Grp94 (Glucose-regulated protein 94) is an abundant resident endoplasmic reticulum (ER) lumenal stress protein, which together with cytosolic Hsp90 belongs to the Hsp90 family of molecular chaperones. Grp94 expression is upregulated by stress conditions such as glucose starvation and heat shock, which promote protein misfolding or unfolding. In addition to a homeostatic role in protein folding and assembly, Grp94 can function in the intracellular trafficking of peptides from the extracellular space to the MHC class I antigen processing pathway of antigen presentation cells.
Shipping: Available products typically ship within 24/48h, via priority shipping.
Do you need support? Contact Customer Service or Technical Support.
Online Account
Access or Create Your Account
This antibody is covered by our Worry-Free Guarantee.
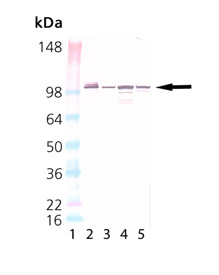
Western Blot Analysis of Grp94: Lane 1: MW Marker, Lane 2: Grp94 (canine), (recombinant) (Prod No. ADI-SPP-766), Lane 3: HeLa, (cell lysate) (Prod No. ADI-LYC-HL100), Lane 4: Mouse Liver Lysate, Lane 5: Vero Cell Lysate
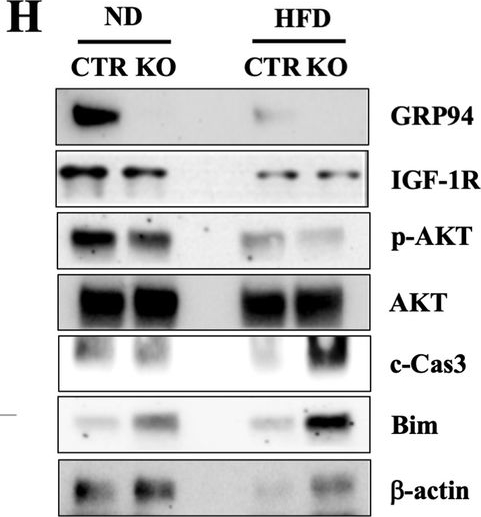
GRP94 deletion increases β cell susceptibility to HFD-induced β cell death and diabetes progression.GRP94 KO (n = 12) and Cre control (n = 12) mice fed normal diet (ND) or HFD for 20 weeks. Random-fed blood glucose levels (A), blood glucose levels during an IPGTT (B), and area under the curve (AUC) during an IPGTT after HFD (C). *p < 0.05 versus control-ND, #p < 0.05 versus KO-ND, $p < 0.05 versus control-HFD, one-way ANOVA. D C-peptide secretion during an IPGTT measured before (0 min), 15 min, and 30 min after glucose injection. *p < 0.05 versus control-ND, #p < 0.05 versus KO-ND, $p < 0.05 versus control-HFD, one-way ANOVA. E β cell mass was analyzed in ND-fed and HFD-fed mice. Ten pancreatic sections from each individual mouse (N = 4 per group) were analyzed. *p < 0.05 versus control-ND, #p < 0.05 versus KO-ND, $p < 0.05 versus control-HFD, one-way ANOVA. F Fluorescence analysis from triple staining for TUNEL, insulin, and DAPI. White arrows point to TUNEL+ cells. G Histogram shows percentages of TUNEL-positive β cells in each group. Scale bar, 50 µm. *p < 0.05 versus control-ND, #p < 0.05 versus KO-ND, $p < 0.05 versus control-HFD; one-way ANOVA. H Protein expression in mouse islets isolated from all 4 treatment groups at week 21. Immunoblot shows relative protein expression of GRP94, IGF-1R, p-AKT, AKT, c-Cas-3, and β-actin. *P < 0.05.
Image collected and cropped by CiteAb under a CC-BY license from the following publication: GRP94 is an IGF-1R chaperone and regulates beta cell death in diabetes. Cell Death Dis (2024)
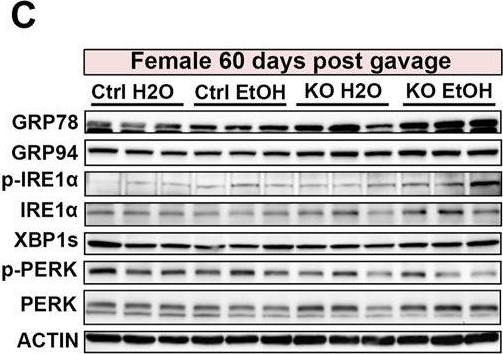
Effects of binge alcohol exposure and neuronal MANF deficiency on neuronal ER homeostasis. (A–D) Representative immunoblots (A, C) and quantification (B, D) of ER stress markers in female control and MANF KO cerebral cortex 1 day (A, B) or 60 days (C–D) post H2O or EtOH treatment. (E, H) Representative immunoblots (E, G) and quantification (F, H) of ER stress markers in male control and MANF KO cerebral cortex 1 day (E, F) or 60 days (G, H) post H2O or EtOH treatment. All data were expressed as mean ± SEM. n = 3 per group. Two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 when compared to H2O treated control. #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001 when compared to EtOH treated control. @p < 0.05, @@p < 0.01 when compared to H2O treated KO.
Image collected and cropped by CiteAb under a CC-BY license from the following publication: Sex-specific effects of alcohol on neurobehavioral performance and endoplasmic reticulum stress: an analysis using neuron-specific MANF deficient mice. Front Pharmacol (2024)
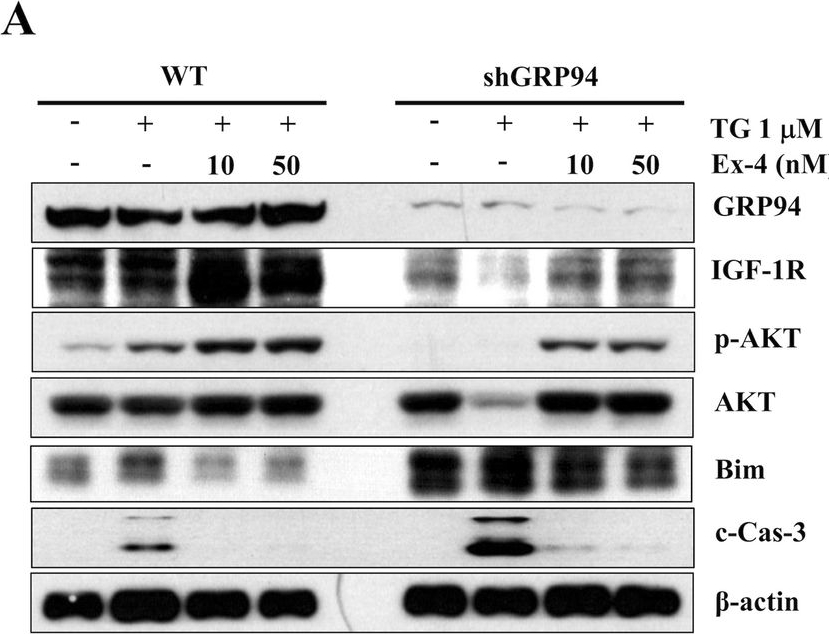
Treatment with Exendin-4 or overexpression of IGF-1R or GRP94 protects β cells from TG-induced apoptosis.A WT and GRP94 KD cells were treated with 1 μM TG in the absence or presence of 10 nM or 50 nM Exendin-4 for 6 h. Total cell extracts were analyzed by immunoblot for GRP94, IGF-1R, p-AKT, AKT, Bim, c-Cas-3, and β-actin. B WT and GRP94 KD cells were transfected with control plasmid (p.babe plasmid) or IGF-1R overexpression (p.babe-IGF-1R) plasmid and then treated with TG for 6 h or TU for 48 h. Total cell extracts were then analyzed by immunoblot for GRP94, IGF-1R, p-AKT, AKT, Bim, c-Cas-3, and β-actin. C GRP94 KD cells were transfected with GRP94 WT plasmid. Total cell extracts were then analyzed by immunoblot for GRP94, IGF-1R, p-AKT, Bim, and β-actin.
Image collected and cropped by CiteAb under a CC-BY license from the following publication: GRP94 is an IGF-1R chaperone and regulates beta cell death in diabetes. Cell Death Dis (2024)
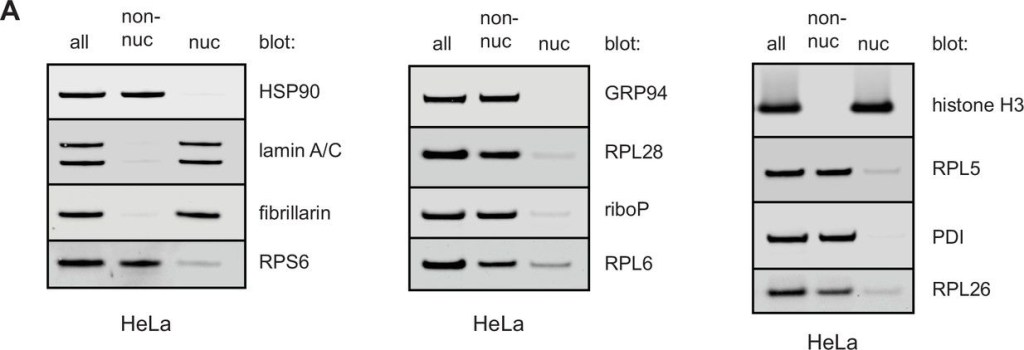
Fractionation of HeLa or T cells reveals few ribosomal components in nuclear lysates.HeLa cells (A), freshly isolated resting OT-I T cells (B), or OT-I T cells stimulated with PMA/ionomycin and IL-2 in vitro for 2 days (C) were either lysed directly in sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) extraction buffer (all) or subjected to a hypotonic lysis procedure to isolate non-nuclear lysates and nuclear lysates. Equal amounts of each fraction were subjected to immunoblotting for markers typical of the cytosol, ER, and nucleus. Antibodies against ribosomal proteins were used to determine where the majority of ribosomal proteins (and therefore ribosomes) fractionated. Controls with antibodies specific for nucleolar located fibrillarin, histone H3, and lamin A/C establish lack of nuclear contamination in non-nuclear fractions. ER and cytoplasmic proteins HSP90, GRP94, PDI, and actin indicate lack of contamination in the nuclear fraction. Representative of two experiments.Figure 6—figure supplement 1—source data 1.Uncropped and outlined immunoblot images related to Figure 6—figure supplement 1.Figure 6—figure supplement 1—source data 2.Uncropped immunoblot images related to Figure 6—figure supplement 1.Uncropped and outlined immunoblot images related to Figure 6—figure supplement 1.Uncropped immunoblot images related to Figure 6—figure supplement 1.
