Increases the stimulation of B cells
Shipping: Available products typically ship within 24/48h, via priority shipping.
Do you need support? Contact Customer Service or Technical Support.
Online Account
Access or Create Your Account
![2µg/ml of goat anti-human µ chain antibody and with the indicated concentration of CD40L in the presence and absence of 1µg/ml enhancer (Prod. No. ALX-804-034). Cells were pulsed for an additional 6 hours with [3H]thymidine (1µCi/well) and harvested. [3H]thymidine incorporation was monitored by liquid scintillation counting."""""](https://www.enzo.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/01/522-015-2.gif?w=516)
Figure 2: Stimulation of B cells by CD40L, Soluble (human) (rec.). Dose dependent costimulation of CD19+ cells by CD40L in the presence of 10ng/ml of IL-4 and of 2µg/ml anti-µ antibodies. Note that in the presence of enhancer (Prod. No. ALX-804-034)
![2µg/ml of goat anti-human µ chain antibody and with the indicated concentration of CD40L in the presence and absence of 1µg/ml enhancer (Prod. No. ALX-804-034). Cells were pulsed for an additional 6 hours with [3H]thymidine (1µCi/well) and harvested. [3H]thymidine incorporation was monitored by liquid scintillation counting."""""](https://www.enzo.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/01/522-015-2.gif?w=516)
Product Details
| Alternative Name |
CD154, TNFSF 5, gp39 |
|---|---|
| Application Notes |
ELISA: binds to CD40 receptor at 1-10 ng/ml. |
| Concentration |
0.1mg/ml after reconstitution. |
| Endotoxin Content |
<0.1EU/µg purified protein (LAL test; Associates of Cape Cod). |
| Formulation |
Lyophilized. Contains PBS. |
| MW |
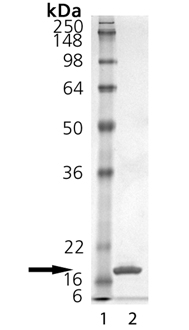
~18kDa (SDS-PAGE). |
| Purity |
≥95% (SDS-PAGE) |
| Purity Detail |
Purified by Multi-Step Chromatography. |
| Reconstitution |
Reconstitute each tube with 100µl sterile water. Further dilutions should be made with medium containing 5% fetal calf serum or a carrier protein. |
| Source |
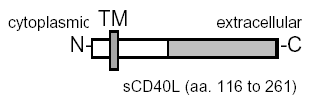
Produced in E. coli. The extracellular domain of human CD40L (CD154) (aa 116-261) is fused at the N-terminus to a linker peptide (6 aa) and a FLAG®-tag. |
| Specificity |
Binds to human CD40. |
| Technical Info / Product Notes |
Historical data has shown that CD40L stimulates growth of B cells. The activity of rhsCD40L increases 1’000-fold (stimulation in the ng/ml range) in the presence of cross-linking enhancer (see Set Prod. No. ALX-850-064). For stimulation of mouse cells via CD40 use CD40L, Soluble (mouse) (recombinant) (Prod. No. ALX-522-070 or ALX-850-075). FLAG is a registered trademark of Sigma-Aldrich Co. |
| UniProt ID |
P29965 |
Handling & Storage
| Use/Stability |
Stable for at least 6 months after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
|---|---|
| Handling |
Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. After reconstitution, prepare aliquots and store at -20°C. |
| Long Term Storage |
-20°C |
| Shipping |
Blue Ice |
| Regulatory Status |
RUO – Research Use Only |
|---|
- Epstein-Barr virus-transformed B-cells from a hypoxia model of the germinal center requires external unsaturated fatty acids.: Havey, L., You, H., et al.; PLoS Pathog. 21, e1013694 (2025), Abstract
- Nef defect attenuates HIV viremia and immune dysregulation in the bone marrow-liver-thymus-spleen (BLTS) humanized mouse model: S. Birada, et al.; Virology 598, 110192 (2024), Abstract
- Stage-Specific Non-Coding RNA Expression Patterns during In Vitro Human B Cell Differentiation into Antibody Secreting Plasma Cells: R.C. Tschumper, et al.; Noncoding RNA 8, 15 (2022), Abstract
- BTK inhibition limits B-cell–T-cell interaction through modulation of B-cell metabolism: implications for multiple sclerosis therapy: R. Li, et al.; Acta Neuropathol. 143, 505 (2022), Abstract
- Human T-bet+ B cell development is associated with BTK activity and suppressed by evobrutinib: L. Rijvers, et al.; JCI Insight 7, e160909 (2022), Abstract
- Temporal multiomic modeling reveals a B-cell receptor proliferative program in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: C. Schleiss, et al.; Leukemia 35, 1463 (2021), Abstract — Full Text
