0.2 mM stock in dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO). DMSO stock may be stored at -20°C. The 0.2 mM stock will be diluted 100-fold in 1x Developer II in order to stop HDAC activity at the start of the signal development process. To prepare a stock for use in testing trichostatin inhibition (i.e. for addition to the deacetylation phase of the reaction), dilute 0.2 mM stock to 10 µM in HDAC
Assay Buffer II (e.g. 5 µl plus 95 µl) and keep on ice. Addition of 2.5 µl of this 10 µM stock per well will result in strong inhibition (final [trichostatin A] = 500 nM)
FLUOR DE LYS® Developer II (5x Concentrate, Prod. No. BML-KI176)*
Shortly before use, dilute 5x stock solution to 1x plus 2 μM trichostatin A. For example, prepare 1 ml by mixing 200 µl of the 5x Concentrate, 790 µl HDAC Assay Buffer II (BML-KI422) and 10 µl 0.2 mM trichostatin A in DMSO. Store the 1x Developer II plus trichostatin on ice until use. Do not store excess, but prepare freshly as needed.
FLUOR DE LYS® Deacetylated Standard (Prod. No. BML-KI142)*
Dilute the 10 mM stock in DMSO to 1 µM with HDAC Assay Buffer II (Prod. No. BML-KI422).
½ Volume 96-well white micro-plate (BML-KI110)*
*Components of the HDAC1 FLUOR DE LYS® Fluorescent Activity Assay (Prod. No. BML-AK511), which are also sold separately.
Reaction Condition Examples:
- Designate wells for four reactions: 30 min rxn; 30 min rxn plus trichostatin A; 0 min rxn and a Standard well.
- Add 20 µl of HDAC Assay Buffer II to the 30 min rxn well and the 0 min rxn well. To the third well (30 min. plus trichostatin) add 2.5 μl of 10 μM trichostatin A plus 17.5 µl of HDAC Assay Buffer II. Allow to equilibrate to assay temperature (37°C). (Leave Standard well empty until step 7).
- Add 50 µl of 1x Developer II plus trichostatin A to both 30 min. reaction wells.
- To the 0 min rxn well, add 50 µl of 1x Developer II plus trichostatin A, immediately followed by 25 µl of 2x substrate.
- For the standard, mix 50 µl of 1 μM standard with 50 µl of 1x Developer II plus trichostatin A in the fourth well.
- Allow 45 min. at 37°C for signal to develop and then read plate in a microplate-reading fluorimeter capable of excitation at a wavelength in the range of 350-380 and detection of emitted light in the range of 440-460 nm.
- Data analysis: Determine the ΔAFU (Arbitrary Fluorescence Units) for the two 30 min rxns. (AFU of 30 min rxn. (with or without trichostatin) minus AFU of the 0 min rxn). Determine AFU/pmol by dividing the Deacetylated standard reading (AFU) by 50 pmol. Calculate pmol of substrate deacetylated in 30 min (divide ΔAFU by AFU/pmol).
<li<Add 5 µl of diluted HDAC1 (BML-SE456, 0.1 µg/µl) to the wells for the 0 min, 30 min, and 30 min. plus trichostatin rxns.
To start reactions, add 25 µl of the 2x Substrates (37°C) to both 30 min reaction wells. Allow reactions to run 30 min at 37C.
Certificate of Analysis
Please enter the lot number as featured on the product label
SDS
Enzo Life Science provides GHS Compliant SDS
If your language is not available please fill out the SDS request form
 Lab Essentials
Lab Essentials AMPIVIEW® RNA probes
AMPIVIEW® RNA probes Enabling Your Projects
Enabling Your Projects  GMP Services
GMP Services Bulk Solutions
Bulk Solutions Research Travel Grant
Research Travel Grant Have You Published Using an Enzo Product?
Have You Published Using an Enzo Product?