Image collected and cropped by CiteAb under a CC-BY license from the following publication: Paradoxical imbalance between activated lymphocyte protein synthesis capacity and rapid division rate. Elife (2024)
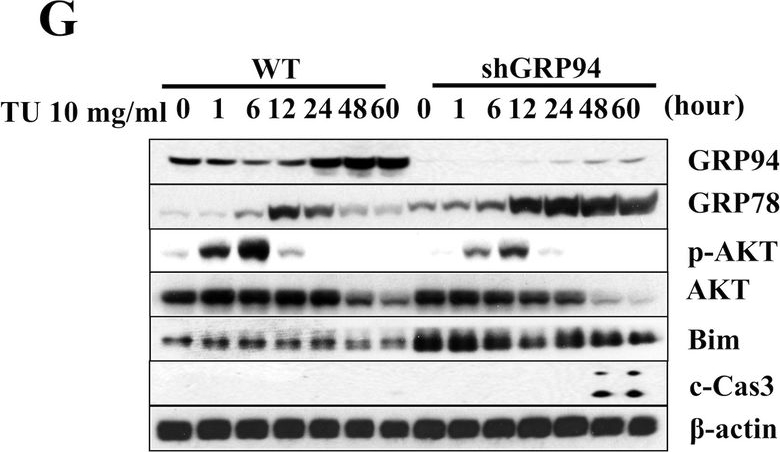
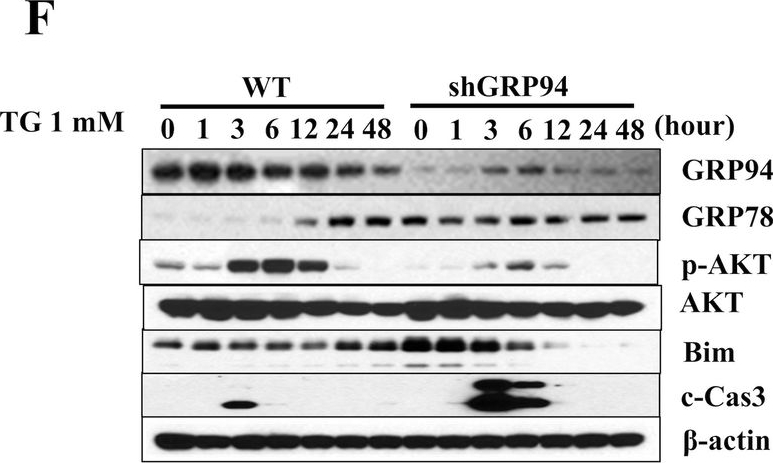
GRP94 KD cells are more susceptible to stress-induced cell death.A Relative GRP94 mRNA expression in WT control and Knockdown cells (shGRP94). B Protein expression of GRP94 in WT and KD cells. C Viability of WT control (white columns) and KD (black columns) cells after TG (1 μM)*p < 0.05 versus con WT, #p < 0.05 versus con shGRP94, $p < 0.05 versus 24 h WT, %p < 0.05 versus 24 h shGRP94, ^p < 0.05 versus 48 h WT, one-way ANOVA, D TU (10 μg/ml)*p < 0.05 versus con WT, #p < 0.05 versus con shGRP94, $p < 0.05 versus 48 h WT, %p < 0.05 versus 48 h shGRP94, ^p < 0.05 versus 72 h WT, one-way ANOVA, or E Pal (200 μM)*p < 0.05 versus con WT, #p < 0.05 versus con shGRP94, $p < 0.05 versus 24 h WT, %p < 0.05 versus 24 h shGRP94, ^p < 0.05 versus 48 h WT, one-way ANOVA, at different time after treatment. Cell death was measured by trypan blue (n = 3). F–H Protein expression of GRP94, GRP78, p-AKT, AKT, Bim, cleaved Caspase-3 (c-Cas-3), and β-actin in WT control and GRP94 KD cells at indicated times after TG, TU, or Pal treatment as analyzed by immunoblot.
Image collected and cropped by CiteAb under a CC-BY license from the following publication: GRP94 is an IGF-1R chaperone and regulates beta cell death in diabetes. Cell Death Dis (2024)
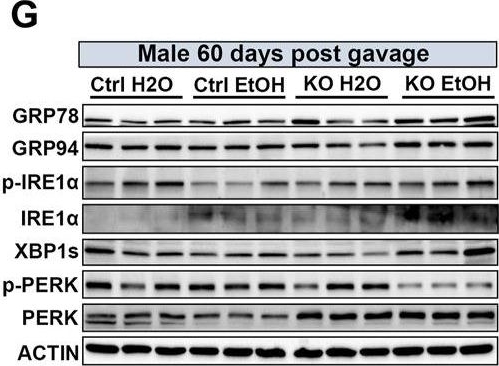
Effects of binge alcohol exposure and neuronal MANF deficiency on neuronal ER homeostasis. (A–D) Representative immunoblots (A, C) and quantification (B, D) of ER stress markers in female control and MANF KO cerebral cortex 1 day (A, B) or 60 days (C–D) post H2O or EtOH treatment. (E, H) Representative immunoblots (E, G) and quantification (F, H) of ER stress markers in male control and MANF KO cerebral cortex 1 day (E, F) or 60 days (G, H) post H2O or EtOH treatment. All data were expressed as mean ± SEM. n = 3 per group. Two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 when compared to H2O treated control. #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001 when compared to EtOH treated control. @p < 0.05, @@p < 0.01 when compared to H2O treated KO.
Image collected and cropped by CiteAb under a CC-BY license from the following publication: Sex-specific effects of alcohol on neurobehavioral performance and endoplasmic reticulum stress: an analysis using neuron-specific MANF deficient mice. Front Pharmacol (2024)
GRP94 KD cells are more susceptible to stress-induced cell death.A Relative GRP94 mRNA expression in WT control and Knockdown cells (shGRP94). B Protein expression of GRP94 in WT and KD cells. C Viability of WT control (white columns) and KD (black columns) cells after TG (1 μM)*p < 0.05 versus con WT, #p < 0.05 versus con shGRP94, $p < 0.05 versus 24 h WT, %p < 0.05 versus 24 h shGRP94, ^p < 0.05 versus 48 h WT, one-way ANOVA, D TU (10 μg/ml)*p < 0.05 versus con WT, #p < 0.05 versus con shGRP94, $p < 0.05 versus 48 h WT, %p < 0.05 versus 48 h shGRP94, ^p < 0.05 versus 72 h WT, one-way ANOVA, or E Pal (200 μM)*p < 0.05 versus con WT, #p < 0.05 versus con shGRP94, $p < 0.05 versus 24 h WT, %p < 0.05 versus 24 h shGRP94, ^p < 0.05 versus 48 h WT, one-way ANOVA, at different time after treatment. Cell death was measured by trypan blue (n = 3). F–H Protein expression of GRP94, GRP78, p-AKT, AKT, Bim, cleaved Caspase-3 (c-Cas-3), and β-actin in WT control and GRP94 KD cells at indicated times after TG, TU, or Pal treatment as analyzed by immunoblot.
Image collected and cropped by CiteAb under a CC-BY license from the following publication: GRP94 is an IGF-1R chaperone and regulates beta cell death in diabetes. Cell Death Dis (2024)
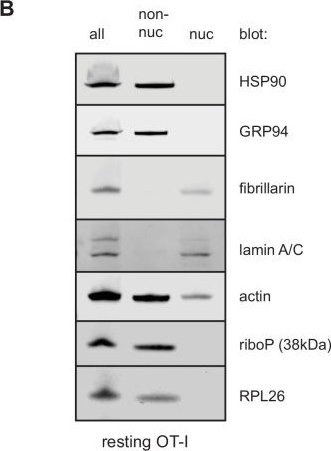
Fractionation of HeLa or T cells reveals few ribosomal components in nuclear lysates.HeLa cells (A), freshly isolated resting OT-I T cells (B), or OT-I T cells stimulated with PMA/ionomycin and IL-2 in vitro for 2 days (C) were either lysed directly in sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) extraction buffer (all) or subjected to a hypotonic lysis procedure to isolate non-nuclear lysates and nuclear lysates. Equal amounts of each fraction were subjected to immunoblotting for markers typical of the cytosol, ER, and nucleus. Antibodies against ribosomal proteins were used to determine where the majority of ribosomal proteins (and therefore ribosomes) fractionated. Controls with antibodies specific for nucleolar located fibrillarin, histone H3, and lamin A/C establish lack of nuclear contamination in non-nuclear fractions. ER and cytoplasmic proteins HSP90, GRP94, PDI, and actin indicate lack of contamination in the nuclear fraction. Representative of two experiments.Figure 6—figure supplement 1—source data 1.Uncropped and outlined immunoblot images related to Figure 6—figure supplement 1.Figure 6—figure supplement 1—source data 2.Uncropped immunoblot images related to Figure 6—figure supplement 1.Uncropped and outlined immunoblot images related to Figure 6—figure supplement 1.Uncropped immunoblot images related to Figure 6—figure supplement 1.
