Fas ligand
Shipping: Available products typically ship within 24/48h, via priority shipping.
Do you need support? Contact Customer Service or Technical Support.
Online Account
Access or Create Your Account
Product Details
| Alternative Name |
APO-1L, CD95L, CD178, TNFSF 6 |
|---|---|
| Application Notes |
ELISA: binds to Fas receptor at 1-100 ng/ml. |
| Biological Activity |
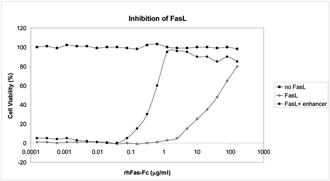
Kills Jurkat cells in the absence of a cross-linker. Cross-linking enhancer (see Set Prod. No. ALX-850-014) increases the activity of rhsFasL approx. 50-fold. |
| Concentration |
0.1mg/ml after reconstitution. |
| Endotoxin Content |
<0.1EU/µg purified protein (LAL test; Associates of Cape Cod). |
| Formulation |
Lyophilized. Contains PBS. |
| MW |
~32kDa (non-glycosylated), ~35kDa (glycosylated) (SDS-PAGE). |
| Purity |
≥95% (SDS-PAGE) |
| Purity Detail |
Purified by multi-step chromatography. |
| Reconstitution |
Reconstitute with 100µl sterile water. Further dilutions should be made with medium containing 5% fetal calf serum. |
| Source |
Produced in HEK 293 cells. The extracellular domain of human FasL (APO-1L; CD95L; CD178) (aa 103-281) is fused at the N-terminus to a linker peptide (26 aa) and a FLAG®-tag. Glycosylation of rhsFasL is similar to that of natural human FasL. |
| Specificity |
Binds to human, mouse and rat Fas (CD95; APO-1). |
| Technical Info / Product Notes |
Historical lots have shown that FasL kills Jurkat cells at concentrations of >10ng/ml in the absence of a cross-linker. Historical lots have also shown an ED50 of 50ng/ml (A20 cells). |
| UniProt ID |
P48023 |
Handling & Storage
| Use/Stability |
Stable for at least 6 months after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
|---|---|
| Handling |
Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. After reconstitution, prepare aliquots and store at -20°C. |
| Long Term Storage |
-20°C |
| Shipping |
Blue Ice |
| Regulatory Status |
RUO – Research Use Only |
|---|
- Quantifying requirements for mitochondrial apoptosis in CAR T killing of cancer cells: A.L. Pourzia, et al.; Cell Death Dis. 14, 267 (2023), Abstract
- The non-apoptotic function of Caspase-8 in negatively regulating the CDK9-mediated Ser2 phosphorylation of RNA polymerase II in cervical cancer: R. Mandal, et al.; Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 79, 597 (2022), Abstract
- Mitochondrial reactive oxygen is critical for IL-12/IL-18-induced IFN-γ production by CD4+ T cells and is regulated by Fas/FasL signaling: G. Rackov, et al.; Cell Death Dis. 13, 531 (2022), Abstract
- Caspase-9 acts as a regulator of necroptotic cell death: Molnár, T., Pallagi, P., et al.; FEBS J. 288, 6476 (2021), Abstract
- Auto-aggressive CXCR6+ CD8 T cells cause liver immune pathology in NASH: Dudek, M., Pfister, D., et al.; Nature 592, 444 (2021), Abstract
- Fas-FasL interaction in cytotoxic T cell-mediated vitiligo: The role of lesional expression of tumor necrosis factor-α and interferon-γ in Fas-mediated melanocyte apoptosis: H. Jimbo, et al.; Exp. Dermatol. 29, 61 (2020), Abstract
- Tumor Suppressor Death-Associated Protein Kinase 1 Inhibits Necroptosis by p38 MAPK Activation: Y. Wu, et al.; Cell Death Dis. 11, 305 (2020), Abstract — Full Text
- Efficient apoptosis requires feedback amplification of upstream apoptotic signals by effector caspase-3 or -7: McComb, S., Chan, P. K., et al.; Sci. Adv. 5, eaau9433 (2019), Abstract
- Fas activation alters tight junction proteins in acute lung injury: R. Herrero, et al.; Thorax 74, 69 (2019), Abstract
- Flagellin increases death receptor-mediated cell death in a RIP1-dependent manner: D. Hancz, et al.; Immunol. Lett. 193, 42 (2018), Abstract
- Pevonedistat, a Nedd8-activating enzyme inhibitor, sensitizes neoplastic B-cells to death receptor-mediated apoptosis: C. Paiva, et al.; Oncotarget 8, 21128 (2017), Abstract — Full Text
