First-to-market by the leader in Epigenetics research tools
- Useful for assaying lysates, immunoprecipitates or inhibitor screening using the nuclear extract provided
- Includes HeLa nuclear extract, a rich source of HDACs 1 & 2 for use as a positive control or as a source of HDAC activity for screening
- Compatible with class I & IIb HDAC and sirtuins (with addition of NAD+)
- Includes enough reagent for 100-200 assays
No radioactivity. No extractions. HTS friendly-mix and read on one 96-well plate. For class I and class II HDACs/sirtuins. Applications include cell-based assays and assay of immunoprecipitates.
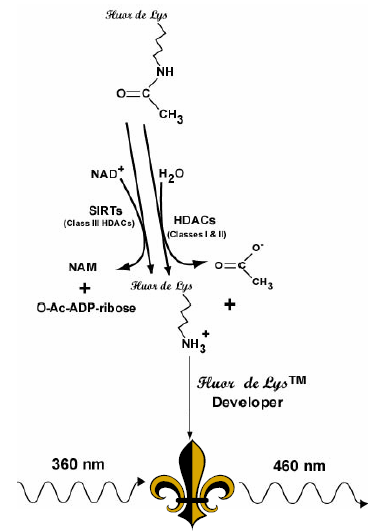
Histone deacetylase inhibitors have shown promise as anti-tumor agents and naturally this has stimulated interest in the screening of compounds for HDAC inhibition. The FLUOR DE LYS® HDAC fluorometric activity assay kit is a sensitive and convenient alternative to protocols utilizing radiolabeled, acetylated histones or peptide/HPLC methods for the assay of histone deacetylases. It is based on the unique FLUOR DE LYS® (Fluorimetric Histone deAcetylaseLysyl) substrate and developer combination and provides an assay that can be carried out in two simple mixing steps, all on the same 96-well plate. First, the FLUOR DE LYS® substrate which comprises an acetylated lysine side chain, is incubated with a sample containing HDAC activity (HeLa nuclear or other extract, purified enzyme, bead bound immunocomplex, etc.). Deacetylation of the substrate sensitizes the substrate so that, in the second step, mixing with the FLUOR DE LYS® developer generates a fluorophore. The assay has been used successfully with preparations of all the known class I HDACs-HDAC1, HDAC2, HDAC3 and HDAC8 (see product data sheet) with class II HDACs 4-7, 9 and 10 and with the human Sir2 homolog, SIRT1 (see product data sheet). Work at Enzo Life Sciences has shown that the FLUOR DE LYS® substrate is cell-permeable and is deacetylated in situ by cellular HDACs. The deacetylated substrate accumulates inside cells and may be quantified by addition of FLUOR DE LYS® developer to a cell lysate.
Shipping: Available products typically ship within 24/48h, via priority shipping.
Do you need support? Contact Customer Service or Technical Support.
