Multiplex Solutions for Spatial Biology

Multiplexing is essential to modern spatial biology, and Enzo delivers the tools to do it right.
In spatial biology, understanding the complex interplay between multiple biomolecules within a single sample is crucial. Multiplexing allows detection and analysis of several targets simultaneously, preserving samples while delivering more comprehensive data. Enzo’s advanced multiplexing tools are designed to simplify this process and provide unmatched accuracy.
Versatile solutions that can combine detection of multiple targets (ISH-ISH, ISH-IHC, ISH-IF, IF-IF, IHC-IHC, FISH)
Highly reproducible results, reducing false positives and enhancing research accuracy
Flexible and adaptable solutions
Multiplex Nucleic Acid and Protein to Monitor Neural Regeneration
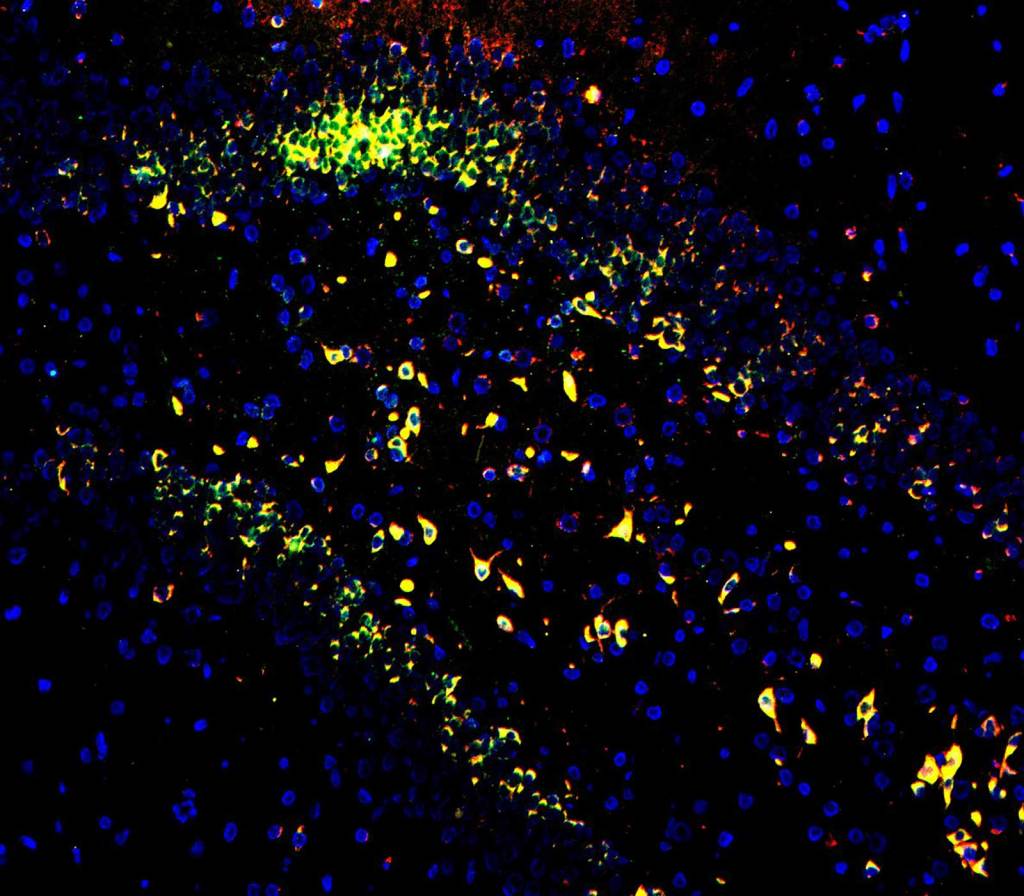
Nestin protein (red), long non-coding RNA NORAD (green), and circular RNA Circ018 (grey) detected in rat brain tissue with Nestin anitbody, AMPIVIEW® NORAD (AS) Fluorescein RNA Probes and AMPIVIEW® Circ018 (AS) Dig RNA Probes. DAPI (blue) was used as a nuclear marker. Co-localization of Nestin protein and NORAD is indicated by yellow signal.
