Shipping: Available products typically ship within 24/48h, via priority shipping.
Do you need support? Contact Customer Service or Technical Support.
Online Account
Access or Create Your Account
This antibody is covered by our Worry-Free Guarantee.
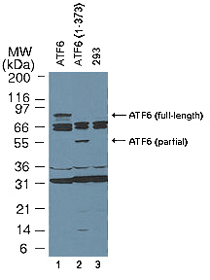
Figure 2: Western blot analysis of ATF6 using MAb to ATF6 (70B1413.1) (Prod. No. ALX-804-381). Method: Western blots were probed with 4µg/ml of MAb to ATF6 (70B1413.1), followed by an HRP-conjugated second step and visualized with PicoTect Western Blot Chemiluminescence Substrate. Film was exposed for 1 min. The top arrow corresponds to the ~90kDa form of ATF6 described as full-length in the literature. Lane 1: 293 cells transfected with full-length ATF6. Lane 2: 293 cells transfected with partial length ATF6 (aa 1-373). Lane 3: Untransfected 293 cells. The human full-length and partial length ATF6 plasmids are described in Luo and Lee (2002) [1].
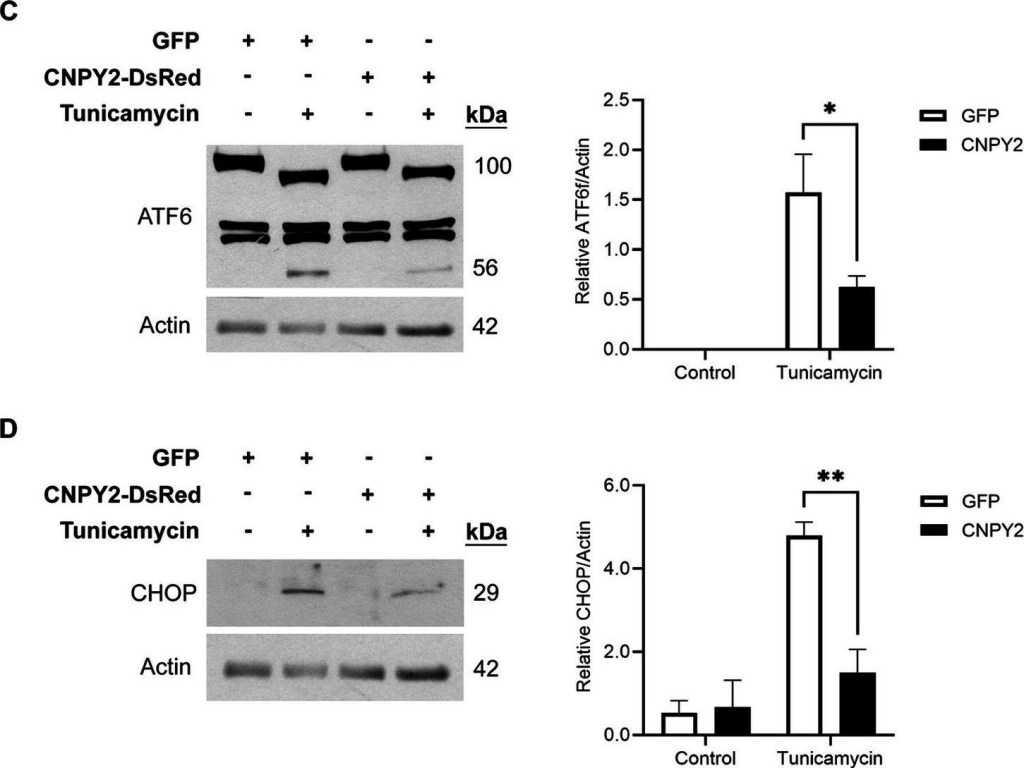
CNPY2 regulates UPR signaling pathways. SH-SY5Y cells were transfected with control plasmid or with CNPY2-Myc-DDK (A,B) or CNPY2-dsRed (C,D) expressing plasmid for 24 h and cells were further treated with 2.5 μg/mL tunicamycin (Tun) for different times followed by immunoblotting as described above using β-actin (42 kDa) or GAPHD (37 kDa) as controls. Left, immunoblots, Right, quantification. Values are means ± SD, n = 4–5. *p < 0.05 or **p < 0.01 for CNPY2 + Tun vs. Tun. (A,B) Tun was added for 6 h. The level of spliced XBP1 (XBP1s) was increased by Tun and was further elevated by CNPY2 expression (A). The level of phosphorylated eIF2α was increased by Tun but was not significantly affected by CNPY2 expression (B). (C) Tun was added for 16 h to study ATF6α signaling. The processing of ATF6α was induced by Tun as shown by the decrease in full length protein (100 kDa) and the appearance of the cleaved ATF6α fragment (56 kDa) in the immunoblots. CNPY2 expression reduced this ATF6α processing. (D) Tun was added for 24 h. The transcription factor CHOP (27 kDa) was induced by Tun and was decreased by CNPY2 expression.