- Attenuation of lung fibrosis in mice with a clinically relevant inhibitor of glutathione-S-transferase: D.H. McMillan, et al.; JCI Insight 1, e85717 (2016), Abstract — Full Text
- Regulation of PERK-eIF2α signalling by tuberous sclerosis complex-1 controls homoeostasis and survival of myelinating oligodendrocytes: M. Jiang, et al.; Nat. Commun. 7, 12185 (2016), Abstract — Full Text
- Id3 Controls Cell Death of 2B4+ Virus-Specific CD8+ T Cells in Chronic Viral Infection: A.J. Menner, et al.; J. Immunol. 195, 2103 (2015), Abstract
- The soluble Decoy Receptor 3 is regulated by a PI3K-dependent mechanism and promotes migration and invasion in renal cell carcinoma: D. Weissinger, et al.; Mol. Cancer 12, 120 (2013), Abstract — Full Text
- Glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta regulates Snail and β-catenin expression during Fas-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in gastrointestinal cancer: H. Zheng, et al.; Eur. J. Cancer 49, 2734 (2013), Abstract
- The Fas/FasL pathway impairs the alveolar fluid clearance in mouse lungs: R. Herrero, et al.; Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 305, L377 (2013), Application(s): Death induction of primary mouse alveolar epithelial and endothelial cells, Abstract
- Role of the cell cycle in regression of the corpus luteum: S.M. Quirk, et al.; Reproduction 145, 161 (2013), Application(s): Death induction of bovine luteal cells, Abstract — Full Text
- Notochordal cells protect nucleus pulposus cells from degradation and apoptosis: implications for the mechanisms of intervertebral disc degeneration: W.M. Erwin, et al.; Arthritis Res. Ther. 13, R215 (2011), Abstract — Full Text
- Different Signaling Pathways Stimulate a Disintegrin and Metalloprotease-17 (ADAM17) in Neutrophils during Apoptosis and Activation: Y. Wang, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 286, 38980 (2011), Application(s): Death induction of Jurkat cells, Abstract — Full Text
- A novel TNFR1-triggered apoptosis pathway mediated by class IA PI3Ks in neutrophils: B. Geering, et al.; Blood 117, 5953 (2011), Application(s): Death induction of murine bone marrow neutrophils, Abstract — Full Text
- CD40·FasL and CTLA-4·FasL fusion proteins induce apoptosis in malignant cell lines by dual signaling: A. Orbach, et al.; Am. J. Pathol. 177, 3159 (2010), Abstract — Full Text
- Primary and malignant cholangiocytes undergo CD40 mediated Fas dependent apoptosis, but are insensitive to direct activation with exogenous Fas ligand: E.H. Humphreys, et al.; PLoS One 5, e14037 (2010), Abstract — Full Text
- A role for cFLIP in B cell proliferation and stress MAPK regulation: H. Zhang, et al.; J. Immunol. 182, 207 (2009), Abstract — Full Text
- Redox amplification of apoptosis by caspase-dependent cleavage of glutaredoxin 1 and S-glutathionylation of Fas: V. Anathy, et al.; J. Cell Biol. 184, 241 (2009), Application(s): Death induction of C10 cells, Fibroblasts and CD4+ T lymphocytes, Abstract — Full Text
- Caspase-8 Cleaves Histone Deacetylase 7 and Abolishes Its Transcription Repressor Function: F.L. Scott, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 283, 19499 (2008), Application(s): Death induction of primary mouse thymocytes, Abstract — Full Text
- Loss of the BH3-only protein Bmf impairs B cell homeostasis and accelerates gamma irradiation-induced thymic lymphoma development: V. Labi, et al.; J. Exp. Med. 205, 641 (2008), Abstract — Full Text
- Cytoskeleton-mediated death receptor and ligand concentration in lipid rafts forms apoptosis-promoting clusters in cancer chemotherapy: C. Gajate & F. Mollinedo; J. Biol. Chem. 280, 11641 (2005), Abstract — Full Text
- CD4-Dependent Signaling Is Required for a Late Checkpoint during Th2 Development Associated with Resistance to Activation-Induced Cell Death: Z. Tatari-Calderone, et al.; J. Immunol. 175, 5629 (2005), Application(s): Death induction of murine T cells, Abstract — Full Text