- Identification and validation of expressed HLA-binding breast cancer neoepitopes for potential use in individualized cancer therapy: H. Reimann, et al.; J. Immunother. Cancer 9, 2605 (2021), Abstract
- BCR-associated factors driving chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells proliferation ex vivo: C. Schleiss, et al.; Sci. Rep. 9, 701 (2020), Abstract — Full Text
- Platelets Fuel the Inflammasome Activation of Innate Immune Cells: Rolfes, V., Ribeiro, L. S., et al.; Cell Rep. 31, 107615 (2020), Abstract
- Autophagy in T cells from aged donors is maintained by spermidine and correlates with function and vaccine responses: Alsaleh, G., Panse, I., et al.; Elife 9, (2020), Abstract
- PD-1-expressing B cells suppress CD4+ and CD8+ T cells via PD-1/PD-L1-dependent pathway: X. Wang, et al.; Mol. Immunol. 109, 20 (2019), Abstract
- CD40-targeting KGYY15 peptides do not efficiently block the CD40-CD40L interaction: Bojadzic, D., Buchwald, P., et al.; Diabetologia 62, 2158 (2019), Abstract
- In vitro antineoplastic effects of auranofin in canine lymphoma cells: H. Zhang, et al.; BMC Cancer 18, 522 (2018), Abstract — Full Text
- Soluble CD40 ligand disrupts the blood-brain barrier and exacerbates inflammation in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis: H. Masuda, et al.; J. Neuroimmunol. 316, 117 (2018), Abstract
- Artesunate shows potent anti-tumor activity in B-cell lymphoma: T. K. Vatsveen, et al.; J. Hematol. Oncol. 11, 23 (2018), Abstract — Full Text
- CD40 signaling in Graves’ disease is mediated through canonical and non-canonical thyroidal NF-κB activation: H.J. Lee, et al.; Endocrinology 158, 410 (2017), Abstract
- B-cell activation with CD40L or CpG measures the function of B-cell subsets and identifies specific defects in immunodeficient patients: E. Marasco, et al.; Eur. J. Immunol. 47, 131 (2017), Application(s): Human PBMC culture, Abstract — Full Text
- Soluble CD40 ligand contributes to dendritic cell-mediated T-cell dysfunction in HIV-1 infection: E.A. Miller, et al.; AIDS 29, 1287 (2015), Application(s): WB, Abstract — Full Text
- Identification and characterization of agonist epitopes of the MUC1-C oncoprotein: C. Jochems, et al.; Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 63, 161 (2014), Application(s): Stimulation of dendritic cells, Abstract
- Suppression by Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol of the Primary Immunoglobulin M Response by Human Peripheral Blood B cells is Associated with Impaired STAT3 Activation: T. Ngaotepprutaram, et al.; Toxicology 310, 84 (2013), Application(s): Flow Cytometry, Abstract — Full Text
- Immunological targeting of tumor cells undergoing an epithelial-mesenchymal transition via a recombinant brachyury-yeast vaccine: D.H. Hamilton, et al.; Oncotarget 4, 1777 (2013), Application(s): Stimulation of dendritic cells, Abstract — Full Text
- Elevated serum soluble CD40 ligand in cancer patients may play an immunosuppressive role: J. Huang, et al.; Blood 120, 3030 (2012), Application(s): Cell Culture, Abstract — Full Text
- Leukotriene C4 induces migration of human monocyte-derived dendritic cells without loss of immunostimulatory function: J. Dannull, et al.; Blood 119, 3113 (2012), Application(s): Intracellular calcium release in human monocyte derived dendritic cells with Tecan Infinite plate reader, Abstract — Full Text
- Targeting HIV-1 Envelope Glycoprotein Trimers to B Cells by Using APRIL Improves Antibody Responses: M. Melchers, et al.; J. Virol. 86, 2488 (2012), Application(s): Cell Culture, Abstract — Full Text
- The death domain kinase RIP1 links the immunoregulatory CD40 receptor to apoptotic signaling in carcinomas: P. G. Knox, et al.; J. Cell Biol. 192, 391 (2011), Abstract — Full Text
- Primary and malignant cholangiocytes undergo CD40 mediated Fas dependent apoptosis, but are insensitive to direct activation with exogenous Fas ligand: E.H. Humphreys, et al.; PLoS One 5, e14037 (2010), Abstract — Full Text
- Adenovirus delivery of human CD40 ligand gene confers direct therapeutic effects on carcinomas: L. Vardouli, et al.; Cancer Gene Ther. 16, 848 (2009), Application(s): Cell Culture, Abstract