Application Note
Detecting Non-Coding RNAs with AMPIVIEW® ISH Probes
Multiplex Detection of PD-1, PD-L1, and CD19 in Different Tissue Type
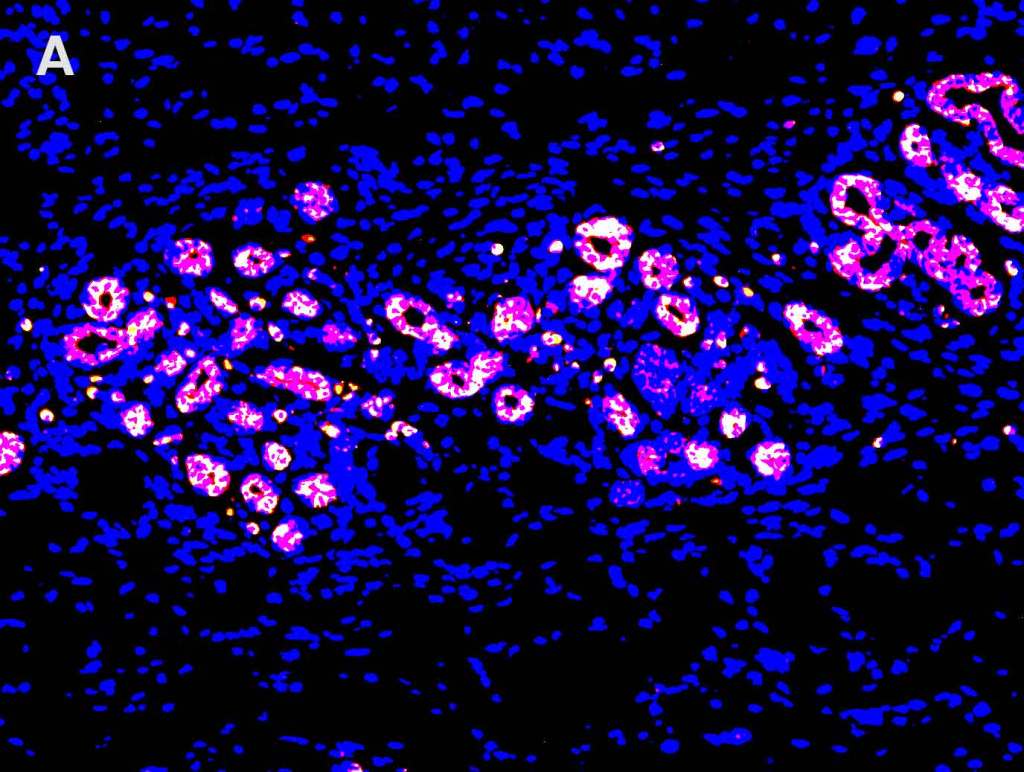
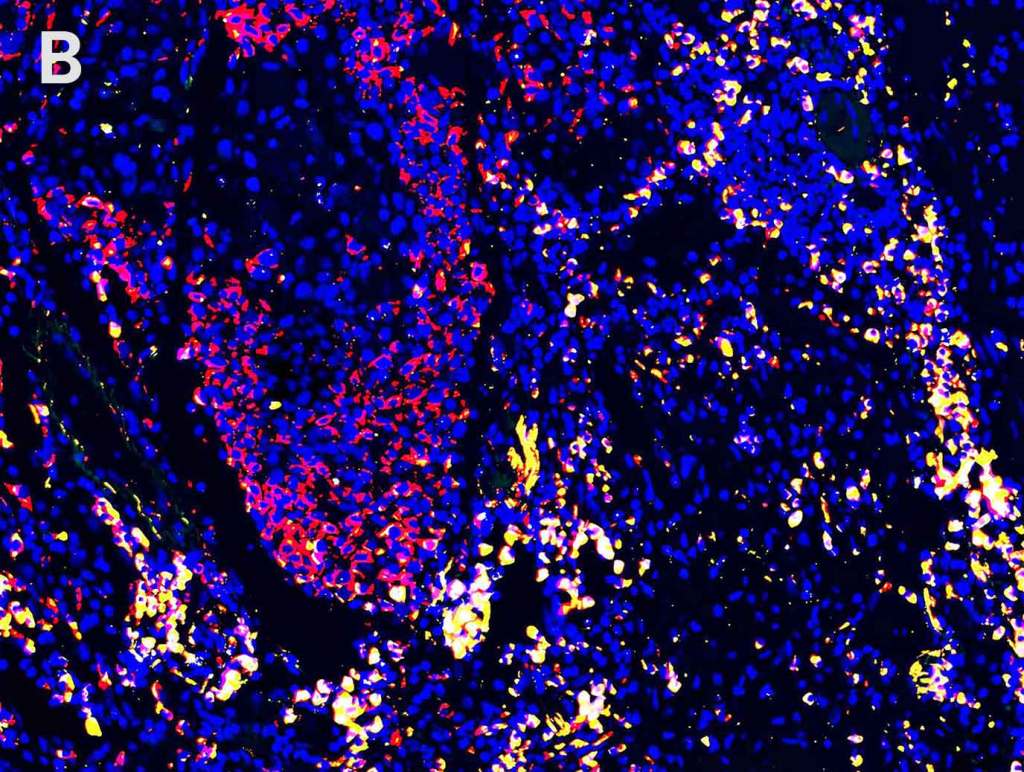
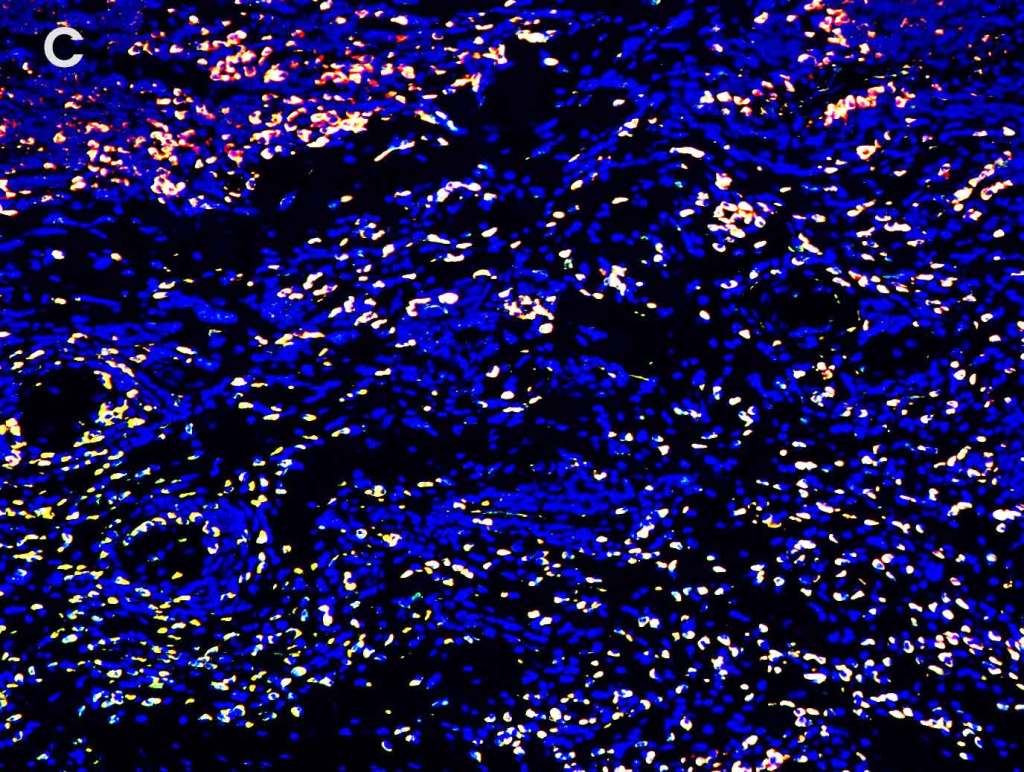
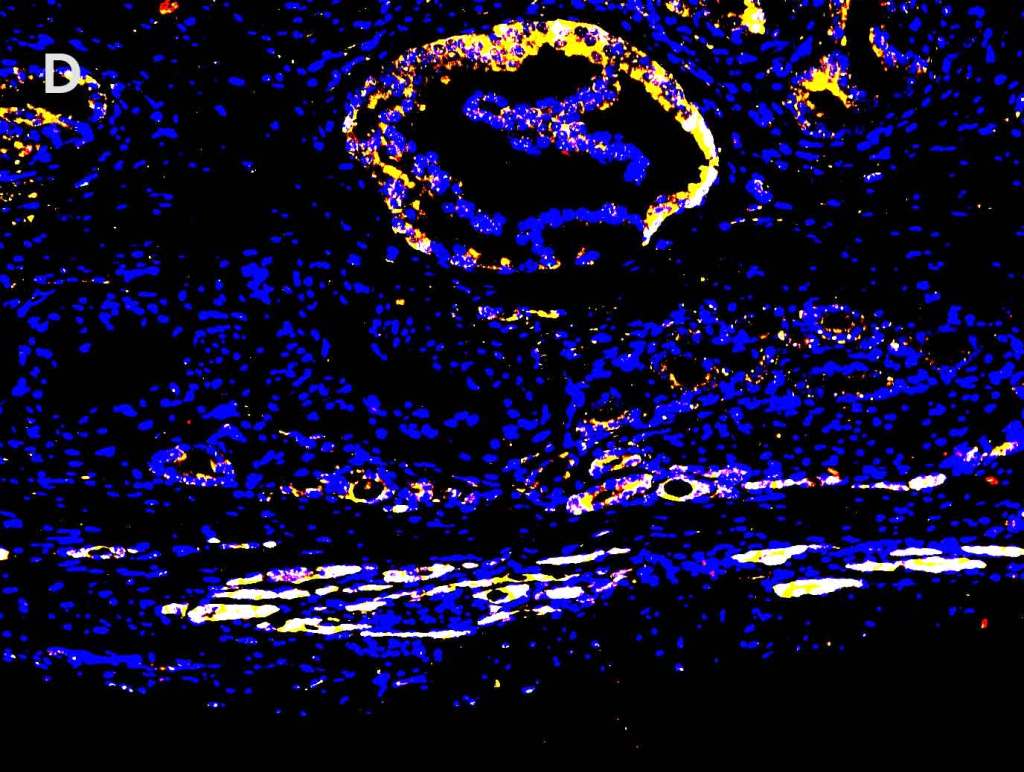
