Centromere protein A (CENP-A), a 17-19 kDa centromere-specific histone variant, is 62% identical to the carboxy-terminal domain of histone H3. In the presence of DNA, CENP-A forms an octameric complex with histones H4, H2A, and H2B. CENP-A defines active centromere regions by forming centromere-specific nucleosomes on which kinetochores are assembled. CENP-A resides specifically in the inner plate of the kinetochore, and is essential for kinetochore targeting of CENP-C and other kinetochore components. CENP-A is required for nucleosomal packaging of centromeric DNA at interphase.
Shipping: Available products typically ship within 24/48h, via priority shipping.
Do you need support? Contact Customer Service or Technical Support.
Online Account
Access or Create Your Account
This antibody is covered by our Worry-Free Guarantee.
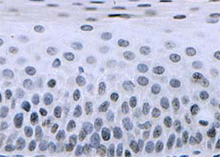
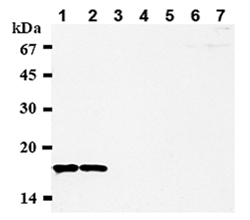

Product Details
| Alternative Name |
Centromere protein A |
|---|---|
| Application |
ICC, IHC, WB |
| Application Notes |
Detects bands of ~18kDa by Western blot. |
| Clone |
3-19 |
| Formulation |
Liquid. In PBS, pH 7.2, containing 50% glycerol. |
| Host |
Mouse |
| Immunogen |
Synthetic peptide corresponding to a portion of human CENP-A . |
| Isotype |
IgG1 |
| Purity Detail |
Protein A affinity purified. |
| Recommendation Dilutions/Conditions |
Immunocytochemistry (10µg/ml)Immunohistochemistry (5µg/ml)Western Blot (1µg/ml)Suggested dilutions/conditions may not be available for all applications.Optimal conditions must be determined individually for each application. |
| Species Reactivity |
Human |
| UniProt ID |
P49450 |
| Worry-free Guarantee |
This antibody is covered by our Worry-Free Guarantee. |
Handling & Storage
| Long Term Storage |
-20°C |
|---|---|
| Shipping |
Blue Ice |
| Regulatory Status |
RUO – Research Use Only |
|---|
- Epigenetically dynamic human centromeres are maintained within a stable DNA methylation signature: Mahlke, M. A., Lumerman, L., et al.; bioRxiv , (2025)
- The formation and propagation of human Robertsonian chromosomes.: de Lima, L. G., Guarracino, A., et al.; Nature 647, 952 (2025), Abstract
- Heterochromatin boundaries maintain centromere position, size and number.: Carty, B. L., Dubocanin, D., et al.; Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. , (2025), Abstract
- DNA methylation influences human centromere positioning and function.: Salinas-Luypaert, C., Dubocanin, D., et al.; Nat. Genet. 57, 2509 (2025), Application(s): ICC-IF, Abstract
- Chromatin remodeling activity of EP400 safeguards chromosomal stability by preventing CENP-A mislocalization.: Sethi, S. C., Shrestha, R. L., et al.; Cell Rep. 44, 116423 (2025), Application(s): ICC-IF, Abstract
- CENP-A is diluted during bovine spermatogenesis and is maintained at internally positioned centromere clusters in mature bull sperm.: Štiavnická, M., Ní Nualláin, A., et al.; Chromosome Res. 33, 20 (2025), Abstract
- CENP-A is diluted during bovine spermatogenesis and is maintained at internally positioned centromere clusters in mature bull sperm: Štiavnická, M., Nualláin, A. N., et al.; Research Square , (2025)
- Centromeric transposable elements and epigenetic status drive karyotypic variation in the eastern hoolock gibbon: Hartley, G. A., Okhovat, M., et al.; Cell Genom. 5, 100808 (2025), Abstract
- Heterochromatin boundaries maintain centromere position, size and number: Carty, B. L., Dubocanin, D., et al.; bioRxiv , (2025)
- Conservation of dichromatin organization along regional centromeres: Dubocanin, D., Hartley, G. A., et al.; Cell Genom. 5, 100819 (2025), Abstract
- Centromeric transposable elements and epigenetic status drive karyotypic variation in the eastern hoolock gibbon: Hartley, G. A., Okhovat, M., et al.; bioRxiv , (2024)
- β-TrCP-Mediated Proteolysis of Mis18β Prevents Mislocalization of CENP-A and Chromosomal Instability.: Sethi, S. C., Shrestha, R. L., et al.; Mol. Cell. Biol. 44, 429 (2024), Reactant(s): Human, Abstract
- DNAJC9 prevents CENP-A mislocalization and chromosomal instability by maintaining the fidelity of histone supply chains.: Balachandra, V., Shrestha, R. L., et al.; EMBO J. 43, 2166 (2024), Application(s): WB, Abstract
- The variation and evolution of complete human centromeres: Logsdon, G. A., Rozanski, A. N., et al.; Nature 629, 136 (2024), Abstract
- Vertebrate centromeres in mitosis are functionally bipartite structures stabilized by cohesin: Sacristan, C., Samejima, K., et al.; Cell 187, 3006 (2024), Abstract
- The bromodomain inhibitor JQ1 is a molecular glue targeting centromeres: Corless, S., Pratap-Singh, N., et al.; bioRxiv , (2023)
- The histone H3/H4 chaperone CHAF1B prevents the mislocalization of CENP-A for chromosomal stability.: Shrestha, R. L., Balachandra, V., et al.; J. Cell Sci. 136, (2023), Application(s): ICC-IF, WB, Abstract
- WEE1 kinase inhibition triggers severe chromosome pulverization in aneuploid cells: Haykal, M. M., Rodrigues-Ferreira, S., et al.; bioRxiv , (2023)
