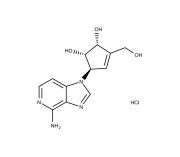
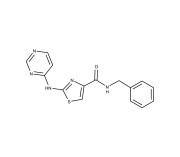
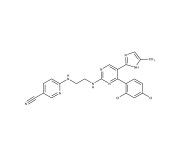
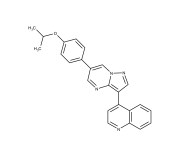
Enzo is excited to announce the launch of its new line of small molecules designed to play pivotal roles in the rapidly advancing field of cell therapy.
Our latest small molecules are engineered to support a wide range of scientific inquiries and therapeutic breakthroughs, enabling enhanced capabilities in stem cell and gene therapy. These small molecules are available as RUO and GMP, offering the highest quality and consistency for therapeutic development.
As an essential tool in biomedical research, small molecules enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of gene therapy by modulating cellular pathways and improving the delivery and expression of therapeutic genes. This significantly influences the behavior of cells, promoting survival, proliferation, and differentiation into a desired cell type. By fine-tuning cellular processes, small molecules play a critical role in optimizing the therapeutic outcomes of both cell and stem cell-based therapies. Our new offerings promise to provide the scientific community with the resources necessary to push the boundaries of therapeutic innovation.
“We are thrilled to introduce these new small molecules to support the development of cell therapies,” states Anthony Rampello, PhD, Product Manager, Small Molecule Chemistry at Enzo. “By improving cellular function and gene expression, we believe these molecules will accelerate progress in stem cell research and help deliver more effective treatments for a variety of conditions.”
Enzo remains committed to advancing healthcare through transformative science, and the launch of these small molecules marks a significant step forward in our mission to support the next generation of therapeutics.
Now for a limited time, Enzo Small Molecules are available at a 25% discount* for orders placed on Enzo.com with promo code SM25WEB2025 (excludes bulk and custom orders or GMP services. See terms and conditions for details). For more information about our small molecules and their potential applications, and our limited time discount offer, please visit Small Molecule Chemistry.
 Lab Essentials
Lab Essentials AMPIVIEW® RNA probes
AMPIVIEW® RNA probes Enabling Your Projects
Enabling Your Projects  GMP Services
GMP Services Bulk Solutions
Bulk Solutions Research Travel Grant
Research Travel Grant Have You Published Using an Enzo Product?
Have You Published Using an Enzo Product?