Detection of PD-1 (yellow), PD-L1 (red), and CD19 (green) in A. breast cancer tissue, B. lung carcinoma tissue, C. lymphoma tissue and D. prostate cancer tissue with AMPIVIEW® PD-1 (AS) Dig RNA Probes, AMPIVIEW® PD-L1 (AS) DNP RNA Probes, AMPIVIEW® CD19 (AS) Dig RNA Probes, and DAPI was used as nuclear marker (blue).
Multiplex Detection of HPV, Ki67, and p16 in Cervical Cancer Tissue
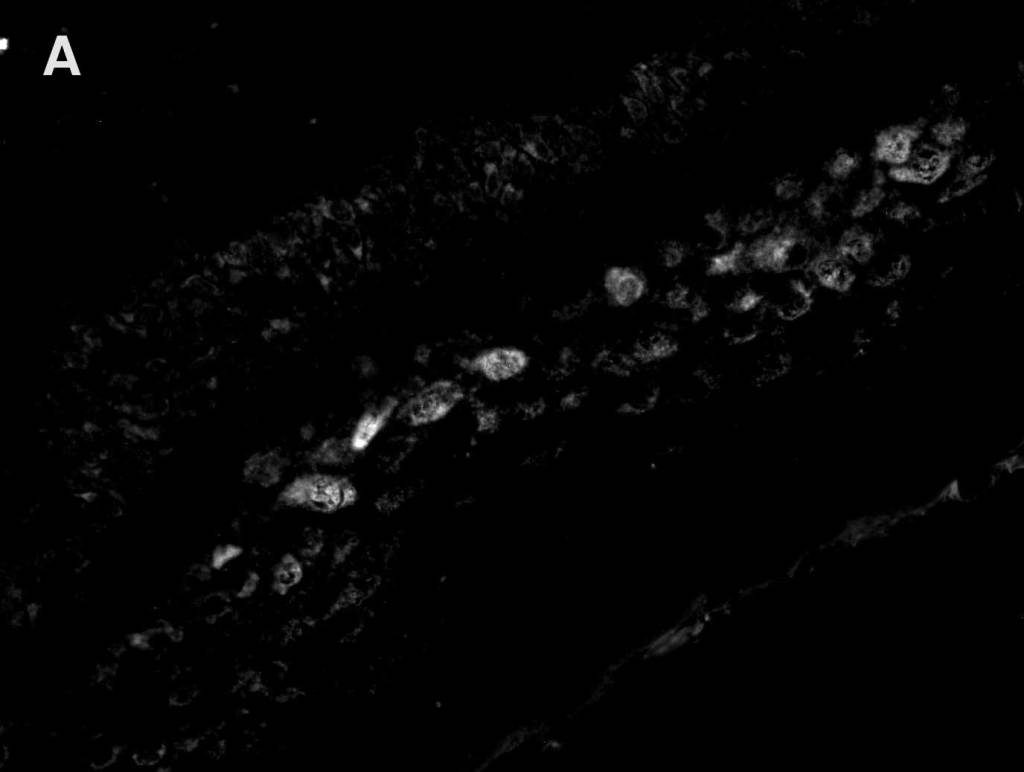
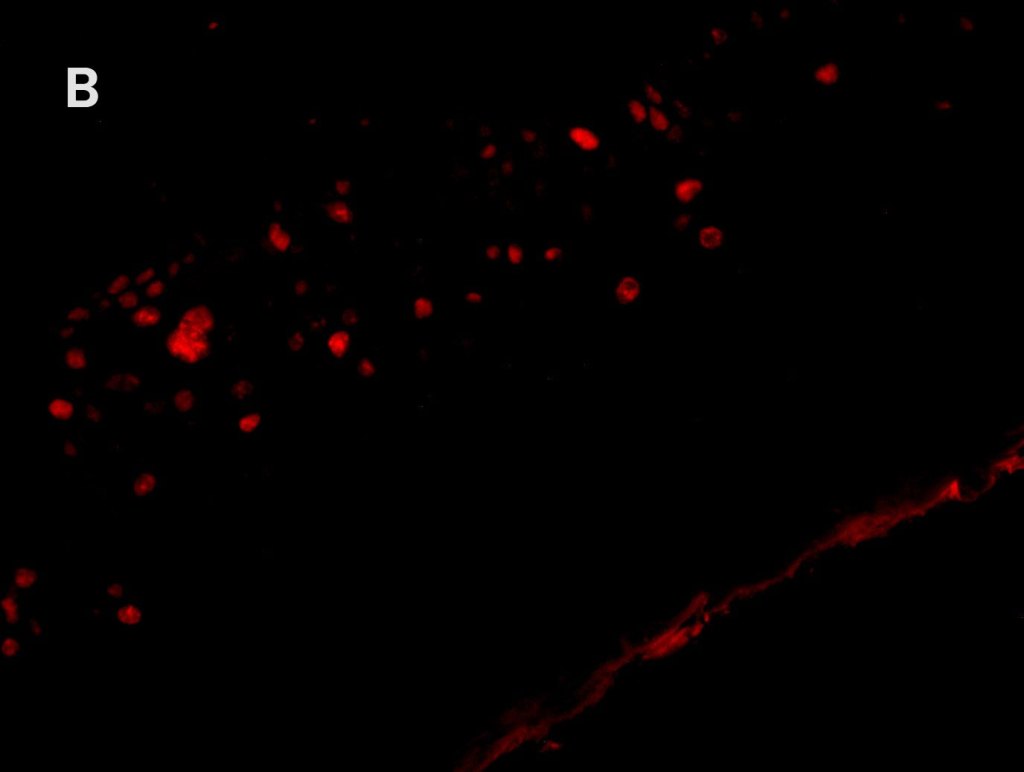
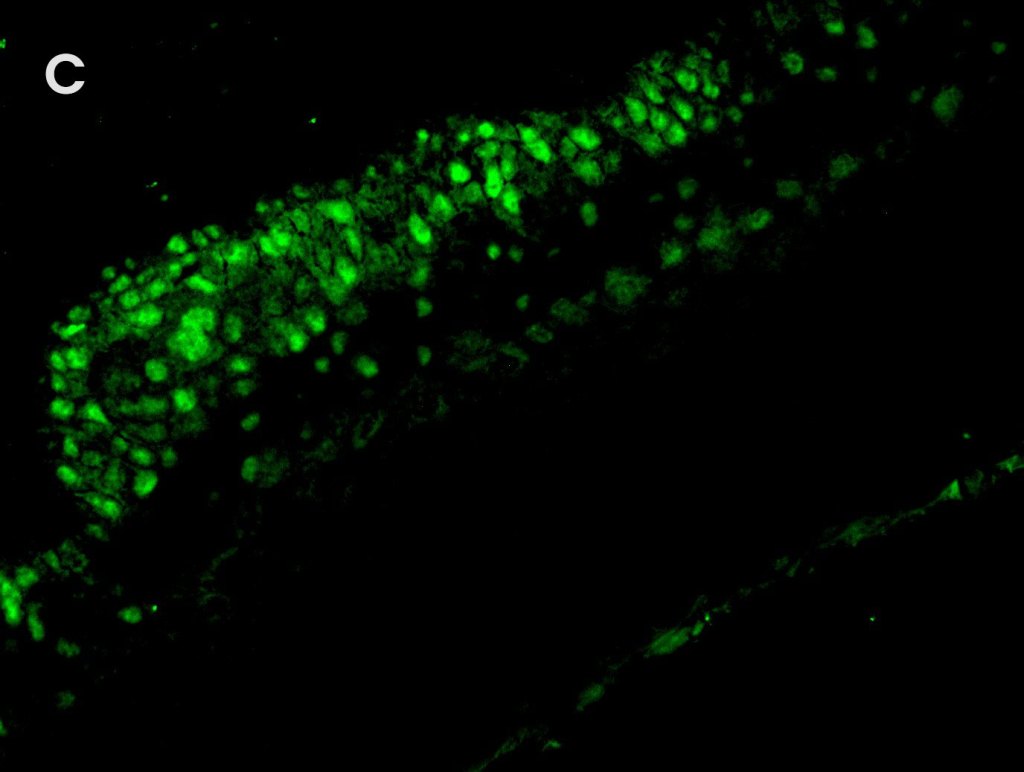
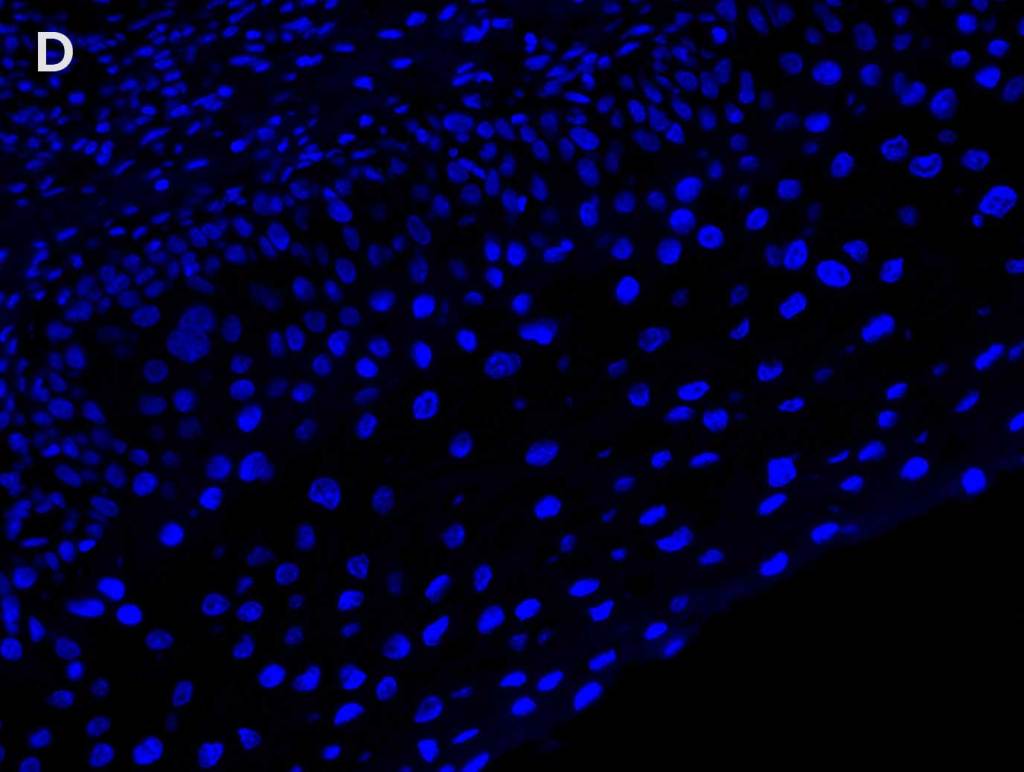
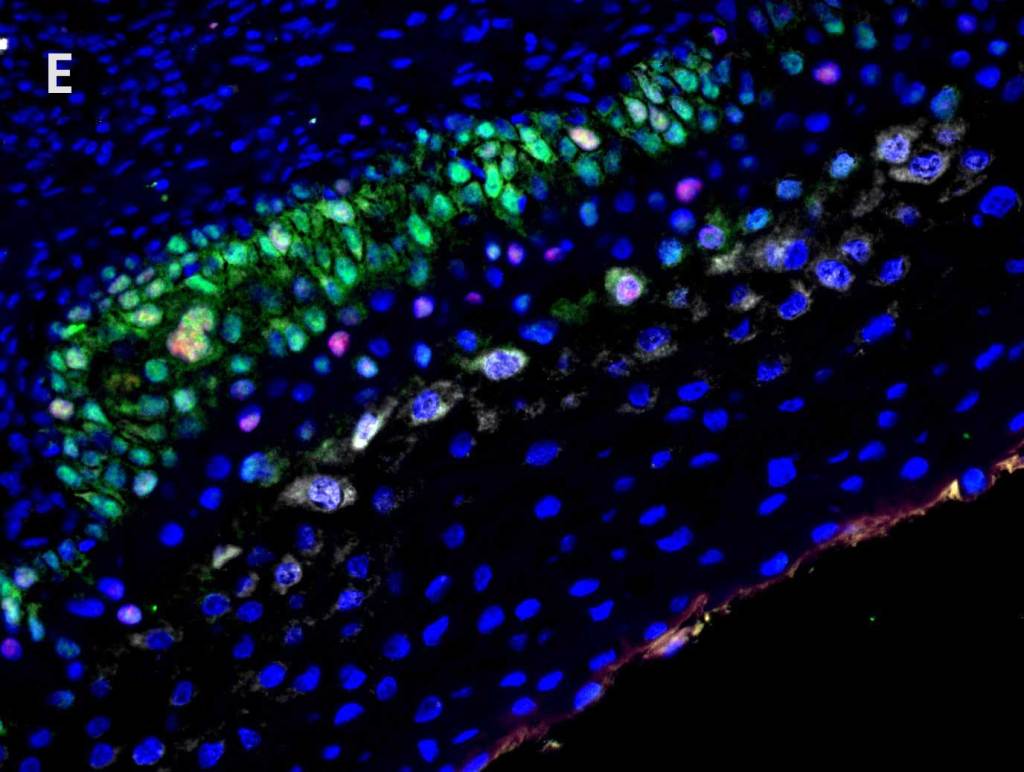
