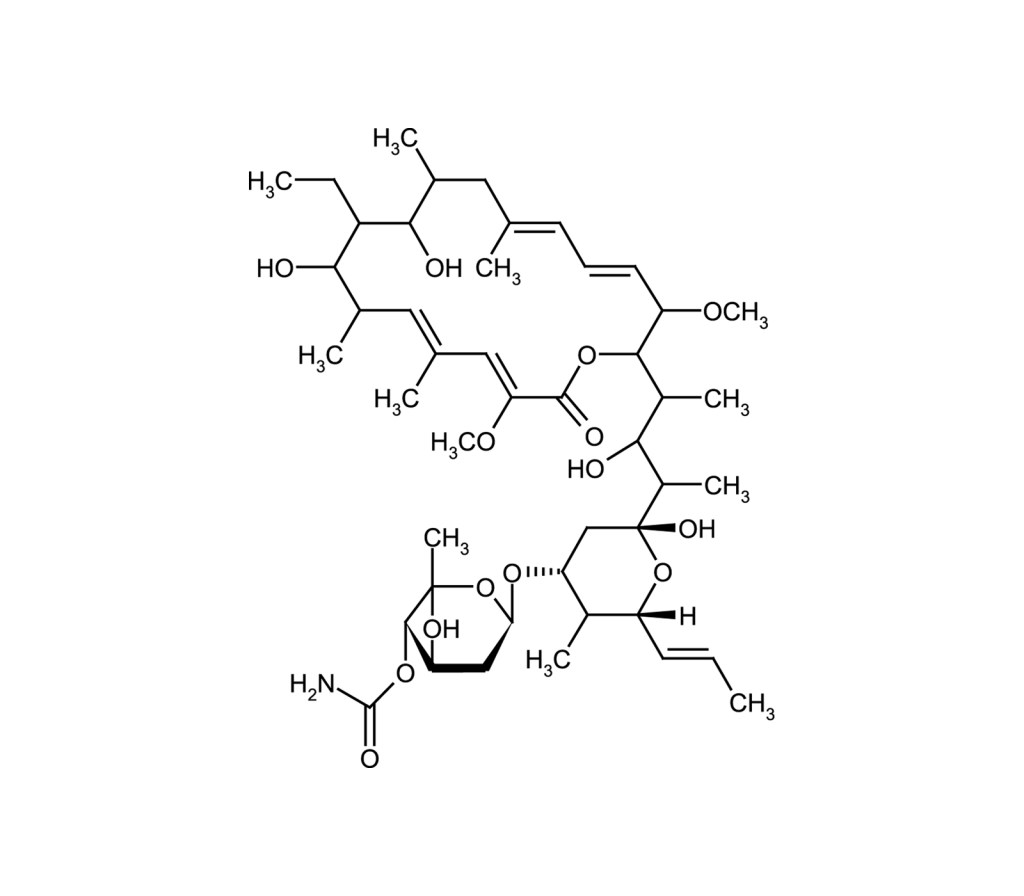
H+ ATPase inhibitor
Antibiotic. More potent and specific H+-ATPase inhibitor than bafilomycin A1 (Prod. No. BML-CM110). Inhibits acidification of organelles such as lysosomes and the Golgi apparatus. Blocks cell surface expression of viral glycoproteins without affecting their synthesis. Exhibits cytotoxic effects in a number of cell lines in a cell viability assay. Induces nitric oxide (NO) production. Inhibits Autophagy.
Shipping: Available products typically ship within 24/48h, via priority shipping.
Do you need support? Contact Customer Service or Technical Support.
Online Account
Access or Create Your Account
Product Details
| Alternative Name |
Folimycin |
|---|---|
| Appearance |
White to off-white solid (sub-milligram quantities will appear as clear film). |
| CAS |
80890-47-7 |
| Couple Target |
ATPase |
| Couple Type |
Inhibitor |
| Formula |
C46H75NO14 |
| MW |
866.1 |
| Purity |
≥95% (HPLC) |
| RTECS |
CB9732000 |
| Solubility |
Soluble in methanol, DMSO or acetonitrile; insoluble in water. |
| Source |
Isolated from Streptomyces sp. |
Handling & Storage
| Use/Stability |
As indicated on product label or CoA when stored as recommended. Stable for at least 1 year after receipt when stored at -20°C. After reconstitution protect from light . Solutions are more stable when stored at -20°C. |
|---|---|
| Short Term Storage |
+4°C |
| Long Term Storage |
-20°C |
| Shipping |
Ambient Temperature |
| Regulatory Status |
RUO – Research Use Only |
|---|
- Calpain-2 mediates SARS-CoV-2 entry via regulating ACE2 levels: Zeng, Q., Antia, A., et al.; Mbio 15, e0228723 (2024), Abstract
- Calpain-2 mediates SARS-CoV-2 entry and represents a therapeutic target: Zeng, Q., Antia, A., et al.; bioRxiv , (2022)
- STING-Mediated IFI16 Degradation Negatively Controls Type I Interferon Production: Li, D., Wu, R., et al.; Cell Rep. 29, 1249 (2019), Abstract
- Identification of V-ATPase as a molecular sensor of SOX11-levels and potential therapeutic target for mantle cell lymphoma: V.K. Emruli, et al.; BMC Cancer 16, 493 (2016), Application(s): Transient knock-down of V-ATPase, Abstract — Full Text
- Ceramide signaling targets the PP2A-like protein phosphatase Sit4p to impair vacuolar function, vesicular trafficking and autophagy in Isc1p deficient cells: V. Teixeira, et al.; Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1861, 21 (2016), Application(s): Cell Culture, Abstract
- Comparative Proteomics Reveals Strain-Specific β-TrCP Degradation via Rotavirus NSP1 Hijacking a Host Cullin-3-Rbx1 Complex: S. Ding, et al.; PLoS Pathology 12, e1005929 (2016), Application(s): Cell treatment, Abstract — Full Text
- Microautophagy of the nucleus coincides with a vacuolar diffusion barrier at nuclear-vacuolar junctions: R. Dawaliby, et al.; Mol. Biol. Cell 21, 4173 (2010), Abstract — Full Text
- Escape of HIV-1-infected dendritic cells from TRAIL-mediated NK cell cytotoxicity during NK-DC cross-talk–a pivotal role of HMGB1: M.T. Melki, et al.; PLoS Pathog. 6, e1000862 (2010), Abstract — Full Text
- Degradation of oxidized proteins by autophagy during oxidative stress in Arabidopsis: Y. Xiong, et al.; Plant Physiol. 143, 291 (2007), Abstract
- Nitric oxide production by the vacuolar-type (H+)-ATPase inhibitors bafilomycin A1 and concanamycin A and its possible role in apoptosis in RAW 264.7 cells: J. Hong, et al.; J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 319, 672 (2006), Abstract
