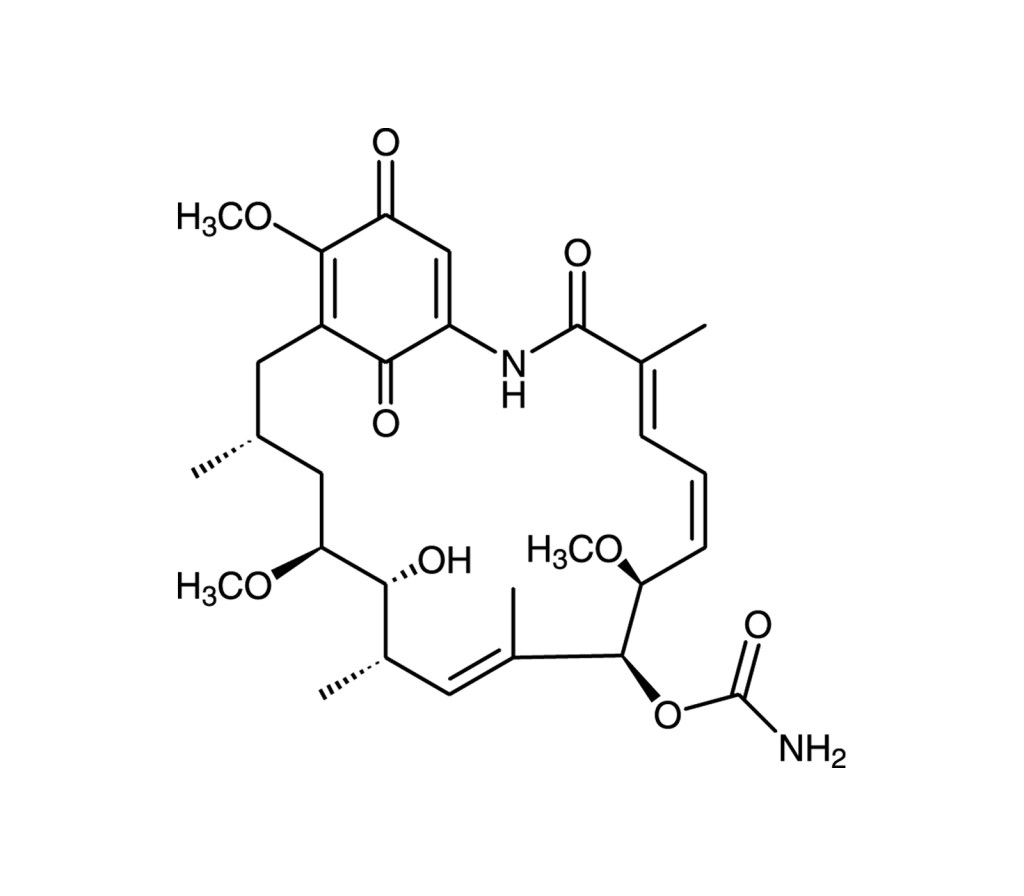
HSP90 inhibitor
Potent antitumor antibiotic. Inhibitor of pp60src tyrosine kinase and of c-myc gene expression in murine lymphoblastoma cells. Inhibits the transforming activity of abl, erbB, fps, src, and yes. Binds specifically to heat shock protein 90 (HSP90) and to its endoplasmic reticulum homolog GP96 (GRP94). Capable of destabilizing several oncogene and proto-oncogene products. Potent inhibitor of the nuclear hormone receptor family. Protects against α-synuclein toxicity to dopaminergic neurons in Drosophila. Destabilizes mutant p53 protein from a number of breast, leukemic, and prostate cell lines. Inhibits basal and hypoxia-induced expression of c-Jun (IC50=75nM) and abolishes hypoxia-induced increase in c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) activity. Inhibits telomerase activity through inhibition of HSP90, a chaperone required for the assembly and activation of telomerase in human cells. Hsp90 inhibitors geldanamycin or 17-DMAG reduces the uptake of Chaperone Mediated Autophagy (CMA) substrates by isolated lysosomes.~10-fold more potent than herbimycin A (Prod. No. BML-EI227)
Shipping: Available products typically ship within 24/48h, via priority shipping.
Do you need support? Contact Customer Service or Technical Support.