Image collected and cropped by CiteAb under a CC-BY license from the following publication: Paradoxical imbalance between activated lymphocyte protein synthesis capacity and rapid division rate. Elife (2024)
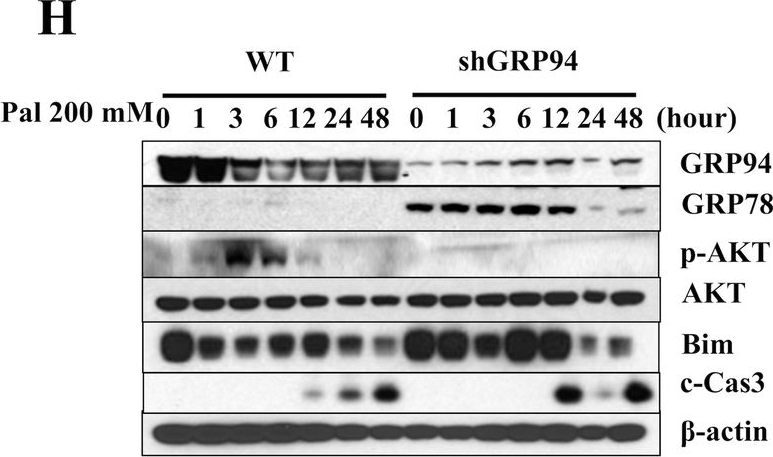
GRP94 KD cells are more susceptible to stress-induced cell death.A Relative GRP94 mRNA expression in WT control and Knockdown cells (shGRP94). B Protein expression of GRP94 in WT and KD cells. C Viability of WT control (white columns) and KD (black columns) cells after TG (1 μM)*p < 0.05 versus con WT, #p < 0.05 versus con shGRP94, $p < 0.05 versus 24 h WT, %p < 0.05 versus 24 h shGRP94, ^p < 0.05 versus 48 h WT, one-way ANOVA, D TU (10 μg/ml)*p < 0.05 versus con WT, #p < 0.05 versus con shGRP94, $p < 0.05 versus 48 h WT, %p < 0.05 versus 48 h shGRP94, ^p < 0.05 versus 72 h WT, one-way ANOVA, or E Pal (200 μM)*p < 0.05 versus con WT, #p < 0.05 versus con shGRP94, $p < 0.05 versus 24 h WT, %p < 0.05 versus 24 h shGRP94, ^p < 0.05 versus 48 h WT, one-way ANOVA, at different time after treatment. Cell death was measured by trypan blue (n = 3). F–H Protein expression of GRP94, GRP78, p-AKT, AKT, Bim, cleaved Caspase-3 (c-Cas-3), and β-actin in WT control and GRP94 KD cells at indicated times after TG, TU, or Pal treatment as analyzed by immunoblot.
Image collected and cropped by CiteAb under a CC-BY license from the following publication: GRP94 is an IGF-1R chaperone and regulates beta cell death in diabetes. Cell Death Dis (2024)
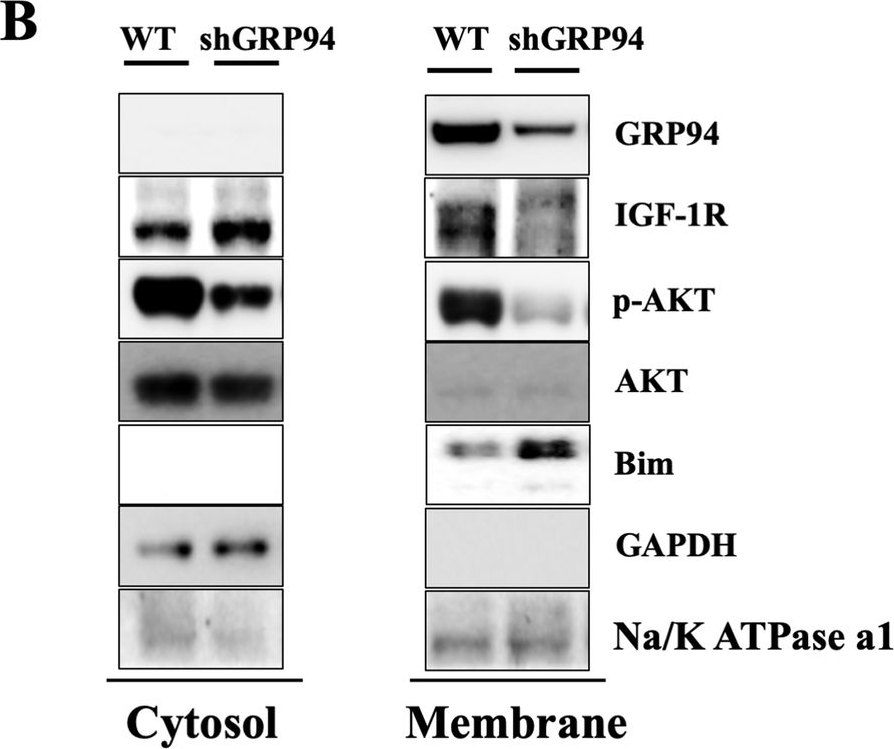
GRP94 is required for membrane expression/maturation of IGF-1R.A Immunoblot analysis of GRP94, IGF-1R, IR, p-AKT, AKT, Bim, and β-actin from total lysates of WT and GRP94 KD cells. B Immunoblot analysis of GRP94, IGF-1R, p-AKT, AKT, Bim, and GAPDH from cytosol or membrane of WT and GRP94 KD cells. C Immunoblot analysis of GRP94, IGF-1R, p-AKT, AKT, Bim, and β-actin in islets harvested from 8-weeks old control or GRP94 KO KO mice. D Immunofluorescence analysis of GRP94 (red), IGF-1R (green), and nucleus (blue) in WT or KO mouse islets. Scale bar, 25 µm.
Image collected and cropped by CiteAb under a CC-BY license from the following publication: GRP94 is an IGF-1R chaperone and regulates beta cell death in diabetes. Cell Death Dis (2024)
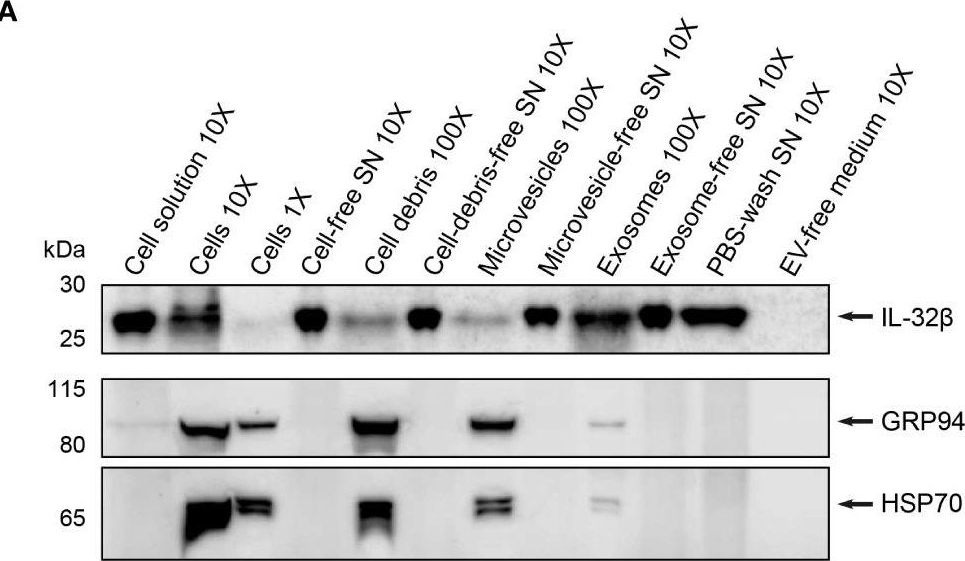
IL-32 is secreted by T cells predominantly as a free protein. (A) Representative WB analyses of IL-32β and the microvesicle/exosome markers GRP94 and HSP70 in lysates of cells, cell-debris, microvesicles and exosomes, into the respective cell solution and cell-free, cell debris-free, microvesicle-free and exosome-free supernatant (SN), the PBS-wash SN, which was used to wash the exosome pellet, and in the EV-free medium used to culture Survivin-specific T cells for 4 h with anti-CD3/CD28 antibodies. The loaded quantity of each lysate and SN sample corresponds to 0.16×106 (1X), 1.6×106 (10X) and 16×106 (100X) Survivin-specific T cells and the amount of PBS-wash SN derived from this cell number or the volume of EV-free medium used to culture this cell number. MW in kDa (IL-32β: 23.1, GRP94: 98, HSP70: 70). IL-32β, GRP94, HSP70: n=4. n represents independent experiments. (B) Cumulative data of quantified IL-32β expression in lysates and supernatants displayed by the Area Under the Curve (AUC) for n=4 independent experiments normalized to 0.16×106 Survivin-specific T cells. Dots depict data from individual experiments, Student’s paired t-test, *p ≤ 0.05.