Image collected and cropped by CiteAb under a CC-BY license from the following publication: CNPY2 protects against ER stress and is expressed by corticostriatal neurons together with CTIP2 in a mouse model of Huntington’s disease. Front Mol Neurosci (2024)


Product Details
| Alternative Name |
Activating transcription factor 6 |
|---|---|
| Application |
ChIP, ICC, IHC (PS), IP, WB |
| Application Notes |
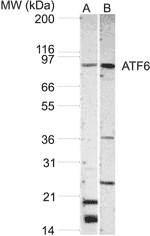
Detects bands of ~90kDa (full length ATF6) and ~50-70kDa (cleaved forms of ATF6) by Western blot. |
| Clone |
70B1413.1 |
| Formulation |
Liquid. In PBS containing 0.05% BSA and 0.05% sodium azide. |
| Host |
Mouse |
| Immunogen |
Partial human ATF6 (activating transcription factor 6) containing aa 1-273. |
| Isotype |
IgG1 |
| Purity Detail |
Protein G-affinity purified. |
| Recommendation Dilutions/Conditions |
Western Blot (1-5µg/ml)Suggested dilutions/conditions may not be available for all applications.Optimal conditions must be determined individually for each application. |
| Species Reactivity |
Hamster, Human, Mouse, Rabbit, Rat |
| UniProt ID |
P18850 |
| Worry-free Guarantee |
This antibody is covered by our Worry-Free Guarantee. |
Handling & Storage
| Use/Stability |
Stable for 6 months when stored at +4°C. |
|---|---|
| Handling |
Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. After opening, prepare aliquots and store at -20°C. |
| Short Term Storage |
+4°C |
| Long Term Storage |
-20°C |
| Shipping |
Blue Ice |
| Regulatory Status |
RUO – Research Use Only |
|---|
- Skeletal muscle atrophy induced by aging and disuse atrophy are strongly associated with the upregulation of the endoplasmic stress protein CHOP in rats: Michel, J. M., Godwin, J. S., et al.; Mol. Biol. Rep. 52, 322 (2025), Abstract
- CNPY2 protects against ER stress and is expressed by corticostriatal neurons together with CTIP2 in a mouse model of Huntington’s disease.: Scordino, M., Stepanova, P., et al.; Front. Mol. Neurosci. 17, 1473058 (2024), Application(s): WB, Abstract
- Combined prenatal to postnatal protein restriction augments protein quality control processes and proteolysis in the muscle of rat offspring: P. Savitikadi, et al.; J. Nutr. Biochem. 114, 109273 (2023), Abstract
- Pathological mechanisms of vacuolar aggregate myopathy arising from a Casq1 mutation: A.D. Hanna, et al.; FASEB J. 35, 21349 (2021), Abstract
- Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis and HCC in a Hyperphagic Mouse Accelerated by Western Diet: Ganguly, S., Muench, G. A., et al.; Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 12, 891 (2021), Abstract
- XBP1 signalling is essential for alleviating mutant protein aggregation in ER-stress related skeletal disease: Pirog, K. A., Dennis, E. P., et al.; PLoS Genet. 15, e1008215 (2019), Abstract
- Resveratrol triggers ER stress-mediated apoptosis by disrupting N-linked glycosylation of proteins in ovarian cancer cells: H. Gwak, et al.; Cancer Lett. 371, 347 (2016), Application(s): Activation of ER stress sensors triggers cellular adaptation, Abstract
- MpzR98C arrests Schwann cell development in a mouse model of early-onset Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 1B: Saporta, M. A., Shy, B. R., et al.; Brain 135, 2032 (2012), Abstract
- Response of myeloma to the proteasome inhibitor bortezomib is correlated with the unfolded protein response regulator XBP-1: S.C. Ling, et al.; Haematologica 97, 64 (2012), Abstract
- ATF6alpha induces XBP1-independent expansion of the endoplasmic reticulum: H. Bommiasamy, et al.; J. Cell Sci. 122, 1626 (2009), Abstract
- Eif-2a protects brainstem motoneurons in a murine model of sleep apnea: Y. Zhu, et al.; J. Neurosci. 28, 2168 (2008), Abstract
- Regulation of ERGIC-53 gene transcription in response to endoplasmic reticulum stress: M. Renna, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 282, 22499 (2007), Abstract — Full Text
- Acetaminophen induces ER dependent signaling in mouse liver: G. Nagy, et al.; Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 459, 273 (2007), Abstract
- Cardiomyocyte apoptosis in autoimmune cardiomyopathy: mediated via endoplasmic reticulum stress and exaggerated by norepinephrine: W. Mao, et al.; Am. J. Heart Circ. Physiol. 293, H1636 (2007), Abstract