- Efficient Formation of Single-copy Human Artificial Chromosomes: Gambogi, C. W., Mer, E., et al.; bioRxiv , (2023)
- Centrosome linker diversity and its function in centrosome clustering and mitotic spindle formation: Theile, L., Li, X., et al.; EMBO J. 42, e109738 (2023), Abstract
- A mitotic chromatin phase transition prevents perforation by microtubules: M.W.G. Schneider, et al.; Nature 609, 183 (2022), Application(s): ICC-IF, Abstract
- A chromatin phase transition protects mitotic chromosomes against microtubule perforation: Schneider, M. W. G., Gibson, B. A., et al.; bioRxiv , (2021)
- Subcellular Euclidean distance measurements with multicolor fluorescence localization imaging in cultured cells: T.E. Germanova, et al.; STAR Protoc. 2, 100774 (2021), Abstract
- CENP-A Subnuclear Localization Pattern as Marker Predicting Curability by Chemoradiation Therapy for Locally Advanced Head and Neck Cancer Patients: P. Verrelle, et al.; Cancers (Basel) 13, 3928 (2021), Application(s): IHC / Reactant(s) Human, Abstract
- The structure, function and evolution of a complete human chromosome 8: G.A. Logsdon, et al.; Nature 593, 101 (2021), Application(s): ChIP, ICC-IF, Abstract
- CENP-A overexpression promotes distinct fates in human cells, depending on p53 status.: Almouzni, G., Podsypanina, K., et al.; Commun. Biol. 4, 417 (2021), Application(s): ICC-IF / Reactant(s): Human, Abstract
- Gene replacement strategies validate the use of functional tags on centromeric chromatin and invalidate an essential role for CENP-AK124ub: C. Salinas-Luypaert, et al.; Cell Rep. 37, 10924 (2021), Application(s): ICC-IF / Reactant(s) Human, Abstract
- CENP-A overexpression drives distinct cell fates depending on p53 status: Almouzni, G., Podsypanina, K., et al.; bioRxiv , (2020), Reactant(s): Human
- A genetic memory initiates the epigenetic loop necessary to preserve centromere position: S. Hoffmann, et al.; EMBO J. 39, e105505 (2020), Application(s): Flow Cytometry, ICC-IF, Abstract
- Ensemble-Level Organization of Human Kinetochores and Evidence for Distinct Tension and Attachment Sensors: E. Roscioli, et al.; Cell Rep. 31, 107535 (2020), Abstract
- Human chromosome-specific aneuploidy is influenced by DNA-dependent centromeric features: Dumont, M., Gamba, R., et al.; EMBO J. 39, e102924 (2020), Abstract
- CENP-A chromatin prevents replication stress at centromeres to avoid structural aneuploidy: Funabiki, H., Smogorzewska, A., et al.; bioRxiv , (2020), Reactant(s): Human
- The structure, function, and evolution of a complete human chromosome 8: Surti, U., Larionov, V., et al.; bioRxiv , (2020), Application(s): ICC-IF
- The N-Terminal Domain of cGAS Determines Preferential Association with Centromeric DNA and Innate Immune Activation in the Nucleus.: Gentili, M., Lahaye, X., et al.; Cell Rep. 26, 2377 (2019), Application(s): ICC-IF / Reactant(s): Human, Abstract
- Phosphorylation of CENP-A on serine 7 does not control centromere function: V. Barra, et al.; Nat. Commun. 10, 175 (2019), Application(s): ICC-IF, IF / Reactant(s) Human, Abstract — Full Text
- Human Artificial Chromosomes that Bypass Centromeric DNA: G.A. Logsdon, et al.; Cell 178, 624 (2019), Application(s): ChIP, Abstract — Full Text
- Structure of the Human Core Centromeric Nucleosome Complex: Allu, P. K., Dawicki-McKenna, J. M., et al.; Curr. Biol. 29, 2625 (2019), Abstract
- Centromeres are maintained by fastening CENP-A to DNA and directing an arginine anchor-dependent nucleosome transition: L.Y. Guo, et al.; Nat. Commun. 8, 15775 (2017), Application(s): IF / Reactant(s) Human, Abstract — Full Text
- CENP-A Modifications on Ser68 and Lys124 Are Dispensable for Establishment, Maintenance, and Long-Term Function of Human Centromeres: D. Fachinetti, et al.; Dev. Cell 40, 104 (2017), Application(s): ICC, ICC-IF / Reactant(s) Human, Abstract — Full Text
- Both tails and the centromere targeting domain of CENP-A are required for centromere establishment.: Guo, L. Y., Bassett, E. A., et al.; J. Cell Biol. 208, 521 (2015), Application(s): ICC-IF, IF / Reactant(s): Human, Abstract
- Sequences associated with centromere competency in the human genome: K.E. Hayden, et al.; Mol. Cell. Biol. 33, 763 (2013), Reactant(s) Human, Abstract — Full Text
- Composition and organization of active centromere sequences in complex genomes: K.E. Hayden, et al.; BMC Genomics 13, 324 (2012), Abstract — Full Text
Last modified: May 29, 2024
Datasheet, Manuals, SDS & CofA
Manuals And Inserts
Certificate of Analysis
Please enter the lot number as featured on the product label
SDS
Enzo Life Science provides GHS Compliant SDS
If your language is not available please fill out the SDS request form
 Lab Essentials
Lab Essentials AMPIVIEW® RNA probes
AMPIVIEW® RNA probes Enabling Your Projects
Enabling Your Projects  GMP Services
GMP Services Bulk Solutions
Bulk Solutions Research Travel Grant
Research Travel Grant Have You Published Using an Enzo Product?
Have You Published Using an Enzo Product?