Online Account
Access or Create Your Account
Product Details
| Appearance |
Yellow solid. |
|---|---|
| CAS |
30562-34-6 |
| Couple Target |
HSP90, Src kinase |
| Couple Type |
Inhibitor |
| Formula |
C29H40N2O9 |
| MW |
560.6 |
| Purity |
≥95% (HPLC) |
| RTECS |
LX8920000 |
| Solubility |
Soluble in DMSO (10mg/ml); insoluble in water. |
| Technical Info / Product Notes |
Replacement for ADI-HPK-102 |
Handling & Storage
| Use/Stability |
As indicated on product label or CoA when stored as recommended. Stable for at least 1 year after receipt when stored, as supplied, at -20°C. Stock solutions are stable for up to 3 months at -20°C. |
|---|---|
| Handling |
Protect from light. |
| Long Term Storage |
-20°C |
| Shipping |
Ambient Temperature |
| Regulatory Status |
RUO – Research Use Only |
|---|
- Hsp90‐mediated regulation of DYRK3 couples stress granule disassembly and growth via mTORC1 signaling: L. Mediani, et al.; EMBO Rep. 2021, e51740 (2021), Abstract
- Attenuation by HSP90 inhibitors of EGF-elicited migration of osteoblasts: involvement of p44/p42 MAP kinase: G. Kuroyanagi, et al.; Connect. Tissue Res. , (2021), Abstract
- Phenotypic Screen with TSC-Deficient Neurons Reveals Heat-Shock Machinery as a Druggable Pathway for mTORC1 and Reduced Cilia: Di Nardo, A., Lenoël, I., et al.; Cell Rep. 31, 107780 (2020), Abstract
- Acidosis Acts through HSP90 in a PHD/VHL-Independent Manner to Promote HIF Function and Stem Cell Maintenance in Glioma: Filatova, A., Seidel, S., et al.; Cancer Res. 76, 5845 (2016), Abstract
- Radicicol induces intracellular accumulation of glycan-deficient clusterin variant: I. Choi, et al.; Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 458, 555 (2015), Application(s): Cell Culture, Abstract
- Elevated Serum Antibody Levels against Cyclin L2 in Patients with Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma: H. Shimada, et al.; J. Cancer Sci. Ther. 7, 60 (2015), Application(s): Cell Culture, Full Text
- Reversing drug resistance of cisplatin by hsp90 inhibitors in human ovarian cancer cells: Z. Zhang, et al.; Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 8, 6687 (2015), Application(s): Cell Culture, Abstract — Full Text
- Histone Deacetylases Positively Regulate Transcription through the Elongation Machinery: Greer, C. B., Tanaka, Y., et al.; Cell Rep. 13, 1444 (2015), Abstract
- The stress protein BAG3 stabilizes Mcl-1 protein and promotes survival of cancer cells and resistance to antagonist ABT-737: Boiani, M., Daniel, C., et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 288, 6980 (2013), Abstract
- STE20-related kinase adaptor protein α (STRADα) regulates cell polarity and invasion through PAK1 signaling in LKB1-null cells: Eggers, C. M., Kline, E. R., et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 287, 18758 (2012), Abstract
- A formal model for analyzing drug combination effects and its application in TNF-alpha-induced NFkappaB pathway: Yan, H., Zhang, B., et al.; BMC Syst. Biol. 4, 50 (2010), Abstract
- Reactive oxygen species mediate hepatotoxicity induced by the Hsp90 inhibitor geldanamycin and its analogs: Samuni, Y., Ishii, H., et al.; Free Radic. Biol. Med. 48, 1559 (2010), Abstract
- Hsp90-inhibitor geldanamycin abrogates G(2) arrest in p53-negative leukemia cell lines through the depletion of Chk1: K. Sugimoto, et al.; Oncogene 27, 3091 (2008), Abstract
- The heat-shock protein 90 inhibitor, geldanamycin, induces apoptotic cell death in Epstein-Barr virus-positive NK/T-cell lymphoma by Akt down-regulation: Y.K. Jeon, et al.; J. Pathol. 213, 170 (2007), Abstract
- Geldanamycin enhances hepatocyte growth factor stimulation of eNOS phosphorylation in endothelial cells: K. Makondo, et al.; Eur. J. Pharmacol. 582, 110 (2007), Abstract
- HSP90 antagonist, geldanamycin, inhibits proliferation, induces apoptosis and blocks migration of rhabdomyosarcoma cells in vitro and seeding into bone marrow in vivo: E. Lesko, et al.; Anticancer Drugs 18, 1173 (2007), Abstract
- Geldanamycin, a HSP90 inhibitor, attenuates the hypoxia-induced vascular endothelial growth factor expression in retinal pigment epithelium cells in vitro: W.C. Wu, et al.; Exp. Eye Res. 85, 721 (2007), Abstract
- Low dose geldanamycin inhibits hepatocyte growth factor and hypoxia-stimulated invasion of cancer cells: F. Koga, et al.; Cell Cycle 6, 1393 (2007), Abstract
- Geldanamycin, a heat-shock protein 90-binding agent, induces thymocyte apoptosis through destabilization of Lck in presence of 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol 13-acetate: K. Ohta, et al.; Biomed. Res. 28, 33 (2007), Abstract — Full Text