Online Account
Access or Create Your Account
Product Details
| Alternative Name |
Histone deacetylase fluorescent assay kit |
|---|---|
| Application |
Activity assay, Fluorescent detection, HTS |
| Contents |
Nuclear Extract from HeLa Cells (human cervical cancer cell line) (Prod. No. BML-KI140-0100) |
Handling & Storage
| Use/Stability |
Store all components, except the microtiter plate, at -80°C for the highest stability. The HeLa Nuclear Extract, BML-KI140, must be handled with particular care in order to retain maximum enzymatic activity. Defrost it quickly in a RT water bath or by rubbing between fingers, then immediately store on an ice bath. The remaining unused extract should be refrozen quickly, by placing at -80°C. If possible, snap freeze in liquid nitrogen or a dry ice/ethanol bath. To minimize the number of freeze/thaw cycles, aliquot the extract into separate tubes and store at -80°C. The FLUOR DE LYS® Substrate, BML-KI104, when diluted in Assay Buffer, may precipitate after freezing and thawing. It is best, therefore, to dilute only the amount needed to perform the assays of that day. |
|---|---|
| Long Term Storage |
-80°C |
| Shipping |
Dry Ice |
| Regulatory Status |
RUO – Research Use Only |
|---|
- A Novel Class I HDAC Inhibitor, AW01178, Inhibits Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition and Metastasis of Breast Cancer: Liu, X., Chen, Y., et al.; Int. J. Mol. Sci. 25, (2024), Abstract
- The activation of histone deacetylases 4 prevented endothelial dysfunction: A crucial mechanism of HuangqiGuizhiWuwu Decoction in improving microcirculation dysfunction in diabetes: M. Chen, et al.; J. Ethnopharmacol. 307, 116240 (2023), Abstract
- Nutritional stress-induced regulation of microtubule organization and mRNP transport by HDAC1 controlled α-tubulin acetylation: Wippich, F., Vaishali, et al.; Commun. Biol. 6, 776 (2023), Abstract
- HDAC1 is Involved in Neuroinflammation and Blood-Brain Barrier Damage in Stroke Pathogenesis: Wang, H. K., Su, Y. T., et al.; J. Inflamm. Res. 16, 4103 (2023), Abstract
- A Bifunctional PARP-HDAC Inhibitor with Activity in Ewing Sarcoma: Ramos, L., Truong, S., et al.; Clin. Cancer Res. 29, 3541 (2023), Abstract
- Four New Anthraquinones with Histone Deacetylase Inhibitory Activity from Ventilago denticulata Roots: N. Hangsamai, et al.; Molecules 27, 1088 (2022), Abstract
- A bi-functional PARP-HDAC inhibitor with activity in Ewing sarcoma: Ramos, L., Truong, S., et al.; bioRxiv , (2022)
- Ulleunganilines A–C, Trichostatin Analogues Bearing a Modified Side Chain from Streptomyces sp. 13F051: G.J. Hwang, et al.; J. Nat. Prod. 84, 2420 (2021), Abstract
- Prolactin and Estradiol are Epigenetic Modulators in Bovine Mammary Epithelial Cells during Staphylococcus aureus Infection: M.G. Salgado-Lora, et al.; Pathogens 9, 520 (2020), Abstract — Full Text
- The Contribution of Romidepsin to the Herbicidal Activity of Burkholderia rinojensis Biopesticide: D.K. Owens, et al.; J. Nat. Prod. 83, 843 (2020), Abstract
- HDAC1 dysregulation induces aberrant cell cycle and DNA damage in progress of TDP-43 proteinopathies: Wu, C. C., Jin, L. W., et al.; EMBO Mol. Med. 12, e10622 (2020), Abstract
- Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Novel Thiazolyl-Coumarin Derivatives as Potent Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors with Antifibrotic Activity: Pardo-Jimenez, V., Navarrete-Encina, P., et al.; Molecules 24, (2019), Abstract
- Efficacy of Azatyrosine-Phenylbutyric Hydroxamides, a Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor, on Chemotherapy-Induced Gastrointestinal Mucositis: P.L. Liao, et al.; Int. J. Mol. Sci. 20, E249 (2019), Abstract
- Monomeric and oligomeric flavanols maintain the endogenous glucocorticoid response in human macrophages in pro-oxidant conditions in vitro: G. Verissimo, et al.; Chem. Biol. Interact. 291, 237 (2018), Abstract