Image collected and cropped by CiteAb under a CC-BY license from the following publication: IL-2 and TCR stimulation induce expression and secretion of IL-32β by human T cells. Front Immunol (2024)
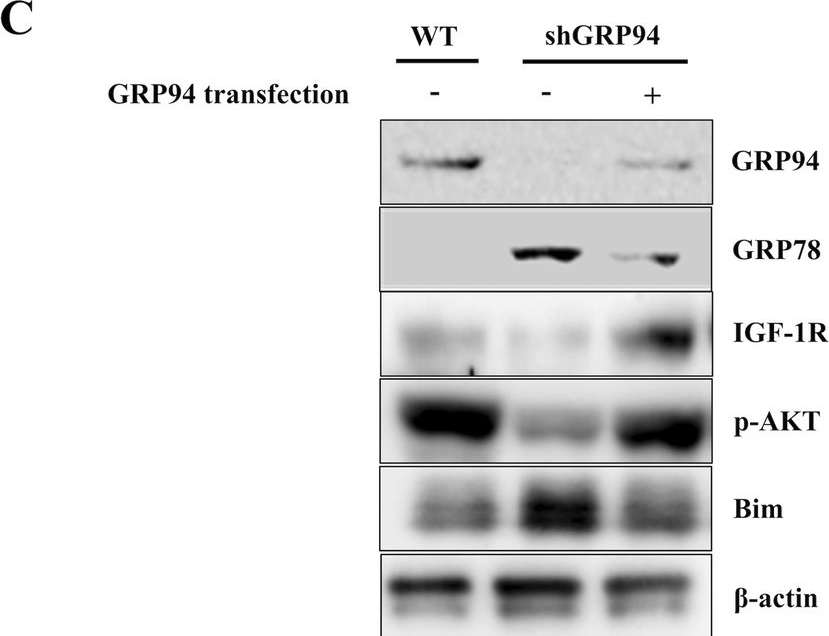
Treatment with Exendin-4 or overexpression of IGF-1R or GRP94 protects β cells from TG-induced apoptosis.A WT and GRP94 KD cells were treated with 1 μM TG in the absence or presence of 10 nM or 50 nM Exendin-4 for 6 h. Total cell extracts were analyzed by immunoblot for GRP94, IGF-1R, p-AKT, AKT, Bim, c-Cas-3, and β-actin. B WT and GRP94 KD cells were transfected with control plasmid (p.babe plasmid) or IGF-1R overexpression (p.babe-IGF-1R) plasmid and then treated with TG for 6 h or TU for 48 h. Total cell extracts were then analyzed by immunoblot for GRP94, IGF-1R, p-AKT, AKT, Bim, c-Cas-3, and β-actin. C GRP94 KD cells were transfected with GRP94 WT plasmid. Total cell extracts were then analyzed by immunoblot for GRP94, IGF-1R, p-AKT, Bim, and β-actin.
Image collected and cropped by CiteAb under a CC-BY license from the following publication: GRP94 is an IGF-1R chaperone and regulates beta cell death in diabetes. Cell Death Dis (2024)
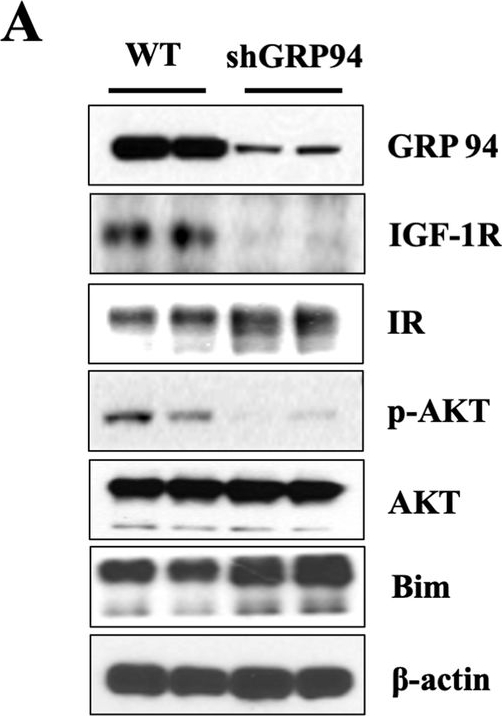
GRP94 is required for membrane expression/maturation of IGF-1R.A Immunoblot analysis of GRP94, IGF-1R, IR, p-AKT, AKT, Bim, and β-actin from total lysates of WT and GRP94 KD cells. B Immunoblot analysis of GRP94, IGF-1R, p-AKT, AKT, Bim, and GAPDH from cytosol or membrane of WT and GRP94 KD cells. C Immunoblot analysis of GRP94, IGF-1R, p-AKT, AKT, Bim, and β-actin in islets harvested from 8-weeks old control or GRP94 KO KO mice. D Immunofluorescence analysis of GRP94 (red), IGF-1R (green), and nucleus (blue) in WT or KO mouse islets. Scale bar, 25 µm.
Image collected and cropped by CiteAb under a CC-BY license from the following publication: GRP94 is an IGF-1R chaperone and regulates beta cell death in diabetes. Cell Death Dis (2024)
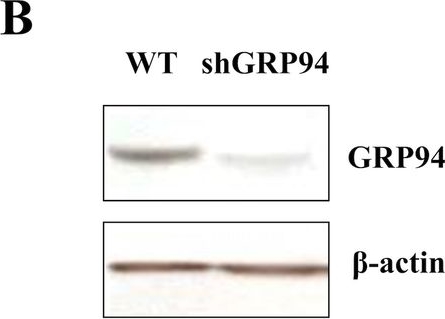
GRP94 KD cells are more susceptible to stress-induced cell death.A Relative GRP94 mRNA expression in WT control and Knockdown cells (shGRP94). B Protein expression of GRP94 in WT and KD cells. C Viability of WT control (white columns) and KD (black columns) cells after TG (1 μM)*p < 0.05 versus con WT, #p < 0.05 versus con shGRP94, $p < 0.05 versus 24 h WT, %p < 0.05 versus 24 h shGRP94, ^p < 0.05 versus 48 h WT, one-way ANOVA, D TU (10 μg/ml)*p < 0.05 versus con WT, #p < 0.05 versus con shGRP94, $p < 0.05 versus 48 h WT, %p < 0.05 versus 48 h shGRP94, ^p < 0.05 versus 72 h WT, one-way ANOVA, or E Pal (200 μM)*p < 0.05 versus con WT, #p < 0.05 versus con shGRP94, $p < 0.05 versus 24 h WT, %p < 0.05 versus 24 h shGRP94, ^p < 0.05 versus 48 h WT, one-way ANOVA, at different time after treatment. Cell death was measured by trypan blue (n = 3). F–H Protein expression of GRP94, GRP78, p-AKT, AKT, Bim, cleaved Caspase-3 (c-Cas-3), and β-actin in WT control and GRP94 KD cells at indicated times after TG, TU, or Pal treatment as analyzed by immunoblot.
Image collected and cropped by CiteAb under a CC-BY license from the following publication: GRP94 is an IGF-1R chaperone and regulates beta cell death in diabetes. Cell Death Dis (2024)
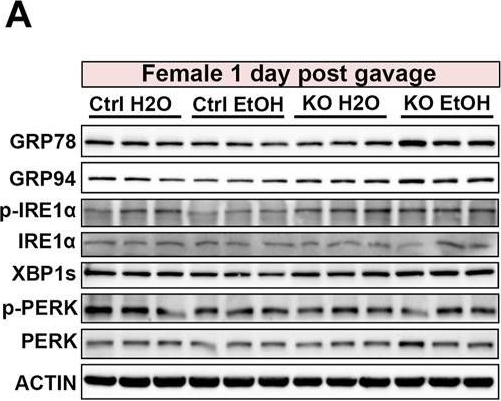
Effects of binge alcohol exposure and neuronal MANF deficiency on neuronal ER homeostasis. (A–D) Representative immunoblots (A, C) and quantification (B, D) of ER stress markers in female control and MANF KO cerebral cortex 1 day (A, B) or 60 days (C–D) post H2O or EtOH treatment. (E, H) Representative immunoblots (E, G) and quantification (F, H) of ER stress markers in male control and MANF KO cerebral cortex 1 day (E, F) or 60 days (G, H) post H2O or EtOH treatment. All data were expressed as mean ± SEM. n = 3 per group. Two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 when compared to H2O treated control. #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001 when compared to EtOH treated control. @p < 0.05, @@p < 0.01 when compared to H2O treated KO.
Image collected and cropped by CiteAb under a CC-BY license from the following publication: Sex-specific effects of alcohol on neurobehavioral performance and endoplasmic reticulum stress: an analysis using neuron-specific MANF deficient mice. Front Pharmacol (2024)
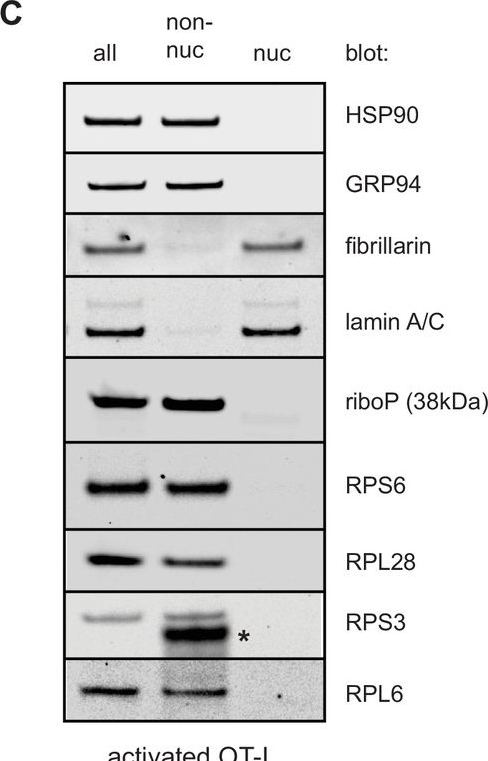
Fractionation of HeLa or T cells reveals few ribosomal components in nuclear lysates.HeLa cells (A), freshly isolated resting OT-I T cells (B), or OT-I T cells stimulated with PMA/ionomycin and IL-2 in vitro for 2 days (C) were either lysed directly in sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) extraction buffer (all) or subjected to a hypotonic lysis procedure to isolate non-nuclear lysates and nuclear lysates. Equal amounts of each fraction were subjected to immunoblotting for markers typical of the cytosol, ER, and nucleus. Antibodies against ribosomal proteins were used to determine where the majority of ribosomal proteins (and therefore ribosomes) fractionated. Controls with antibodies specific for nucleolar located fibrillarin, histone H3, and lamin A/C establish lack of nuclear contamination in non-nuclear fractions. ER and cytoplasmic proteins HSP90, GRP94, PDI, and actin indicate lack of contamination in the nuclear fraction. Representative of two experiments.Figure 6—figure supplement 1—source data 1.Uncropped and outlined immunoblot images related to Figure 6—figure supplement 1.Figure 6—figure supplement 1—source data 2.Uncropped immunoblot images related to Figure 6—figure supplement 1.Uncropped and outlined immunoblot images related to Figure 6—figure supplement 1.Uncropped immunoblot images related to Figure 6—figure supplement 1.
