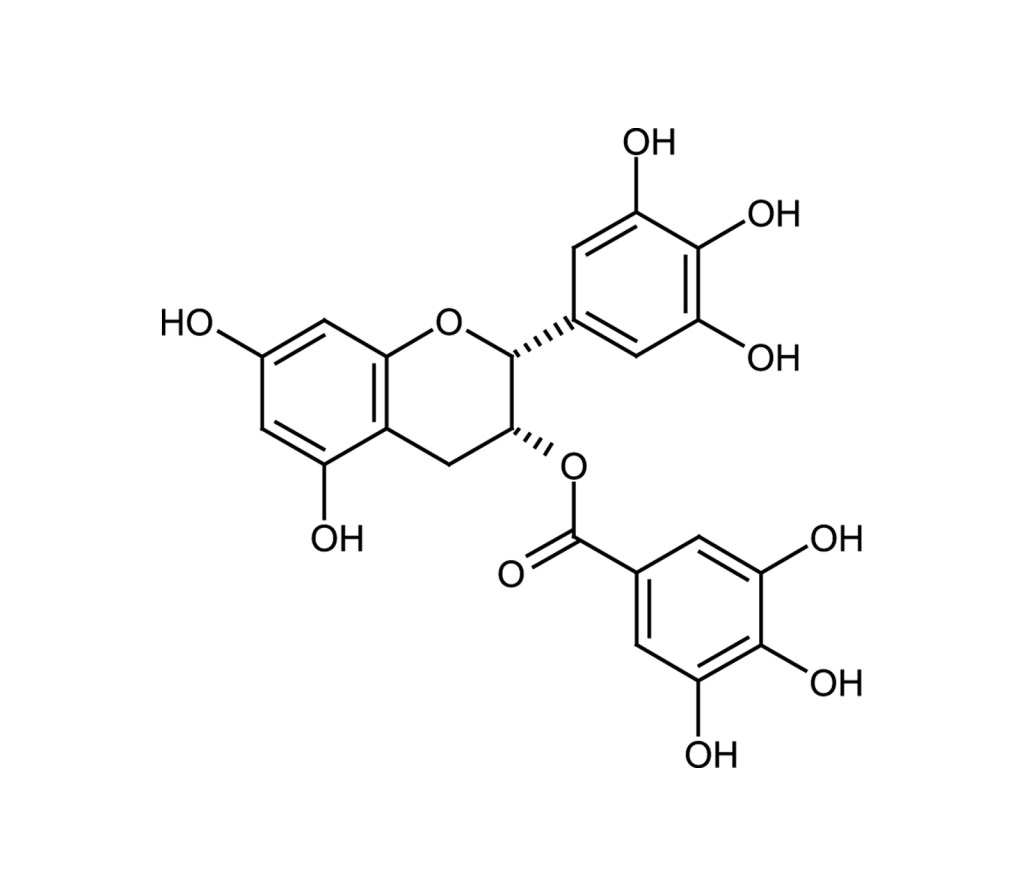
Inhibitor of NOS, telomerase and Dnmt
Antitumor reagent. Antioxidant. Protects cells from lipid peroxidation and DNA damage induced by reactive free radicals. Inhibits inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS; NOS II). Chemopreventive anticancer agent. Induces apoptosis in human cancer cell lines. Inhibits MAP kinase mediated signalling pathways. Inhibits angiogenesis. Inhibits telomerase and DNA methyltransferase. Anti-inflammatory agent.
Shipping: Available products typically ship within 24/48h, via priority shipping.
Do you need support? Contact Customer Service or Technical Support.