- Sulforaphane restores acetyl-histone H3 binding to Bcl-2 promoter and prevents apoptosis in ethanol-exposed neural crest cells and mouse embryos: F. Yuan, et al.; Exp. Neurol. 300, 60 (2018), Abstract
- Exploration of the Fluorescent Properties and the Modulated Activities against Sirtuin Fluorogenic Assays of Chromenone-Derived Natural Products: Wen, H., Xue, N., et al.; Molecules 23, (2018), Abstract
- Metformin overcomes high glucose-induced insulin resistance of podocytes by pleiotropic effects on SIRT1 and AMPK: D. Rogacka, et al.; Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 1864, 115 (2018), Abstract
- Mechanisms involved in epigenetic down-regulation of Gfap under maternal hypothyroidism: P. Kumar, et al.; Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 502, 375 (2018), Abstract
- Loss of DBC1 (CCAR2) affects TNFα-induced lipolysis and Glut4 gene expression in murine adipocytes: A.A. Able, et al.; J. Mol. Endocrinol. 61, 195 (2018), Abstract
- SIRT1/FoxO3 axis alteration leads to aberrant immune responses in bronchial epithelial cells: S. Di Vincenzo, et al.; J. Cell. Mol. Med. 22, 2272 (2018), Abstract — Full Text
- Differences in Functional Expression of Connexin43 and NaV1.5 by Pan- and Class-Selective Histone Deacetylase Inhibition in Heart: X. Zhang, et al.; Int. J. Mol. Sci. 19, E2288 (2018), Abstract — Full Text
- The first-in-class alkylating deacetylase inhibitor molecule tinostamustine shows antitumor effects and is synergistic with radiotherapy in preclinical models of glioblastoma: C. Festuccia, et al.; J. Hematol. Oncol. 11, 32 (2018), Abstract — Full Text
- SIRT4 Is a Lysine Deacylase that Controls Leucine Metabolism and Insulin Secretion: K.A. Anderson, et al.; Cell Metab. 25, 838 (2017), Abstract — Full Text
- Antiproliferative effects of TSA, PXD‑101 and MS‑275 in A2780 and MCF7 cells: Acetylated histone H4 and acetylated tubulin as markers for HDACi potency and selectivity: V.P. Androutsopoulos, et al.; Oncol. Rep. 38, 3412 (2017), Abstract — Full Text
- Design, synthesis and evaluation of novel N-hydroxybenzamides/N-hydroxypropenamides incorporating quinazolin-4(3H)-ones as histone deacetylase inhibitors and antitumor agents: D.T. Hieu, et al.; Bioorg. Chem. 76, 258 (2017), Abstract
- Adiponectin corrects premature cellular senescence and normalizes antimicrobial peptide levels in senescent keratinocytes: T. Jin, et al.; Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 16, 31037 (2016), Application(s): Deacetylation activity measurement, Abstract
- Synthesis, biological characterization and molecular modeling insights of spirochromanes as potent HDAC inhibitors: F. Thaler, et al.; Eur. J. Med. Chem. 108, 53 (2016), Abstract
- Identification of new quinic acid derivatives as histone deacetylase inhibitors by fluorescence-based cellular assay: D. Son, et al.; Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 26, 2365 (2016), Abstract
- Investigating the Sensitivity of NAD+-Dependent Sirtuin Deacylation Activities to NADH: A.S. Madsen, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 291, 7128 (2016), Abstract — Full Text
- Reversible Glutathionylation of Sir2 by Monothiol Glutaredoxins Grx3/4 Regulates Stress Resistance: N. Vall-Llaura, et al.; Free Radic. Biol. Med. 96, 45 (2016), Application(s): In vitro Sir2 activity was assayed, Abstract
- Hybrid Enzalutamide Derivatives with Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor Activity Decrease Heat Shock Protein 90 and Androgen Receptor Levels and Inhibit Viability in Enzalutamide-Resistant C4-2 Prostate Cancer Cells: R. Rosati, et al.; Mol. Pharmacol. 90, 225 (2016), Abstract — Full Text
- False HDAC Inhibition by Aurone Compound: Itoh, Y., Suzuki, M., et al.; Chem. Pharm. Bull. (Tokyo) 64, 1124 (2016), Abstract
- Wnt Protein Signaling Reduces Nuclear Acetyl-CoA Levels to Suppress Gene Expression during Osteoblast Differentiation: C.M. Karner, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 291, 13028 (2016), Abstract — Full Text