Image collected and cropped by CiteAb under a CC-BY license from the following publication: Paradoxical imbalance between activated lymphocyte protein synthesis capacity and rapid division rate. Elife (2024)
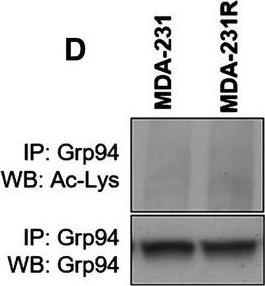
Altered NQO1 levels, HDAC family member expression and altered acetylation status in 17‐AAG‐resistant cell lines. Analysis of parental and resistant cell lines demonstrated altered expression levels of a number of molecules. Semiquantitative PCR demonstrated that the expression levels of NQO1 in resistant MDA‐435 cells were decreased when compared with parental cells, while no alteration was noted between MDA‐231 and MDA‐231R cell lines (A). Western blot analysis of parental and resistant MDA‐231 total cell lysates examining levels of HDAC family members in the presence and absence of 17‐AAG for a period of 24 h (B). Analysis of acetylated HSP90 by immunoprecipitation of HSP90 and western blot analysis with antiacetylated lysine antibody of total cell lysates of parental and resistant MDA‐231 cells treated with and without 17‐AAG demonstrated increased acetylated HSP90 (C). Analysis of acetylation of Grp94 (D) and Trap1 (E) by immunoprecipitation and western blot analysis of MDA‐231 and MDA‐231R total cell lysates demonstrated no alteration in acetylation status. Acetylated lysine residue was detected by western blotting. Western blot analysis of acetylated histone 3 in parental and resistant MDA‐231 cells treated with and without 17‐AAG demonstrated decreased nuclear acetylation (F).
Image collected and cropped by CiteAb under a CC-BY license from the following publication: Histone deacetylase activity mediates acquired resistance towards structurally diverse HSP90 inhibitors. Mol Oncol (2017)
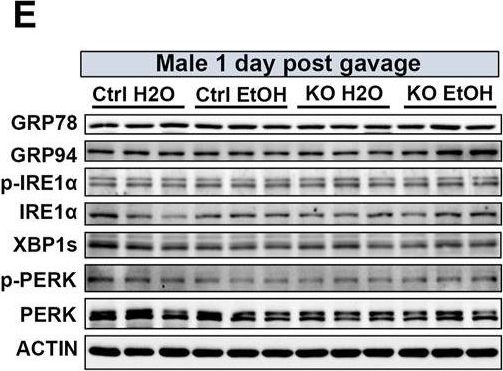
Effects of binge alcohol exposure and neuronal MANF deficiency on neuronal ER homeostasis. (A–D) Representative immunoblots (A, C) and quantification (B, D) of ER stress markers in female control and MANF KO cerebral cortex 1 day (A, B) or 60 days (C–D) post H2O or EtOH treatment. (E, H) Representative immunoblots (E, G) and quantification (F, H) of ER stress markers in male control and MANF KO cerebral cortex 1 day (E, F) or 60 days (G, H) post H2O or EtOH treatment. All data were expressed as mean ± SEM. n = 3 per group. Two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 when compared to H2O treated control. #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001 when compared to EtOH treated control. @p < 0.05, @@p < 0.01 when compared to H2O treated KO.
Image collected and cropped by CiteAb under a CC-BY license from the following publication: Sex-specific effects of alcohol on neurobehavioral performance and endoplasmic reticulum stress: an analysis using neuron-specific MANF deficient mice. Front Pharmacol (2024)
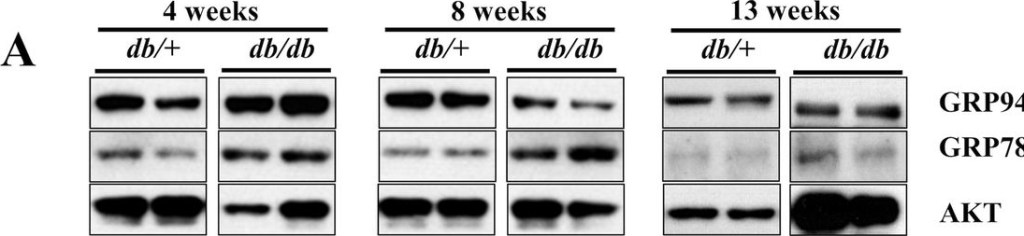
Dynamic change of GRP94 expression in db/db mice at different ages.Expression of GRP94 and GRP78 in mouse islets isolated from 4, 8, and 13-week-old diabetic db/db mice and their heterozygous littermates controls by Western blot (A) and quantification (B). Immunoblots of GRP78, GRP94, and densitometry analyses are shown. *p < 0.05 versus 4wks db/+, #p < 0.05 versus 4wks db/db, $p < 0.05 versus 8wks db/+, %p < 0.05 versus 8wks db/db, ^p < 0.05 versus 4wks db/+, one-way ANOVA. C Immunostaining for GRP94 (green), insulin (red), and nucleus (blue) in sections from 4 and 13-week-old diabetic db/db mice. Scale bar, 50 µm. D Histograms show corrected total cell fluorescence (CTCF) of GRP94 fluorescence quantified by ImageJ software. The CTCF = Integrated Density – (Area of selected cell x Mean fluorescence of background readings). *p < 0.05, Student’s t-test.
Image collected and cropped by CiteAb under a CC-BY license from the following publication: GRP94 is an IGF-1R chaperone and regulates beta cell death in diabetes. Cell Death Dis (2024)
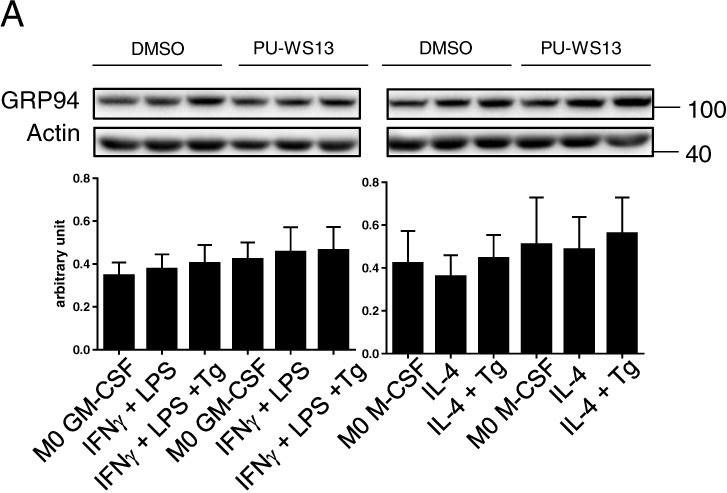
Inhibition of GRP94 by PU-WS13 impairs the effect of Tg-induced ER stress on M2 macrophages.M1 and M2 macrophages from PBMC healthy volunteers were activated in the presence of GM-CSF and M-CSF, respectively. Tg was added to cell cultures during the 48 h activation period. PU-WS13 or DMSO as vehicle was added in cell culture medium at the concentration of 25 μM 24 h before and during all the activation period. A Intracellular GRP94 western-blot analysis (n = 3). B FACS analysis of membrane GRP94 expression (n = 6). C GRP94 quantification by ELISA in activated M2 cell culture supernatants (n = 6). D CD80 and CD206 analysis by flow cytometry (n = 4). E, F Western blot analysis of MMP9 in activated M2 macrophages (n = 4) (E) and of the signalization proteins pSTAT1/STAT1, pSTAT6/STAT6 and pIκB/ IκB (n = 4) (F). G Analysis of pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines in M2 cell culture supernatants (n = 5–7). IL-1β, IL-6, IFNγ and TNFα were quantified by the Multiplex™ method and TGF-β was quantified by ELISA (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.005; ****p < 0.001).
Image collected and cropped by CiteAb under a CC-BY license from the following publication: The HSP GRP94 interacts with macrophage intracellular complement C3 and impacts M2 profile during ER stress. Cell Death Dis (2021)
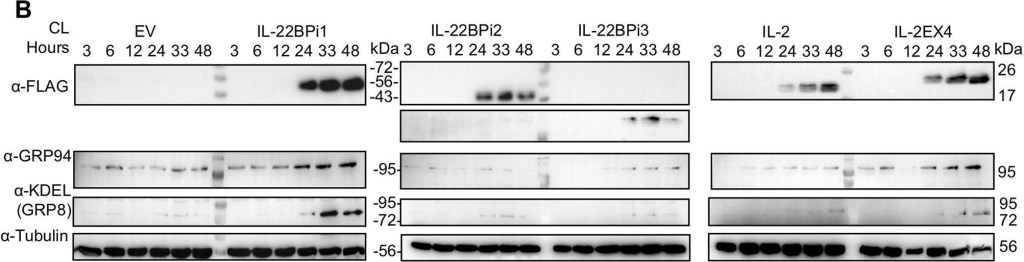
IL-22BPi1 and IL-2EX4 induce unfolded protein response (UPR) genes. HEK293 cells were transiently transfected with IL-22BPi1, IL-22BPi2, IL-22BPi3, IL-2, IL-2EX4 or empty vector (EV) as control. Cells were collected at the indicated hours after transfection. (A) Expression of different genes related to ER function or UPR were analyzed by RT-qPCR. Each gene expression value is represented as fold change relative to the same time-point expression value of the EV condition and relative to the housekeeping gene GAPDH. Mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. All primers are listed in Supplementary Table 2. (B) GRP78 and GRP94 protein levels correlate with mRNA levels observed in (A). Cell lysates (CL) were immunoblotted for FLAG, GRP94, KDEL and tubulin as loading control. (C) IL-22BPi1 and IL-2EX4 cause XPB1 splicing. XBP1 splicing was detected with conventional PCR for the indicated conditions and times. Un-spliced and spliced XBP1 are indicated as XBP1-u or XBP-1s respectively. (D) IL-22BPi2 secretion was not increased when co-expressed with different ratios of IL-22BPi1. HEK293 cells were co-expressed with different ratios of EV:IL-22BPi1:IL-22BPi2 expression plasmids. 48 h later, secreted IL-22BP in conditioned media (CM) was quantified by ELISA (mean ± SEM; n = 3). (E) Cell viability measured with alamarBlue was not compromised by any of the conditions in two different cell lines. Reduction of alamarBlue was measured after 48 h of transfection and assayed for the indicated times and cell lines. Values are represented as percentage of reduction in each condition relative to EV (mean ± SEM; n = 3).
