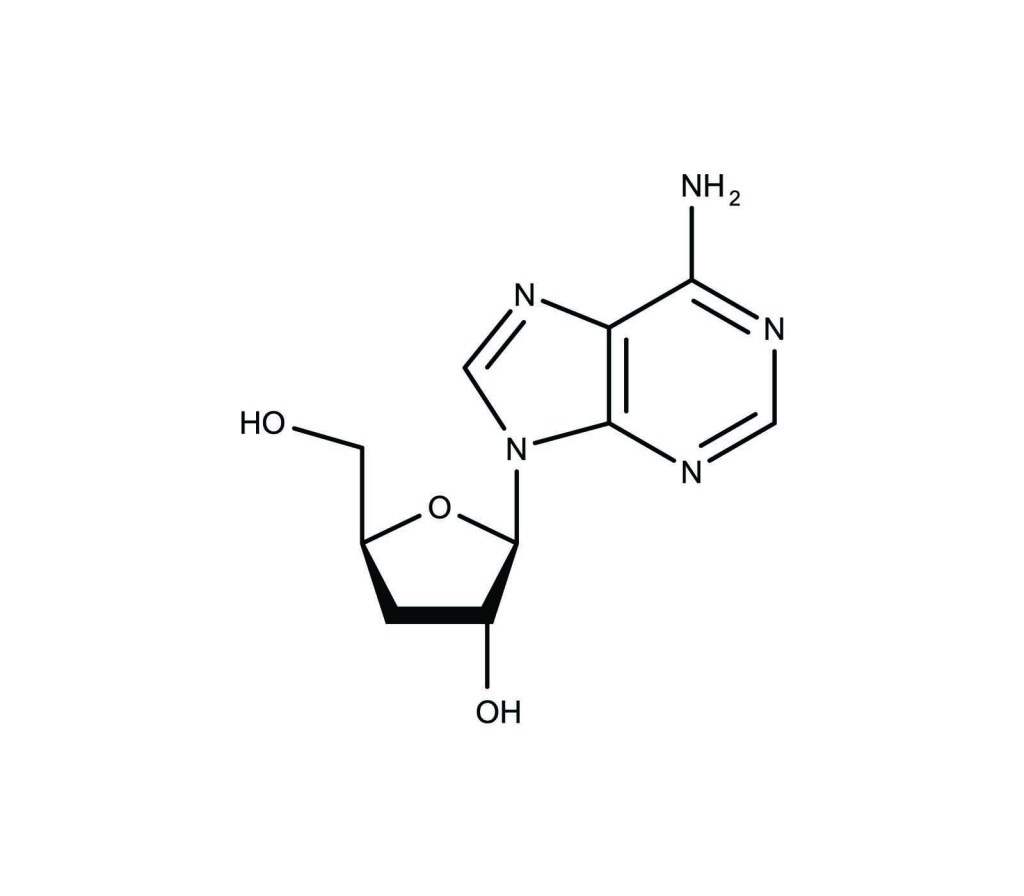
Cordycepin is a naturally occurring nucleoside analog derived from Cordyceps militaris. It is structurally similar to adenosine but lacks a hydroxyl group at the 3′ position, allowing it to interfere with RNA synthesis. Cordycepin exhibits potent biological activity, including anticancer, antifungal, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant effects. It inhibits RNA polymerase and induces apoptosis in various cancer cell lines, with reported IC50 values ranging from 10 to 50 µM, depending on the cell type.
Key features and applications include:
- RNA Chain Termination: Incorporates into RNA and halts elongation, making it a valuable tool for studying transcriptional regulation.
- Apoptosis Induction: Triggers caspase-dependent cell death in cancer cells via mitochondrial dysfunction and ROS generation.
- AMPK Activation: Modulates energy metabolism and inflammation through AMPK signaling.
- Broad-Spectrum Activity: Exhibits antifungal, antibacterial, and anti-metastatic properties.
Research Applications:
- Cancer biology and apoptosis studies
- RNA synthesis and gene expression regulation
- Inflammation and metabolic disease models
- Neuroprotection and aging research
Relevant disease states include:
- Cancer: Demonstrates cytotoxicity in breast, leukemia, and colon cancer models by disrupting RNA synthesis and promoting apoptosis.
- Inflammatory Diseases: Reduces pro-inflammatory cytokine expression and oxidative stress in models of arthritis and liver inflammation.
- Neurodegenerative Disorders: Investigated for neuroprotective effects via modulation of oxidative stress and mitochondrial function.
- Infectious Diseases: Active against gram-positive bacteria and mycobacteria, with potential antifungal applications.
Shipping: Available products typically ship within 24/48h, via priority shipping.
Do you need support? Contact Customer Service or Technical Support.
Online Account
Access or Create Your Account
| Regulatory Status |
RUO – Research Use Only |
|---|
Last modified: July 28, 2025
 Lab Essentials
Lab Essentials AMPIVIEW® RNA probes
AMPIVIEW® RNA probes Enabling Your Projects
Enabling Your Projects  GMP Services
GMP Services Bulk Solutions
Bulk Solutions Research Travel Grant
Research Travel Grant Have You Published Using an Enzo Product?
Have You Published Using an Enzo Product?