- Endoplasmic reticulum stress and neurodegeneration in rats neonatally infected with borna disease virus: B.L. Williams and W.I. Lipkin; J. Virol. 80, 8613 (2006), Abstract
- Glia-specific activation of all pathways of the unfolded protein response in vanishing white matter disease: B. van Kollenburg, et al.; J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 65, 707 (2006), Abstract
- Flavivirus infection activates the XBP1 pathway of the unfolded protein response to cope with endoplasmic reticulum stress: C.Y. Yu, et al.; J. Virol. 80, 11868 (2006), Abstract — Full Text
- Dynamic recruitment of transcription factors and epigenetic changes on the ER stress response gene promoters: G. Donati, et al.; Nucleic Acids Res. 34, 3116 (2006), Abstract — Full Text
- Intrinsic capacities of molecular sensors of the unfolded protein response to sense alternate forms of endoplasmic reticulum stress: J.B. DuRose, et al.; Mol. Biol. Cell 17, 3095 (2006), Abstract — Full Text
- Intramembrane proteolytic cleavage by human signal peptide peptidase like 3 and malaria signal peptide peptidase: A.C. Nyborg, et al.; FASEB J. 20, 1671 (2006), Abstract
- Involvement of a novel Q-SNARE, D12, in quality control of the endomembrane system: A.J. Okumura, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 281, 4495 (2006), Abstract — Full Text
- Cytoprotective gene bi-1 is required for intrinsic protection from endoplasmic reticulum stress and ischemia-reperfusion injury: B. Bailly-Maitre, et al.; PNAS 103, 2809 (2006), Abstract — Full Text
- Nitric oxide-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress activates the expression of cargo receptor proteins and alters the glycoprotein transport to the Golgi complex: M. Renna, et al.; Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 38, 2040 (2006), Abstract
- 3,3’-diindolylmethane (DIM) and its derivatives induce apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cells through endoplasmic reticulum stress-dependent upregulation of DR5: M. Abdelrahim, et al.; Carcinogenesis 27, 717 (2006), Abstract — Full Text
- Spinal cord endoplasmic reticulum stress associated with a microsomal accumulation of mutant superoxide dismutase-1 in an ALS model: H. Kikuchi, et al.; PNAS 103, 6025 (2006), Abstract — Full Text
- The unfolded protein response modulates toxicity of the expanded glutamine androgen receptor: M. Thomas, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 280, 21264 (2005), Abstract — Full Text
- Underglycosylation of ATF6 as a novel sensing mechanism for activation of the unfolded protein response: M. Hong, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 279, 11354 (2004), Abstract — Full Text
- A signal peptide peptidase (SPP) reporter activity assay based on the cleavage of type II membrane protein substrates provides further evidence for an inverted orientation of the SPP active site relative to presenilin: A.C. Nyborg, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 279, 43148 (2004), Abstract — Full Text
- Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-infected primary effusion lymphoma has a plasma cell gene expression profile: R.G. Jenner, et al.; PNAS 100, 10399 (2003), Abstract
- Requirement of the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signalling pathway for the induction of the 78 kDa glucose-regulated protein/immunoglobulin heavy-chain binding protein by azetidine stress: activating transcription factor 6 as a target for stress-i: S. Luo and A.S. Lee; Biochem. J. 366, 787 (2002), Abstract — Full Text
Last modified: May 29, 2024
Datasheet, Manuals, SDS & CofA
Manuals And Inserts
Certificate of Analysis
Please enter the lot number as featured on the product label
SDS
Enzo Life Science provides GHS Compliant SDS
If your language is not available please fill out the SDS request form
 Lab Essentials
Lab Essentials AMPIVIEW® RNA probes
AMPIVIEW® RNA probes Enabling Your Projects
Enabling Your Projects  GMP Services
GMP Services Bulk Solutions
Bulk Solutions Research Travel Grant
Research Travel Grant Have You Published Using an Enzo Product?
Have You Published Using an Enzo Product?