- Screening and profiling assays for HDACs and sirtuins: K.T. Howitz; Drug Discov. Today Technol. 18, 38 (2015), Abstract
- Hybrids from 4-anilinoquinazoline and hydroxamic acid as dual inhibitors of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 and histone deacetylase: F.W. Peng, et al.; Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 25, 5137 (2015), Application(s): Measurement of HDAC inhibitory activity , Abstract
- NBM-T-BBX-OS01, Semisynthesized from Osthole, Induced G1 Growth Arrest through HDAC6 Inhibition in Lung Cancer Cells: J.T. Pai, et al.; Molecules 20, 8000 (2015), Application(s): Assay using human H1299 cell lysates, Abstract — Full Text
- The effect of sulforaphane on histone deacetylase activity in keratinocytes: Differences between in vitro and in vivo analyses: S.E. Dickinson, et al.; Mol. Carcinog. 54, 1513 (2015), Abstract — Full Text
- Macrocyclic compounds as anti-cancer agents: Design and synthesis of multi-acting inhibitors against HDAC, FLT3 and JAK2: C. Q. Ning, et al.; Eur. J. Med. Chem. 95, 104 (2015), Abstract
- Synthesis and anticancer activities of thieno[3,2-d]pyrimidines as novel HDAC inhibitors: Q. Tan, et al.; Bioorg. Med. Chem. 22, 358 (2014), Application(s): Assay, Abstract
- RNA-dependent dynamic histone acetylation regulates MCL1 alternative splicing: Khan, D. H., Gonzalez, C., et al.; Nucleic Acids Res. 42, 1656 (2014), Abstract
- NL-103, a novel dual-targeted inhibitor of histone deacetylases and hedgehog pathway, effectively overcomes vismodegib resistance conferred by Smo mutations: J. Zhao, et al.; Pharmacol. Res- Perspect. 2, e00043 (2014), Abstract — Full Text
- Molecular mechanism of sphingosine-1-phosphate action in Duchenne muscular dystrophy: D.H. Nguyen-Tran, et al.; Dis. Model Mech. 7, 41 (2014), Application(s): Assay, Abstract — Full Text
- Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of di-substituted cinnamic hydroxamic acids bearing urea/thiourea unit as potent histone deacetylase inhibitors: C. Ning, et al.; Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 23, 6432 (2013), Application(s): Assay, Abstract
- Dual-Acting Histone Deacetylase-Topoisomerase I Inhibitors: W. Guerrant, et al.; Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 23, 3283 (2013), Application(s): Assay, Abstract — Full Text
- Novel N-hydroxyfurylacrylamide-based histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors with branched CAP group (Part 2): T. Feng, et al.; Bioorg. Med. Chem. 21, 5339 (2013), Abstract
- Efficient new constructs against triple negative breast cancer cells: synthesis and preliminary biological study of ferrocifen-SAHA hybrids and related species: J.D.J. Cazares Marinero, et al.; Dalton Trans. 42, 15489 (2013), Abstract
- Rejuvenating sirtuins: the rise of a new family of cancer drug targets: S. Bruzzone, et al.; Curr. Pharm. Des. 19, 614 (2013), Abstract — Full Text
- Benzofused hydroxamic acids: useful fragments for the preparation of histone deacetylase inhibitors. Part 1: hit identification: E. Marastoni, et al.; Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 23, 4091 (2013), Application(s): Assay, Abstract
- Lactate, a product of glycolytic metabolism, inhibits histone deacetylase activity and promotes changes in gene expression: T. Latham, et al.; Nucleic Acids Res. 40, 4794 (2012), Abstract — Full Text
- Macrocyclic peptoid-Peptide hybrids as inhibitors of class I histone deacetylases: Olsen, C. A., Montero, A., et al.; ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 3, 749 (2012), Abstract
- Synthesis, evaluation and molecular modeling of cyclic tetrapeptide histone deacetylase inhibitors as anticancer agents: D. Huang, et al.; J. Pep. Sci. 18, 242 (2012), Abstract
- A novel series of l-2-benzyloxycarbonylamino-8-(2-pyridyl)-disulfidyloctanoic acid derivatives as histone deacetylase inhibitors: design, synthesis and molecular modeling study: D. Huang, et al.; Eur. J. Med. Chem. 52, 111 (2012), Abstract