Detection of A. high-risk HPV (gray) with AMPIVIEW® High Risk (AS) DNP RNA Probes, B. Ki 67 (red) with Ki67 monoclonal antibody, C. p16 (green) with p16INK4a monoclonal antibody, D. nuclear marker (blue) stained with DAPI. E. Positive correlation between Ki67, p16, and HPV infection can be seen (white) in the merged image.
Multiplex Detection of MAP2, α-Synuclein and aggressomes Show that α-Synuclein Fibrilization Promotes Apoptosis
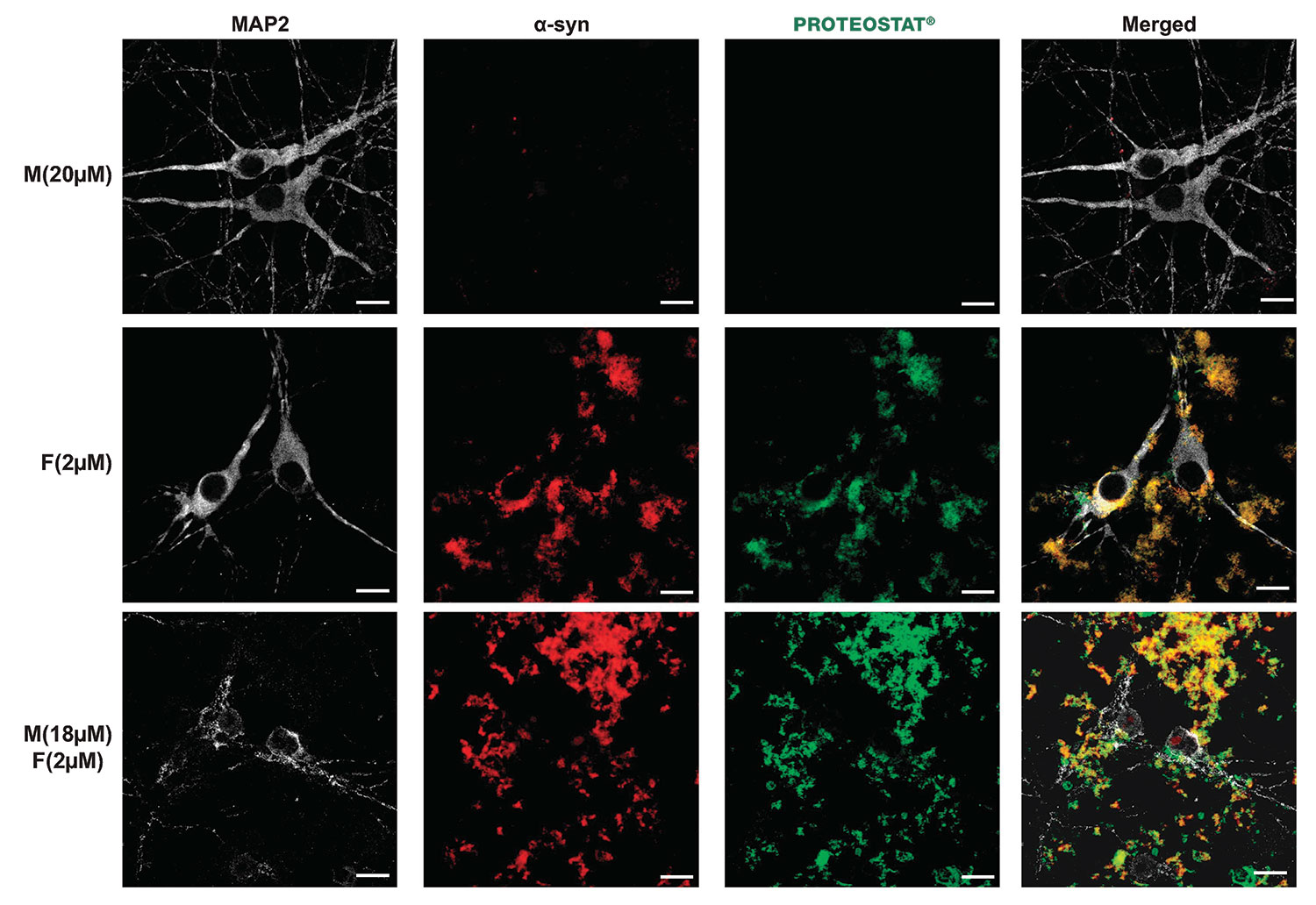
α-Syn mixture forms growing aggregates at the cell plasma membrane of hippocampal primary neurons. Hippocampal primary neurons were treated with