- The anti-apoptotic factor Bcl-2 can functionally substitute for the B cell survival but not for the marginal zone B cell differentiation activity of BAFF: A. Tardivel, et al.; Eur. J. Immunol. 34, 509 (2004), Abstract
- Cathepsin-B-dependent apoptosis triggered by antithymocyte globulins: a novel mechanism of T-cell depletion: M. C. Michallet, et al.; Blood 102, 3719 (2004), Abstract
- A second step of chemotaxis after transendothelial migration: keratinocytes undergoing apoptosis release IFN-gamma-inducible protein 10, monokine induced by IFN-gamma, and IFN-gamma-inducible alpha-chemoattractant for T cell chemotaxis toward epidermis in: S. Klunker, et al.; J. Immunol. 171, 1078 (2003), Abstract — Full Text
- Theileria parva-Transformed T Cells Show Enhanced Resistance to Fas/Fas Ligand-Induced Apoptosis: P. Küenzi, et al.; J. Immunol. 171, 1224 (2003), Application(s): Death induction of Theileria parva-infected TpM(803) T cells, Abstract — Full Text
- BCR engagement induces Fas resistance in primary B cells in the absence of functional Bruton’s tyrosine kinase: J.R. Tumang, et al.; J. Immunol. 168, 2712 (2002), Abstract
- Hepatic natural killer cells exclusively kill splenic/blood natural killer-resistant tumor cells by the perforin/granzyme pathway: D. Vermijlen, et al.; J. Leukoc. Biol. 72, 668 (2002), Application(s): Death induction of P815 cells, Abstract — Full Text
- T cell costimulation by the TNF ligand BAFF: B. Huard, et al.; J. Immunol. 167, 6225 (2001), Abstract
- Fas ligand overexpression on allograft endothelium inhibits inflammatory cell infiltration and transplant-associated intimal hyperplasia: M. Sata, et al.; J. Immunol. 166, 6964 (2001), Abstract
- Fas-associated death domain protein (FADD) and caspase-8 mediate up-regulation of c-Fos by Fas ligand and tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) via a FLICE inhibitory protein (FLIP)-regulated pathway: D. Siegmund, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 276, 32585 (2001), Abstract — Full Text
- Mechanisms underlying neuronal death induced by chromogranin A-activated microglia: J. Ciesielski-Treska, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 276, 13113 (2001), Abstract — Full Text
- Crosstalk Between Keratinocytes and T Lymphocytes via Fas/Fas Ligand Interaction: Modulation by Cytokines: R. Arnold, et al.; J. Immunol. 162, 7140 (1999), Application(s): Death induction of Jurkat cells, Abstract — Full Text
- Fas-Mediated Suicide of Tumor-Reactive T Cells Following Activation by Specific Tumor: Selective Rescue by Caspase Inhibition: T.Z. Zaks, et al.; J. Immunol. 162, 3273 (1999), Application(s): Death induction of tumor-specific CD8+ T cells, Abstract — Full Text
- Inhibition of Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis by Blockade of CD95 with Human Intravenous Immunoglobulin: I. Viard, et al.; Science 282, 490 (1998), Application(s): Death induction of human keratinocytes, Abstract
- Agonist antibody and Fas ligand mediate different sensitivity to death in the signaling pathways of Fas and cytoplasmic mutants: A.R. Thilenius, et al.; Eur. J. Immunol. 27, 1108 (1997), Abstract
- Characterization of Fas (Apo-1, CD95)-Fas ligand interaction: P. Schneider, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 272, 18827 (1997), Abstract — Full Text
Related Products
Last modified: May 29, 2024
Datasheet, Manuals, SDS & CofA
Manuals And Inserts
Certificate of Analysis
Please enter the lot number as featured on the product label
SDS
Enzo Life Science provides GHS Compliant SDS
If your language is not available please fill out the SDS request form
 Lab Essentials
Lab Essentials AMPIVIEW® RNA probes
AMPIVIEW® RNA probes Enabling Your Projects
Enabling Your Projects  GMP Services
GMP Services Bulk Solutions
Bulk Solutions Research Travel Grant
Research Travel Grant Have You Published Using an Enzo Product?
Have You Published Using an Enzo Product?