- C4b Binding Protein Binds to CD154 Preventing CD40 Mediated Cholangiocyte Apoptosis: A Novel Link between Complement and Epithelial Cell Survival: K.T. Williams, et al.; PLoS ONE 2, e159 (2007), Application(s): Cell Culture, Abstract — Full Text
- Induction of Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis by the Proteasome Inhibitor PS-341 in Hodgkin Disease Cell Lines Is Independent of Inhibitor of Nuclear Factor-kappaB Mutations or Activation of the CD30, CD40, and RANK Receptors: B. Zheng, et al.; Clin. Cancer Res. 10, 3207 (2004), Abstract
- HIV-1 Nef intersects the macrophage CD40L signalling pathway to promote resting-cell infection: S. Swingler, et al.; Nature 424, 213 (2003), Abstract — Full Text
- Platelet-Activating Factor Mediates CD40-Dependent Angiogenesis and Endothelial-Smooth Muscle Cell Interaction: S. Russo, et al.; J. Immunol. 171, 5489 (2003), Abstract
- Synergy between CD40 ligation and IL-4 on fibroblast proliferation involves IL-4 receptor signaling: S.P. Atamas, et al.; J. Immunol. 168, 1139 (2002), Abstract
- Suppression of IL-12 Production by Soluble CD40 Ligand: Evidence for Involvement of the p44/42 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Pathway: M. Wittmann, et al.; J. Immunol. 168, 3793 (2002), Abstract
- Pro-inflammatory effect of TWEAK/Fn14 interaction on human umbilical vein endothelial cells: N. Harada, et al.; BBRC 299, 488 (2002), Abstract
- Histamine polarizes human dendritic cells into Th2 cell-promoting effector dendritic cells: G. Caron, et al.; J. Immunol. 167, 3682 (2001), Abstract
- Functional expression of receptor activator of nuclear factor kappaB in Hodgkin disease cell lines: P. Fiumara, et al.; Blood 98, 2784 (2001), Abstract — Full Text
- CD45 inhibits CD40L-induced microglial activation via negative regulation of the Src/p44/42 MAPK pathway: J. Tan, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 275, 37224 (2000), Abstract — Full Text
- Conversion of membrane-bound Fas(CD95) ligand to its soluble form is associated with downregulation of its proapoptotic activity and loss of liver toxicity: P. Schneider, et al.; J. Exp. Med. 187, 12051 (1998), Abstract — Full Text
Related Products

| Alternative Name | CD154, TNFSF 5, gp39 |
|---|---|
| Purity | ≥90% (SDS-PAGE) |
| Source | Produced in HEK 293 cells. The extracellular domain of mouse CD40L (CD154) (aa 115-260) is fused at the N-terminus to a linker peptide (8 aa) and a FLAG®-tag. |
MEGACD40L® Protein (soluble) (human), (recombinant)
ALX-522-110
High activity, high purity CD40L protein for co-stimulatory activation of an immune response

| Alternative Name | CD40L:ACRP30headless, CD154:ACRP30headless, TNFSF 5:ACRP30headless, gp39:ACRP30headless |
|---|---|
| Purity | ≥90% (SDS-PAGE) |
| Source | Produced in CHO cells. The extracellular domain of human CD40L (CD154) (aa 116-261) is fused at the N-terminus to mouse ACRP30headless (aa 18-111) and a FLAG®-tag. |
MEGACD40L® Protein (soluble) (mouse), (recombinant)
ALX-522-120
High activity, high purity CD40L protein for co-stimulatory activation of an immune response

| Alternative Name | CD40L:ACRP30headless, CD154:ACRP30headless, TNFSF5:ACRP30headless, gp39:ACRP30headless |
|---|---|
| Purity | ≥95% (SDS-PAGE) |
| Source | Produced in CHO cells. The extracellular domain of mouse CD40L (CD154) (aa 115-260) is fused at the N-terminus to mouse ACRP30headless (aa 18-111) and a FLAG®-tag. |
CD40L, soluble (human) (recombinant) set
ALX-850-064
Ligand plus enhancer for improved stability and enhanced immune activation.

| Purity | ≥95% (SDS-PAGE). |
|---|
Last modified: May 29, 2024
Datasheet, Manuals, SDS & CofA
Manuals And Inserts
Certificate of Analysis
Please enter the lot number as featured on the product label
SDS
Enzo Life Science provides GHS Compliant SDS
If your language is not available please fill out the SDS request form
 Lab Essentials
Lab Essentials AMPIVIEW® RNA probes
AMPIVIEW® RNA probes Enabling Your Projects
Enabling Your Projects  GMP Services
GMP Services Bulk Solutions
Bulk Solutions Research Travel Grant
Research Travel Grant Have You Published Using an Enzo Product?
Have You Published Using an Enzo Product?