Online Account
Access or Create Your Account
Product Details
| Alternative Name |
EGCG, (2R,3R)-2-(3,4,5-Trihydroxyphenyl)-3,4-dihydro-1[2H]-benzopyran-3,5,7-triol 3-(3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoate) |
|---|---|
| Appearance |
White powder. |
| CAS |
989-51-5 |
| Couple Target |
Dnmt, NOS, Telomerase |
| Couple Type |
Inhibitor |
| Formula |
C22H18O11 |
| MI |
14: 3526 |
| MW |
458.4 |
| Purity |
≥98% (HPLC) |
| Solubility |
Soluble in 100% ethanol, dimethyl formamide or DMSO; slightly soluble in water. |
| Source |
Isolated from green tea. |
Handling & Storage
| Use/Stability |
As indicated on product label or CoA when stored as recommended. Stock solutions in DMSO are stable for up to 3 months when stored at -20°C. |
|---|---|
| Handling |
Protect from light. Keep under inert gas. After reconstitution, prepare aliquots and store at -20°C. |
| Long Term Storage |
+4°C |
| Shipping |
Ambient Temperature |
| Regulatory Status |
RUO – Research Use Only |
|---|
- Epigallocatechin Gallate/Layered Double Hydroxide Nanohybrids: Preparation, Characterization, and In Vitro Anti-Tumor Study: S.S. Shafiei, et al.; PLoS One 10, e0136530 (2015), Application(s): Cell Viability, Abstract — Full Text
- Tea flavanols inhibit angiotensin-converting enzyme activity and increase nitric oxide production in human endothelial cells: I.A. Persson, et al.; J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 58, 1139 (2006), Abstract
- Neuroprotective effects of (-)-epigallocatechin gallate following hypoxia-ischemia-induced brain damage: novel mechanisms of action: B.A. Sutherland, et al.; FASEB J. 19, 258 (2005), Abstract — Full Text
- Epigallocatechin-3-gallate inhibits epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway. Evidence for direct inhibition of ERK1/2 and AKT kinases: J.F. Sah, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 279, 12755 (2004), Abstract
- Inhibition of c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase activity improves ischemia/reperfusion injury in rat lungs: M. Ishii, et al.; J. Immunol. 172, 2569 (2004), Abstract
- Epigallocatechin-3-gallate, constituent of green tea, suppresses the LPS-induced phenotypic and functional maturation of murine dendritic cells through inhibition of mitogen-activated protein kinases and NF-kappaB: S.C. Ahn, et al.; BBRC 313, 148 (2004), Abstract
- A constituent of green tea, epigallocatechin-3-gallate, activates endothelial nitric oxide synthase by a phosphatidylinositol-3-OH-kinase-, cAMP-dependent protein kinase-, and Akt-dependent pathway and leads to endothelial-dependent vasorelaxation: M. Lorenz, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 279, 6190 (2004), Abstract — Full Text
- Green tea polyphenols prevent toxin-induced hepatotoxicity in mice by down-regulating inducible nitric oxide-derived prooxidants: J.H. Chen, et al.; Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 80, 742 (2004), Abstract — Full Text
- The specificities of protein kinase inhibitors: an update:: J. Bain, et al.; Biochem. J. 371, 199 (2003), Abstract — Full Text
- Inhibitory effects of green tea catechins on the activity of human matrix metalloproteinase 7 (matrilysin): H. Oneda et al.; J. Biochem. 133, 571 (2003), Abstract
- Selective inhibition of ADAMTS-1, -4 and -5 by catechin gallate esters: M.N. Vankemmelbeke, et al.; Eur. J. Biochem. 270, 2394 (2003), Abstract
- Fenton reaction is primarily involved in a mechanism of (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate to induce osteoclastic cell death: H. Nakagawa et al.; Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 292, 94 (2002), Abstract
- (-)Epigallocatechin-3-gallate inhibits leukocyte elastase: potential of the phyto-factor in hindering inflammation, emphysema, and invasion: L. Sartor et al.; J. Leukoc. Biol. 71, 73 (2002), Abstract
- Epigallocatechin gallate, a constituent of green tea, represses hepatic glucose production: M.E. Waltner-Law, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 277, 34933 (2002), Abstract — Full Text
- Tumor gelatinases and invasion inhibited by the green tea flavanol epigallocatechin-3-gallate: S. Garbisa et al.; Cancer 91, 822 (2001), Abstract
- Green tea epigallocatechin gallate: a natural inhibitor of fatty-acid synthase: X. Wang & W. Tian; BBRC 288, 1200 (2001), Abstract
- Matrix metalloproteinase inhibition by green tea catechins: M. Demeule et al.; Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1478, 51 (2000), Abstract