Image collected and cropped by CiteAb under a CC-BY license from the following publication: Long Interleukin-22 Binding Protein Isoform-1 Is an Intracellular Activator of the Unfolded Protein Response. Front Immunol (2019)
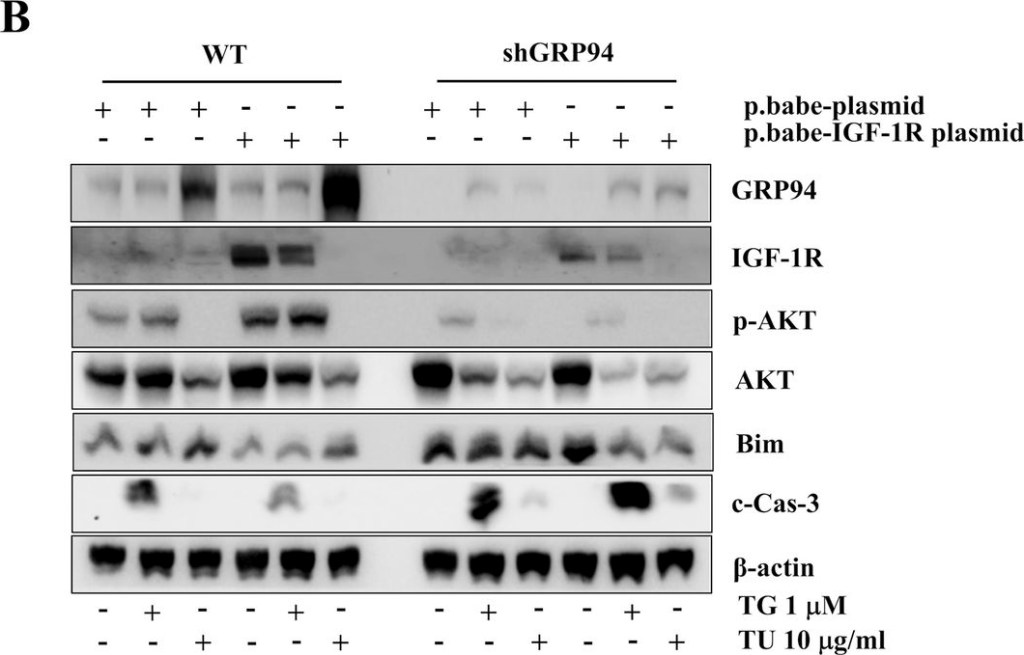
Treatment with Exendin-4 or overexpression of IGF-1R or GRP94 protects β cells from TG-induced apoptosis.A WT and GRP94 KD cells were treated with 1 μM TG in the absence or presence of 10 nM or 50 nM Exendin-4 for 6 h. Total cell extracts were analyzed by immunoblot for GRP94, IGF-1R, p-AKT, AKT, Bim, c-Cas-3, and β-actin. B WT and GRP94 KD cells were transfected with control plasmid (p.babe plasmid) or IGF-1R overexpression (p.babe-IGF-1R) plasmid and then treated with TG for 6 h or TU for 48 h. Total cell extracts were then analyzed by immunoblot for GRP94, IGF-1R, p-AKT, AKT, Bim, c-Cas-3, and β-actin. C GRP94 KD cells were transfected with GRP94 WT plasmid. Total cell extracts were then analyzed by immunoblot for GRP94, IGF-1R, p-AKT, Bim, and β-actin.
Image collected and cropped by CiteAb under a CC-BY license from the following publication: GRP94 is an IGF-1R chaperone and regulates beta cell death in diabetes. Cell Death Dis (2024)























Product Details
| Alternative Name |
Endoplasmin, Tra1, Hsp90B1, Gp96 |
|---|---|
| Application |
Electron microscopy, ICC, IF, IHC (PS), IP, WB |
| Application Notes |
Detects a band of ~98kDa by Western blot. |
| Clone |
9G10 |
| Formulation |
Liquid. In PBS containing 50% glycerol and 0.09% sodium azide. |
| GenBank ID |
M14772 |
| Host |
Rat |
| Immunogen |
Native chicken Grp94. |
| Isotype |
IgG2a |
| Purity Detail |
Protein G affinity purified. |
| Recommendation Dilutions/Conditions |
Immunoprecipitation (1:100)Western Blot (1:1,000, ECL)Suggested dilutions/conditions may not be available for all applications.Optimal conditions must be determined individually for each application. |
| Source |
Purified from ascites. |
| Species Reactivity |
Bovine, Chicken, Dog, Guinea pig, Hamster, Human, Monkey, Mouse, Porcine, Rabbit, Rat, Sheep, Xenopus |
| UniProt ID |
P08110 |
| Worry-free Guarantee |
This antibody is covered by our Worry-Free Guarantee. |
Handling & Storage
| Handling |
Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
|---|---|
| Long Term Storage |
-20°C |
| Shipping |
Blue Ice |
| Regulatory Status |
RUO – Research Use Only |
|---|
- A multichaperone condensate enhances protein folding in the endoplasmic reticulum: A. Leder, et al.; Nat. Cell Biol. 27, 1422 (2025), Abstract
- Bioorthogonal Non-Canonical Amino Acid Tagging (BONCAT) to detect newly synthesized proteins in cells and their secretome: Anim, E. P., Mezzanotte, J., et al.; PLoS One 20, e0329857 (2025), Abstract
- Monitoring Pseudoprogression Using Circulating Small Extracellular Vesicles Expressing PD-L1 in a Melanoma Patient Treated With Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: Nardin, C., Vautrot, V., et al.; J. Extracell. Biol. 4, e70066 (2025), Abstract
- Functional characterisation of missense ceruloplasmin variants and real-world prevalence assessment of Aceruloplasminemia using population data: Ziliotto, N., Lencioni, S., et al.; EBioMedicine 113, 105625 (2025), Abstract
- Pharmacological chaperones restore proteostasis of epilepsy-associated GABAA receptor variants: Wang, Y. J., Seibert, H., et al.; Pharmacol. Res. 208, 107356 (2024), Abstract
- Paradoxical imbalance between activated lymphocyte protein synthesis capacity and rapid division rate: Yewdell, J. W., Dersh, D., et al.; Elife 12, (2024), Application(s): WB / Reactant(s): Human, Abstract
- IL-2 and TCR stimulation induce expression and secretion of IL-32β by human T cells.: Sanna, F. C., Benešová, I., et al.; Front. Immunol. 15, 1437224 (2024), Application(s): WB / Reactant(s): Human, Abstract
- Sex-specific effects of alcohol on neurobehavioral performance and endoplasmic reticulum stress: an analysis using neuron-specific MANF deficient mice.: Wen, W., Li, H., et al.; Front. Pharmacol. 15, 1407576 (2024), Application(s): WB, Abstract
- GRP94 is an IGF-1R chaperone and regulates beta cell death in diabetes: D.S. Kim, et al.; Cell Death Dis. 15, 374 (2024), Application(s): WB, Abstract
- Adapting the endoplasmic reticulum proteostasis rescues epilepsy-associated NMDA receptor variants.: Zhang, P. P., Benske, T. M., et al.; Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 45, 282 (2024), Reactant(s): Human, Abstract
- Circulating tumour cells and PD-L1-positive small extracellular vesicles: the liquid biopsy combination for prognostic information in patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer: Z. Eslami-S, et al.; Br. J. Cancer 130, 63 (2024), Application(s): WB / Reactant(s) Human, Abstract
- Bone marrow-derived extracellular vesicles carry the TGF-β signal transducer Smad2 to preserve hematopoietic stem cells in mice.: Gautheron, F., Georgievski, A., et al.; Cell Death Discov. 9, 117 (2023), Application(s): WB / Reactant(s): Mouse, Abstract
- How aberrant N-glycosylation can alter protein functionality and ligand binding: An atomistic view.: Castelli, M., Yan, P., et al.; Structure 31, 987 (2023), Reactant(s): Human, Abstract
- SARS-CoV-2 accessory proteins ORF7a and ORF3a use distinct mechanisms to down-regulate MHC-I surface expression: Arshad, N., Laurent-Rolle, M., et al.; PNAS 120, e2208525120 (2023), Abstract
- Potent NKT cell ligands overcome SARS-CoV-2 immune evasion to mitigate viral pathogenesis in mouse models: H. Lu, et al.; PLoS Pathog. 19, e1011240 (2023), Abstract
- Bone marrow-derived extracellular vesicles carry the TGF-β signal transducer Smad2 to preserve hematopoietic stem cells in mice: Quéré, R., Gautheron, F., et al.; Research Square , (2023), Application(s): WB / Reactant(s): Mouse
- A membrane-associated MHC-I inhibitory axis for cancer immune evasion: Chen, X., Lu, Q., et al.; Cell 186, 3903 (2023), Abstract
- Extracellular vesicles from triple negative breast cancer promote pro-inflammatory macrophages associated with better clinical outcome: M. Tkach, et al.; PNAS 119, e2107394119 (2022), Abstract
- SARS-CoV-2 accessory proteins ORF7a and ORF3a use distinct mechanisms to downregulate MHC-I surface expression: Arshad, N., Laurent-Rolle, M., et al.; bioRxiv , (2022)
- Pharmacological activation of ATF6 remodels the proteostasis network to rescue pathogenic GABAA receptors: M. Wang, et al.; Cell Biosci. 12, 48 (2022), Abstract
- Caffeine blocks SREBP2-induced hepatic PCSK9 expression to enhance LDLR-mediated cholesterol clearance.: Lebeau, P. F., Byun, J. H., et al.; Nat. Commun. 13, 770 (2022), Abstract
- The interferon-inducible protein viperin controls cancer metabolic reprogramming to enhance cancer progression: Choi, K. M., Kim, J. J., et al.; J. Clin. Invest. 132, (2022), Abstract
- Characterization of surface markers on extracellular vesicles isolated from lymphatic exudate from patients with breast cancer: K. Ekström, et al.; BMC Cancer 22, 50 (2022), Abstract
- The Endoplasmic Reticulum Membrane Complex Promotes Proteostasis of GABAsub>A/sub> Receptors: Whittsette, A., Wang, Y., et al.; bioRxiv , (2022)
- The endoplasmic reticulum membrane complex promotes proteostasis of GABAA receptors: Whittsette, A. L., Wang, Y. J., et al.; iScience 25, 104754 (2022), Abstract
- TLR or NOD receptor signaling skews monocyte fate decision via distinct mechanisms driven by mTOR and miR-155: A. Coillard, et al.; PNAS 118, e2109225118 (2021), Abstract
- Translational shutdown and evasion of the innate immune response by SARS-CoV-2 NSP14 protein: Hsu, J. C., Laurent-Rolle, M., et al.; PNAS 118, (2021), Application(s): WB, Abstract
- Calcium as a reliable marker for the quantitative assessment of endoplasmic reticulum stress in live cells.: Austin, R. C., Platko, K., et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 296, 100779 (2021), Application(s): WB / Reactant(s): Human, Abstract