- Organization of the biosynthetic gene cluster for the macrolide concanamycin A in Streptomyces neyagawaensis ATCC 27449: S.F. Haydock, et al.; Microbiology 151, 3161 (2005), Abstract — Full Text
- Surface cathepsin B protects cytotoxic lymphocytes from self-destruction after degranulation: Balaji, K. N., Schaschke, N., et al.; J. Exp. Med. 196, 493 (2002), Abstract
- Concanamycin A, the specific inhibitor of V-ATPases, binds to the V(o) subunit c: M. Huss, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 277, 40544 (2002), Abstract
- Specific inhibitors of vacuolar type H(+)-ATPases induce apoptotic cell death: T. Nishihara, et al.; BBRC 212, 255 (1995), Abstract
- Characterization of the ATPase activity of P-glycoprotein from multidrug-resistant Chinese hamster ovary cells: F.J. Sharom, et al.; Biochem. J. 308 (Pt2), 381 (1995), Abstract
- Folimycin (concanamycin A), an inhibitor of V-type H(+)-ATPase, blocks cell-surface expression of virus-envelope glycoproteins: M. Muroi, et al.; BBRC 193, 999 (1993), Abstract
- Inhibitory effect of modified bafilomycins and concanamycins on P- and V-type adenosinetriphosphatases: S. Drose, et al.; Biochemistry 32, 3902 (1993), Abstract
- Purification of vacuolar ATPase with bafilomycin C1 affinity chromatography: T.J. Rautiala, et al.; BBRC 194, 50 (1993), Abstract
- Folimycin (concanamycin A), a specific inhibitor of V-ATPase, blocks intracellular translocation of the glycoprotein of vesicular stomatitis virus before arrival to the Golgi apparatus: M. Muroi, et al.; Cell Struct. Funct. 18, 139 (1993), Abstract
- Involvement of the vacuolar H(+)-ATPases in the secretory pathway of HepG2 cells: M. Yilla, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 268, 19092 (1993), Abstract — Full Text
- Intravesicular acidification correlates with binding of ADP- ribosylation factor to microsomal membranes: S. Zeuzem, et al.; PNAS 89, 6619 (1992), Abstract
- Structure and function of vacuolar class of ATP-driven proton pumps: M. Forgac; Physiol. Rev. 69, 765 (1989), Abstract
- Bafilomycins: a class of inhibitors of membrane ATPases from microorganisms, animal cells, and plant cells: E.J. Bowman, et al.; PNAS 85, 7972 (1988), Abstract
- Isolation and characterization of concanamycins A, B and C: H. Kinashi, et al.; J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 37, 1333 (1984), Abstract
Related Products
Bafilomycin A1
BML-CM110
A selective V-ATPase inhibitor that disrupts lysosomal acidification, essential for autophagy flux analysis and lysosomal function studies.
| Alternative Name | NSC 381866 |
|---|---|
| CAS | 88899-55-2 |
| Couple Type | Inhibitor |
| Purity | ≥95% (HPLC, TLC) |
Last modified: May 29, 2024
Datasheet, Manuals, SDS & CofA
Manuals And Inserts
Certificate of Analysis
Please enter the lot number as featured on the product label
SDS
Enzo Life Science provides GHS Compliant SDS
If your language is not available please fill out the SDS request form
 Lab Essentials
Lab Essentials AMPIVIEW® RNA probes
AMPIVIEW® RNA probes Enabling Your Projects
Enabling Your Projects  GMP Services
GMP Services Bulk Solutions
Bulk Solutions Research Travel Grant
Research Travel Grant Have You Published Using an Enzo Product?
Have You Published Using an Enzo Product?