- Inhibition of heat shock protein 90 impairs epidermal growth factor-mediated signaling in gastric cancer cells and reduces tumor growth and vascularization in vivo: S.A. Lang, et al.; Mol. Cancer Ther. 6, 1123 (2007), Abstract — Full Text
- Relationship among ligand conformations in solution, in the solid state, and at the Hsp90 binding site: geldanamycin and radicicol: P. Thepchatri, et al.; JACS 129, 3127 (2007), Abstract
- Geldanamycin interferes with the 90-kDa heat shock protein, affecting lipopolysaccharide-mediated interleukin-1 expression and apoptosis within macrophages: H.Y. Hsu, et al.; Mol. Pharmacol. 71, 344 (2007), Abstract — Full Text
- Chaperoning oncogenes: HSP90 as a target of geldanamycin: L. Neckers; Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 172, 259 (2006), (Review), Abstract
- Cooperation of heat shock protein 90 and p23 in aryl hydrocarbon receptor signaling: Cox, M. B., Miller, C. A., et al.; Cell Stress Chaperones 9, 4 (2004), Abstract
- Inhibition of telomerase activity by geldanamycin and 17-allylamino, 17-demethoxygeldanamycin in human melanoma cells: R. Villa, et al.; Carcinogenesis 24, 851 (2003), Abstract
- Pharmacological prevention of Parkinson disease in Drosophila: P.K. Auluck & N.M. Bonini; Nat. Med. 8, 1185 (2002), Abstract
- Hsp-90-associated oncoproteins: multiple targets of geldanamycin and its analogs: M.V. Blagosklonny; Leukemia 16, 455 (2002), (Review), Abstract
- Effects of geldanamycin on signaling through activator-protein 1 in hypoxic HT29 human colon adenocarcinoma cells: I.A. Vasilevskaya and P.J. O’Dwyer; Cancer Res. 59, 3935 (1999), Abstract
- Geldanamycin as a potential anti-cancer agent: its molecular target and biochemical activity: L. Neckers, et al.; Invest. New Drugs 17, 361 (1999), (Review), Abstract
- Stable and specific binding of heat shock protein 90 by geldanamycin disrupts glucocorticoid receptor function in intact cells: L. Whitesell & P. Cook; Mol. Endocrinol. 10, 705 (1996), Abstract
- p185erbB2 binds to GRP94 in vivo. Dissociation of the p185erbB2/GRP94 heterocomplex by benzoquinone ansamycins precedes depletion of p185erbB2: C. Chavany, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 271, 4974 (1996), Abstract — Full Text
- Destabilization of Raf-1 by geldanamycin leads to disruption of the Raf-1-MEK-mitogen-activated protein kinase signalling pathway: T.W. Schulte, et al.; Mol. Cell. Biol. 16, 5839 (1996), Abstract
- Polyubiquitination and proteasomal degradation of the p185c-erbB-2 receptor protein-tyrosine kinase induced by geldanamycin: E.G. Mimnaugh, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 271, 22796 (1996), Abstract
- Inhibition of the oncogene product p185erbB-2 in vitro and in vivo by geldanamycin and dihydrogeldanamycin derivatives: R.C. Schnur, et al.; J. Med. Chem. 38, 3806 (1995), Abstract
- Geldanamycin selectively destabilizes and conformationally alters mutated p53: M.V. Blagosklonny, et al.; Oncogene 11, 933 (1995), Abstract
- Inhibition of heat shock protein HSP90-pp60v-src heteroprotein complex formation by benzoquinone ansamycins: essential role for stress proteins in oncogenic transformation: L. Whitesell, et al.; PNAS 91, 8324 (1994), Abstract
- Inhibition of c-myc gene expression in murine lymphoblastoma cells by geldanamycin and herbimycin, antibiotics of benzoquinoid ansamycin group: H. Yamaki, et al.; J. Antibiot. 42, 604 (1989), Abstract
- Phenotypic change from transformed to normal induced by benzoquinonoid ansamycins accompanies inactivation of p60src in rat kidney cells infected with Rous sarcoma virus: Y. Uehara, et al.; Mol. Cell. Biol. 6, 2198 (1986), Abstract
- Geldanamycin, a new antibiotic: C. DeBoer, et al.; J. Antibiot. 23, 442 (1970), Abstract
Related Products
| CAS | 70563-58-5 |
|---|---|
| Couple Type | Inhibitor |
| Purity | ≥98% (HPLC) |
Last modified: May 29, 2024
Datasheet, Manuals, SDS & CofA
Manuals And Inserts
Certificate of Analysis
Please enter the lot number as featured on the product label
SDS
Enzo Life Science provides GHS Compliant SDS
If your language is not available please fill out the SDS request form
 Lab Essentials
Lab Essentials AMPIVIEW® RNA probes
AMPIVIEW® RNA probes Enabling Your Projects
Enabling Your Projects  GMP Services
GMP Services Bulk Solutions
Bulk Solutions Research Travel Grant
Research Travel Grant Have You Published Using an Enzo Product?
Have You Published Using an Enzo Product?