- Antioxidant chemistry of green tea catechins. Identification of products of the reaction of (-)-epigallocatechin gallate with peroxyl radicals: S. Valcic, et al.; Chem. Res. Toxicol. 12, 382 (1999), Abstract
- Antimutagenic and anticarcinogenic activity of tea polyphenols: Y. Kuroda & Y. Hara; Mutat. Res. 436, 69 (1999), Abstract
- Inhibitory effect of green and black tea on tumor growth: A.H. Conney, et al.; Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 220, 229 (1999), Abstract
- Polyphenolic antioxidant (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate from green tea reduces UVB-induced inflammatory responses and infiltration of leukocytes in human skin: S.K. Katiyar, et al.; Photochem. Photobiol. 69, 148 (1999), Abstract
- Pharmacokinetics of the green tea derivative, EGCG, by the topical route of administration in mouse and human skin: K. Dvorakova, et al.; Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 43, 331 (1999), Abstract
- ESR study on the structure-antioxidant activity relationship of tea catechins and their epimers: Q. Guo, et al.; Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1427, 13 (1999), Abstract
- Epigallocatechin suppression of proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells: correlation with c-jun and JNK: L.H. Lu, et al.; Br. J. Pharmacol. 124, 1227 (1998), Abstract
- Telomerase inhibition, telomere shortening, and senescence of cancer cells by tea catechins: I. Naasani, et al.; BBRC 249, 391 (1998), Abstract
- Green tea epigallocatechin gallate shows a pronounced growth inhibitory effect on cancerous cells but not on their normal counterparts: Z.P. Chen et al.; Cancer Lett. 129, 173 (1998), Abstract
- Induction of apoptosis in prostate cancer cell lines by the green tea component, (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate: A.G. Paschka et al.; Cancer Lett. 130, 1 (1998), Abstract
- (-)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate blocks the induction of nitric oxide synthase by down-regulating lipopolysaccharide-induced activity of transcription factor nuclear factor-kappaB: Y.L. Lin & J.K. Lin; Mol. Pharmacol. 52, 465 (1997), Abstract
- Inhibition of inducible nitric oxide synthase gene expression and enzyme activity by epigallocatechin gallate, a natural product from green tea: M.M. Chan, et al.; Biochem. Pharmacol. 54, 1281 (1997), Abstract
- Green tea constituent epigallocatechin-3-gallate and induction of apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in human carcinoma cells: N. Ahmad, et al.; J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 89, 1881 (1997), Abstract
- (-)-Epigallocatechin gallate, a polyphenolic tea antioxidant, inhibits peroxynitrite-mediated formation of 8-oxodeoxyguanosine and 3-nitrotyrosine: E.S. Fiala, et al.; Experientia 52, 922 (1996), Abstract
- Effects of various natural antioxidants on the Cu(2+)-mediated oxidative modification of low density lipoprotein: S. Miura et al.; Biol. Pharm. Bull. 18, 1 (1995), Abstract
- Inhibition of N-methyl-N’-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine-induced carcinogenesis by (-)-epigallocatechin gallate in the rat glandular stomach: T. Yamane, et al.; Cancer Res. 55, 2081 (1995), Abstract
- Inhibition of 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate and other skin tumor-promoter-caused induction of epidermal interleukin-1 alpha mRNA and protein expression in SENCAR mice by green tea polyphenols: S.K. Katiyar, et al.; J. Invest. Dermatol. 105, 394 (1995), Abstract
- Growth inhibition and regression of human prostate and breast tumors in athymic mice by tea epigallocatechin gallate: S. Liao, et al.; Cancer Lett. 96, 239 (1995), Abstract
- Inhibitory effect of topical application of a green tea polyphenol fraction on tumor initiation and promotion in mouse skin: M.T. Huang, et al.; Carcinogenesis 13, 947 (1992), Abstract
Last modified: May 29, 2024
Datasheet, Manuals, SDS & CofA
Manuals And Inserts
Certificate of Analysis
Please enter the lot number as featured on the product label
SDS
Enzo Life Science provides GHS Compliant SDS
If your language is not available please fill out the SDS request form
 Lab Essentials
Lab Essentials AMPIVIEW® RNA probes
AMPIVIEW® RNA probes Enabling Your Projects
Enabling Your Projects  GMP Services
GMP Services Bulk Solutions
Bulk Solutions Research Travel Grant
Research Travel Grant Have You Published Using an Enzo Product?
Have You Published Using an Enzo Product?