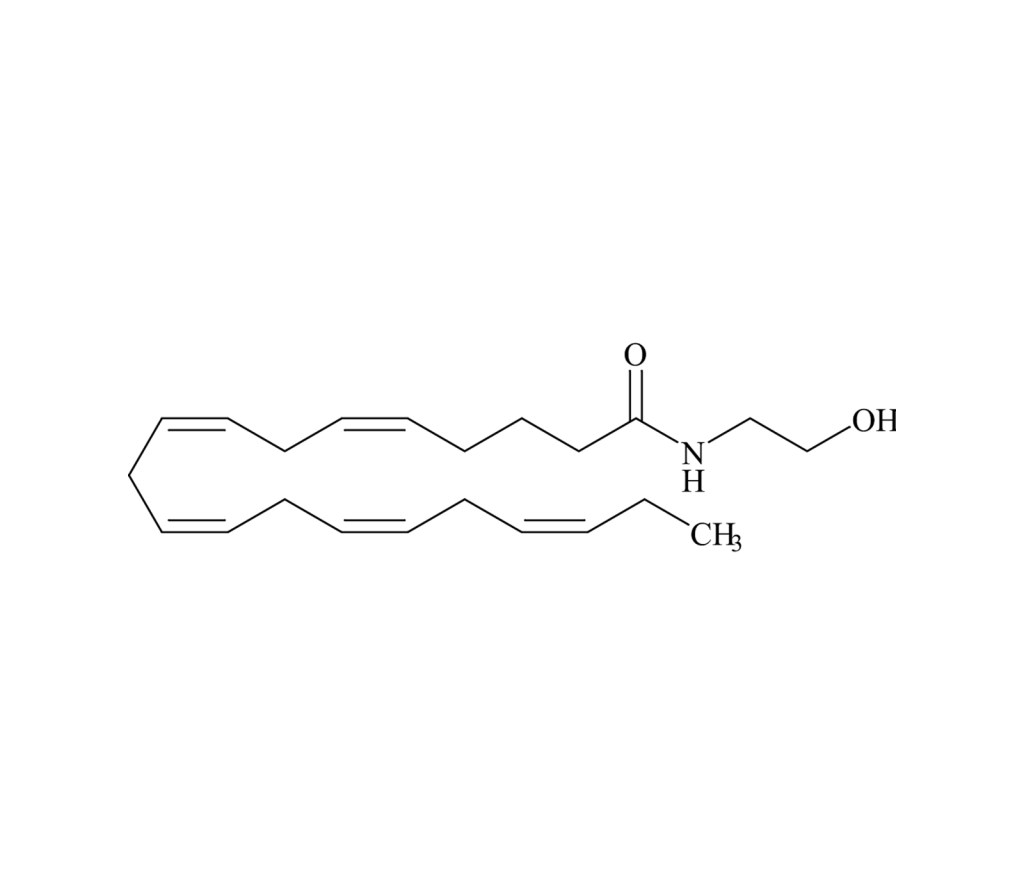
Has been shown to inhibit dietary-restriction-induced lifespan extension in wild-type and TOR pathway mutant nematodes. This data indicates that reduced N-acylethanolamide signaling mediates some of the effect of dietary-restriction-induced lifespan extension and that EPEA, specifically, acts as a metabolic signal that couples nutrient availability with growth and lifespan. EPEA has also been shown to have anti-proliferative effects and anti-inflammatory properties. Compound is subject to oxidation. Protect from air.
Shipping: Available products typically ship within 24/48h, via priority shipping.
Do you need support? Contact Customer Service or Technical Support.
Online Account
Access or Create Your Account
| Regulatory Status |
RUO – Research Use Only |
|---|
Last modified: May 29, 2024
 Lab Essentials
Lab Essentials AMPIVIEW® RNA probes
AMPIVIEW® RNA probes Enabling Your Projects
Enabling Your Projects  GMP Services
GMP Services Bulk Solutions
Bulk Solutions Research Travel Grant
Research Travel Grant Have You Published Using an Enzo Product?
Have You Published Using an Enzo Product?