- Heparanase-mediated loss of nuclear syndecan-1 enhances histone acetyltransferase (HAT) activity to promote expression of genes that drive an aggressive tumor phenotype: A. Purushothanman, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 286, 30377 (2011), Abstract — Full Text
- Activated microglia decrease histone acetylation and Nrf2-inducible anti-oxidant defence in astrocytes: restoring effects of inhibitors of HDACs, p38 MAPK and GSK3β: F. Correa, et al.; Neurobiol. Dis. 44, 142 (2011), Application(s): HDAC activity in astrocytes, Abstract
- Rescue of the mutant CFTR chloride channel by pharmacological correctors and low temperature analyzed by gene expression profiling: E. Sondo, et al.; Am. J. Physiol. Cell. Physiol. 301, C872 (2011), Application(s): HDAC activity in lung cell lines, Abstract — Full Text
- Nuclear import of histone deacetylase 5 by requisite nuclear localization signal phosphorylation: T.M. Greco, et al.; Mol. Cell. Proteomics 10, M110.004317 (2011), Application(s): Activity of immunoprecipitated HDAC5, Abstract — Full Text
- Identification of dehydroxytrichostatin A as a novel up-regulator of the ATP-binding cassette transporter A1 (ABCA1): Y. Xu, et al.; Molecules 16, 7183 (2011), Abstract — Full Text
- HDAC3 is negatively regulated by the nuclear protein DBC1: C.C. Chini, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 285, 40830 (2010), Abstract — Full Text
- Drosophila SIN3 isoforms interact with distinct proteins and have unique biological functions: M.M. Spain, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 285, 27457 (2010), Application(s): HDAC activity in nuclear extracts from S2 Drosophila cells, Abstract — Full Text
- Sulforaphane Retards the Growth of Human PC-3 Xenografts and Inhibits HDAC Activity in Human Subjects: M.C. Myzak, et al.; Exp Biol Med 232, 227 (2007), Application(s): HDAC activity in PBMC lysates, Abstract — Full Text
- Sulforaphane inhibits histone deacetylase in vivo and suppresses tumorigenesis in Apc-minus mice: M.C. Myzak, et al.; FASEB J. 20, 506 (2006), Application(s): HDAC activity in PBMC lysates, Abstract — Full Text
- Histone deacetylase is a target of valproic acid-mediated cellular differentiation: N. Gurvich et al.; Cancer Res. 64, 1079 (2004), Abstract
- Phosphorus-based SAHA analogues as histone deacetylase inhibitors: G.V. Kapustin et al.; Org. Lett. 5, 3053 (2003), Abstract
- Inhibition of silencing and accelerated aging by nicotinamide, a putative negative regulator of yeast sir2 and human SIRT1: K.J. Bitterman et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 277, 45099 (2002), Abstract
- Cloning and characterization of a histone deacetylase, HDAC9: X. Zhou et al.; PNAS 98, 10572 (2001), Abstract
Related Products
FLUOR DE LYS® HDAC fluorometric cellular activity assay kit
BML-AK503
Monitor HDAC activity in cell culture using cell-permeable FLUOR DE LYS® substrate

| Application | Activity assay, Cell-based assays, Fluorescent detection, HTS |
|---|

| Application | Activity assay, Cell-based assays, Fluorescent detection, HTS |
|---|

| Application | Activity assay, Cell-based assays, Fluorescent detection, HTS |
|---|

| Application | Activity assay, Fluorescent detection, HTS |
|---|
Last modified: May 29, 2024
Datasheet, Manuals, SDS & CofA
Certificate of Analysis
Please enter the lot number as featured on the product label
SDS
Enzo Life Science provides GHS Compliant SDS
- Dutch; Flemish (EU) SDS
- Spanish; Castilian (EU) SDS
- English (EU) SDS
- German (EU) SDS
- Italian (EU) SDS
- Finnish (EU) SDS
If your language is not available please fill out the SDS request form
 Lab Essentials
Lab Essentials AMPIVIEW® RNA probes
AMPIVIEW® RNA probes Enabling Your Projects
Enabling Your Projects  GMP Services
GMP Services Bulk Solutions
Bulk Solutions Research Travel Grant
Research Travel Grant Have You Published Using an Enzo Product?
Have You Published Using an Enzo Product?