- Retrograde and Anterograde Transport of Lat-Vesicles during the Immunological Synapse Formation: Defining the Finely-Tuned Mechanism.: Johannes, L., Hivroz, C., et al.; Cells 10, (2021), Application(s): WB, Abstract
- The HSP GRP94 interacts with macrophage intracellular complement C3 and impacts M2 profile during ER stress.: Garrido, C., Kohli, E., et al.; Cell Death Dis. 12, 114 (2021), Application(s): WB / Reactant(s): Mouse, Abstract
- Deletion of mFICD AMPylase alters cytokine secretion and affects visual short-term learning in vivo: N. McCaul, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 297, 100991 (2021), Abstract
- Induction of transposable element expression is central to innate sensing: Rookhuizen, D. C., Bonte, P., et al.; bioRxiv , (2021)
- Oncogene-regulated release of extracellular vesicles: Kilinc, S., Paisner, R., et al.; Dev. Cell 56, 1989 (2021), Abstract
- The heat shock response, determined by QuantiGene multiplex, is impaired in HD mouse models and not caused by HSF1 reduction: C. Gomez-Paredes, et al.; Sci. Rep. 11, 9117 (2021), Abstract
- Proteostasis Regulators Restore Function of Epilepsy-Associated GABAA Receptors: Di, X. J., Wang, Y. J., et al.; Cell Chem. Biol. 28, 46 (2021), Abstract
- Proteomic analysis of the cardiac myocyte secretome reveals extracellular protective functions for the ER stress response.: Katus, H. A., Van Eyk, J. E., et al.; J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 143, 132 (2020), Application(s): WB, Abstract
- Fibroblast-Derived STC-1 Modulates Tumor-Associated Macrophages and Lung Adenocarcinoma Development.: Kamata, T., So, T. Y., et al.; Cell Rep. 31, 107802 (2020), Application(s): ICC, Abstract
- Molecular Stressors Engender Protein Connectivity Dysfunction through Aberrant N-Glycosylation of a Chaperone: Yan, P., Patel, H. J., et al.; Cell Rep. 31, 107840 (2020), Abstract
- Retrograde And Anterograde Transport Of LAT-Vesicles During The Immunological Synapse Formation: Defining The Finely-Tuned Mechanism: Johannes, L., Hivroz, C., et al.; bioRxiv , (2020), Application(s): WB
- Extracellular vesicles derived from macrophages display glycyl-tRNA synthetase 1 and exhibit anti-cancer activity: Goughnour, P. C., Park, M. C., et al.; J. Extracell. Vesicles 10, e12029 (2020), Abstract
- Extracellular vesicles from human mesenchymal stem cells expedite chondrogenesis in 3D human degenerative disc cell cultures: Hingert, D., Ekström, K., et al.; Stem Cell Res. Ther. 11, 323 (2020), Abstract
- GRP94 regulates M1 macrophage polarization and insulin resistance: Song, L., Kim, D. S., et al.; Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 318, E1004 (2020), Abstract
- Exosomes influence the behavior of human mesenchymal stem cells on titanium surfaces: X. Wang, et al.; Biomaterials 230, 119571 (2020), Application(s): WB, Abstract
- Protective Effects of Glucose-Related Protein 78 and 94 on Cisplatin-Mediated Ototoxicity: J. Yi, et al.; Antioxidants (Basel) 9, E686 (2020), Application(s): WB / Reactant(s) Mouse, Abstract — Full Text
- Targeting Antigen to the Surface of EVs Improves the In Vivo Immunogenicity of Human and Non-human Adenoviral Vaccines in Mice: Bliss, C. M., Parsons, A. J., et al.; Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 16, 108 (2020), Abstract
- 4-Phenylbutyrate protects against atherosclerotic lesion growth by increasing the expression of HSP25 in macrophages and in the circulation of Apoe-/- mice: Lynn, E. G., Lhoták, S., et al.; FASEB J. 33, 8406 (2019), Abstract
- A CRISPR Activation Screen Identifies Genes That Protect against Zika Virus Infection: Dukhovny, A., Lamkiewicz, K., et al.; J. Virol. 93, (2019), Abstract
- Cancer-derived small extracellular vesicles promote angiogenesis by heparin-bound, bevacizumab-insensitive VEGF, independent of vesicle uptake: Ko, S. Y., Lee, W., et al.; Commun. Biol. 2, 386 (2019), Abstract
- Chemotherapy elicits pro-metastatic extracellular vesicles in breast cancer models: Keklikoglou, I., Cianciaruso, C., et al.; Nat. Cell Biol. 21, 190 (2019), Abstract
- Diet-induced hepatic steatosis abrogates cell-surface LDLR by inducing de novo PCSK9 expression in mice: Lebeau, P. F., Byun, J. H., et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 294, 9037 (2019), Abstract
- Pcsk9 knockout exacerbates diet-induced non-alcoholic steatohepatitis, fibrosis and liver injury in mice.: Lebeau, P. F., Byun, J. H., et al.; JHEP Rep. 1, 418 (2019), Abstract
- GDF10 blocks hepatic PPARγ activation to protect against diet-induced liver injury.: Platko, K., Lebeau, P. F., et al.; Mol. Metab. 27, 62 (2019), Abstract
- Extracorporeal photochemotherapy induces bona fide immunogenic cell death.: Tatsuno, K., Yamazaki, T., et al.; Cell Death Dis. 10, 578 (2019), Application(s): WB / Reactant(s): Human, Abstract
- LMAN1 (ERGIC-53) promotes trafficking of neuroreceptors: Y.L. Fu, et al.; Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 511, 356 (2019), Abstract
- Molecular profiling and functional analysis of macrophage-derived tumor extracellular vesicles: C. Cianciaruso, et al.; Cell Rep. 27, 3062 (2019), Application(s): ELISA using culture supernatants, Abstract — Full Text
- Interactome of the Autoimmune Risk Protein ANKRD55.: Elortza, F., Azkargorta, M., et al.; Front. Immunol. 10, 2067 (2019), Application(s): WB / Reactant(s): Human, Abstract
- Pharmacological Targeting of the ER-Resident Chaperones GRP94 or Cyclophilin B Induces Secretion of IL-22 Binding Protein Isoform-1 (IL-22BPi1).: Gómez-Fernández, P., Urtasun, A., et al.; Int. J. Mol. Sci. 20, (2019), Application(s): WB / Reactant(s): Human, Abstract
- Identification by proteomics of oviductal sperm-interacting proteins.: Mermillod, P., Labas, V., et al.; Reproduction 155, 457 (2018), Application(s): WB / Reactant(s): Bovine, Abstract
- Rab6-dependent retrograde traffic of LAT controls immune synapse formation and T cell activation.: Goud, B., Dogniaux, S., et al.; J. Exp. Med. 215, 1245 (2018), Application(s): WB / Reactant(s): Mouse, Abstract
- The ESCRT-III Protein CHMP1A Mediates Secretion of Sonic Hedgehog on a Distinctive Subtype of Extracellular Vesicles: Coulter, M. E., Dorobantu, C. M., et al.; Cell Rep. 24, 973 (2018), Abstract
- Carbon Monoxide Inhibits Islet Apoptosis via Induction of Autophagy.: Kim, J. S., Wu, H., et al.; Antioxid. Redox Signal. 28, 1309 (2018), Application(s): WB, Abstract
- GRP94 Is an Essential Regulator of Pancreatic β-Cell Development, Mass, and Function in Male Mice: Kim, D. S., Song, L., et al.; Endocrinology 159, 1062 (2018), Abstract
- Long Interleukin-22 Binding Protein Isoform-1 Is an Intracellular Activator of the Unfolded Protein Response: P. Gomez-Fernandez, et al.; Front. Immunol. 9, 2934 (2018), Application(s): WB / Reactant(s) Human, Abstract — Full Text
- Tumor-associated calreticulin variants functionally compromise the peptide loading complex and impair its recruitment of MHC-I.: Arshad, N., Cresswell, P., et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 293, 9555 (2018), Application(s): WB / Reactant(s): Human, Abstract
- A novel probe to assess cytosolic entry of exogenous proteins.: Lu, Q., Grotzke, J. E., et al.; Nat. Commun. 9, 3104 (2018), Application(s): WB / Reactant(s): Human, Abstract
- Purification of LAT-Containing Membranes from Resting and Activated T Lymphocytes: Hivroz, C., Larghi, P., et al.; Methods Mol. Biol. 1584, 355 (2017), Abstract
- Histone deacetylase activity mediates acquired resistance towards structurally diverse HSP90 inhibitors: R.C. Chai, et al.; Mol. Oncol. 11, 567 (2017), Application(s): WB, WB post IP / Reactant(s) Human, Abstract — Full Text
- CNPY2 is a key initiator of the PERK-CHOP pathway of the unfolded protein response: Hong, F., Liu, B., et al.; Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 24, 834 (2017), Abstract
- GRP78 haploinsufficiency suppresses acinar-to-ductal metaplasia, signaling, and mutant Kras-driven pancreatic tumorigenesis in mice.: Dubeau, L., Lee, A. S., et al.; PNAS 114, E4020 (2017), Reactant(s): Mouse, Abstract
- Characterisation of adipocyte-derived extracellular vesicle subtypes identifies distinct protein and lipid signatures for large and small extracellular vesicles.: Durcin, M., Fleury, A., et al.; J. Extracell. Vesicles 6, 1305677 (2017), Application(s): WB / Reactant(s): Mouse, Abstract
- Bilberry extract administration prevents retinal ganglion cell death in mice via the regulation of chaperone molecules under conditions of endoplasmic reticulum stress.: Nakazawa, T., Sato, K., et al.; Clin. Ophthalmol. 11, 1825 (2017), Application(s): WB / Reactant(s): Mouse, Abstract
- Hermes (Rbpms) is a Critical Component of RNP Complexes that Sequester Germline RNAs during Oogenesis: T. Aguero, et al.; J. Dev. Biol. 4, 2 (2016), Application(s): Immunofluorescence microscopy, Abstract — Full Text
- Subcellular mechanisms involved in apoptosis induced by aminoglycoside antibiotics: Insights on p53, proteasome and endoplasmic reticulum: S. Denamur, et al.; Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 309, 24 (2016), Application(s): Western blot, LLC-PK1 (Lilly Laboratories Culture-Pig Kidney Type 1) cells, Abstract
- Grp94 Delivers γ-aminobutyric Acid Type A (GABAA) Receptors to Hrd1-Mediatd Endoplasmic Reticulum-Associated Degradation: X.J. Di, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 291, 9526 (2016), Application(s): Western blot, Abstract — Full Text
- Agonist-Mediated Activation of STING Induces Apoptosis in Malignant B Cells: C.A. Tang, et al.; Cancer Res. 76, 2137 (2016), Abstract — Full Text
- Resveratrol augments ER stress and the cytotoxic effects of glycolytic inhibition in neuroblastoma by downregulating Akt in a mechanism independent of SIRT1: R.M. Graham, et al.; Exp. Mol. Med. 48, e210 (2016), Application(s): Western blot, Abstract — Full Text
- Cutting Edge: Novel Tmem173 Allele Reveals Importance of STING N Terminus in Trafficking and Type I IFN Production: Surpris, G., Chan, J., et al.; J. Immunol. 196, 547 (2016), Abstract
- The small molecule ferristatin II induces hepatic hepcidin expression in vivo and in vitro: Alkhateeb, A. A., Buckett, P. D., et al.; Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 308, G1019 (2015), Abstract
- A Versatile Cell Death Screening Assay Using Dye-Stained Cells and Multivariate Image Analysis: T.J. Collins, et al.; Assay Drug Dev. Technol. 13, 547 (2015), Application(s): Western Blot, Abstract — Full Text
- Tunicamycin-induced unfolded protein response in the developing mouse brain: H. Wang, et al.; Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 283, 157 (2015), Application(s): Western Blotting, Abstract
- GP96 is a GARP chaperone and controls regulatory T cell functions: Y. Zhang, et al.; J. Clin. Invest. 125, 859 (2015), Application(s): Ion Chromatography, Abstract — Full Text
- EGFR-activated Src family kinases maintain GAB1-SHP2 complexes distal from EGFR: Furcht, C. M., Buonato, J. M., et al.; Sci. Signal. 8, ra46 (2015), Abstract
- The BiP molecular chaperone plays multiple roles during the biogenesis of torsinA, an AAA+ ATPase associated with the neurological disease early-onset torsion dystonia: Zacchi, L. F., Wu, H. C., et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 289, 12727 (2014), Abstract
- Three tapasin docking sites in TAP cooperate to facilitate transporter stabilization and heterodimerization: Leonhardt, R. M., Abrahimi, P., et al.; J. Immunol. 192, 2480 (2014), Abstract
- OS-9 facilitates turnover of nonnative GRP94 marked by hyperglycosylation: Dersh, D., Jones, S. M., et al.; Mol. Biol. Cell 25, 2220 (2014), Abstract
- Cytotoxicity of withaferin A in glioblastomas involves induction of an oxidative stress-mediated heat shock response while altering Akt/mTOR and MAPK signaling pathways.: Grogan, P. T., Samadi, A. K., et al.; Invest. New Drugs 31, 545 (2013), Application(s): WB / Reactant(s): Human, Abstract
- Dynamics of major histocompatibility complex class I association with the human peptide-loading complex: Panter, M. S., Jain, A., et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 287, 31172 (2012), Abstract
- Heat shock protein gp96 is a master chaperone for toll-like receptors and is important in the innate function of macrophages: Z. Li, et al.; Immunity 26, 215 (2007), Application(s): WB, IP, IF, Flow using mouse & human cell lysates & tissue culture, Abstract
- Identifying the membrane proteome of HIV-1 latently infected cells: F. Kashanchi, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 282, 8207 (2007), Application(s): WB using human cell lysates, Abstract
- GRP94 (94 kDa glucose-regulated protein) suppresses ischemic neuronal cell death against ischemia/reperfusion injury: M. Tohyama, et al.; Eur. J. Neurosci. 18, 829 (2003), Application(s): ICC using human samples, Abstract
- Pre-M phase-promoting factor associates with annulate lamellae in Xenopus oocytes and egg extracts: E. Houliston, et al.; Mol. Biol. Cell 14, 1125 (2003), Application(s): ICC, WB using xenopus samples, Abstract
- A novel von Willebrand disease-causing mutation (Arg273Trp) in the von Willebrand factor propeptide that results in defective multimerization and secretion: S. Allen, et al.; Blood 96, 560 (2000), Application(s): WB using monkey samples, Abstract
- Expression of stress protein gp96, a tumor rejection antigen, in human colorectal cancer: P.R. Galle, et al.; Int. J. Cancer 86, 489 (2000), Application(s): IHC, WB using human samples, Abstract
- Increase in vulnerability of middle-aged rat brain to lead by cerebral energy depletion: S. Hoyer, et al.; Brain Res. Bull. 52, 371 (2000), Application(s): IHC, WB using rat samples, Abstract
- Participation of GRP94-related protein in secretion of pancreatic bile salt-dependent lipase and in its internalization by the intestinal epithelium: M. Bendayan, et al.; J. Cell. Sci. 111, 2665 (1998), Application(s): EM, IP, WB, IHC using rat samples, Abstract
- Monoclonal antibodies raised against infectious haematopoietic necrosis virus (IHNV) G protein and a cellular 90 kDa protein neutralize IHNV infection in vitro: J.Y. Lee, et al.; J. Gen. Virol. 77, 1731 (1996), Application(s): Western blot analysis compared to 90 kDa protein, Abstract — Full Text
- Amino acid deprivation-induced stress response in the bovine renal epithelial cell line NBL-1: induction of HSP 70 by phenylalanine: J.D. McGivan, et al.; Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1224, 189 (1994), Application(s): WB using bovine samples, Abstract
- Structural analysis of chicken oviduct progesterone receptor using monoclonal antibodies to the subunit B protein: W.L. McGuire, et al.; Biochemistry 23, 4427 (1984), Application(s): WB using chicken samples, Abstract
Related Products

| Application | ELISA, IHC, WB |
|---|---|
| Host | Rabbit |
| Species Reactivity | Rat |
Grp94 (canine), (recombinant)
ADI-SPP-766
Recombinant canine Grp94, an ER-resident Hsp90-family chaperone that assists in protein folding, assembly, and trafficking, and is upregulated under stress conditions like heat shock or glucose deprivation.

| Alternative Name | Tra1, Tumor rejection antigen 1, Hsp90B1, Gp96, Heat shock protein 90 kDa beta member 1, Endoplasmin |
|---|---|
| Purity | ≥90% (SDS-PAGE; Western blot) |
| Source | Produced in Sf21 insect cells. Produced in a baculovirus expression system. |
Last modified: May 29, 2024
Datasheet, Manuals, SDS & CofA
Manuals And Inserts
Certificate of Analysis
Please enter the lot number as featured on the product label
SDS
Enzo Life Science provides GHS Compliant SDS
If your language is not available please fill out the SDS request form
 Lab Essentials
Lab Essentials AMPIVIEW® RNA probes
AMPIVIEW® RNA probes Enabling Your Projects
Enabling Your Projects  GMP Services
GMP Services Bulk Solutions
Bulk Solutions Research Travel Grant
Research Travel Grant Have You Published Using an Enzo Product?
Have You Published Using an Enzo Product?