Tris buffer (negative control) or α-syn species for the indicated times. After 3 days, primary hippocampal neurons were washed 3 times before fixation, stained with the proteostat dye to specifically detect aggregates and immunostained against α-syn (red) and against MAP2, a specific neuronal marker (gray). Scale bars= 10 μm.
Mahul-Mellier AL,et al. Cell Death Differ. 2015 Dec;22(12):2107-22. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2015.79.
Epub 2015 Jul 3. PMID: 26138444; PMCID: PMC4816119.
Multiplex Detection of Aggresomes and p62 in HeLa Cells
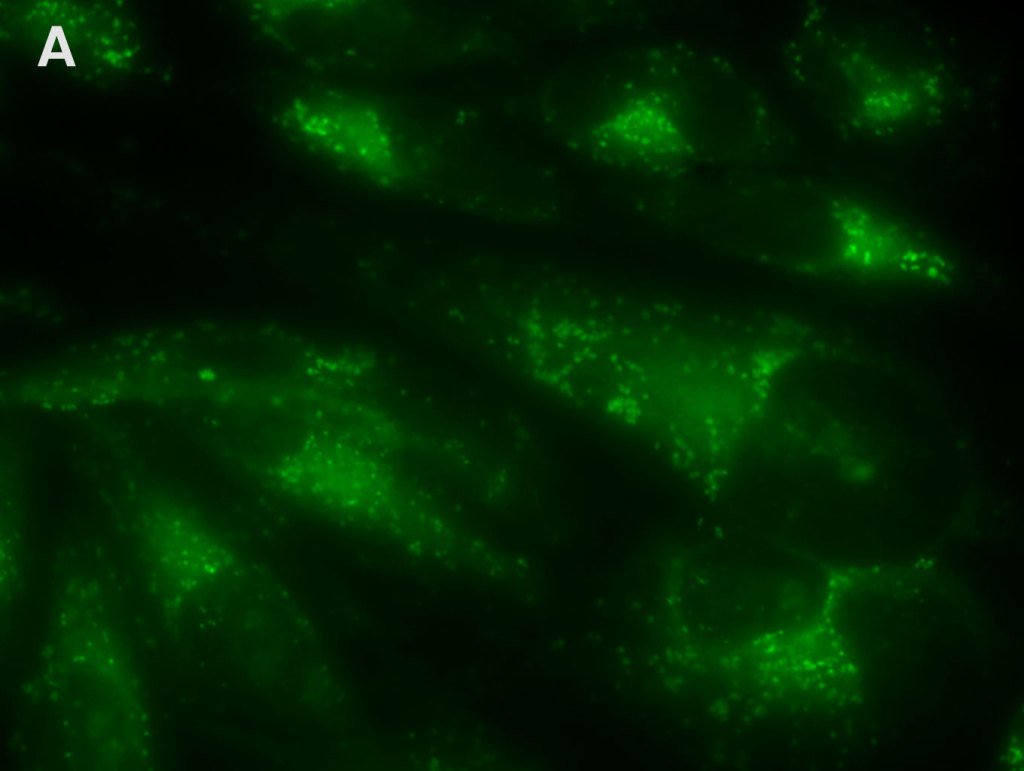
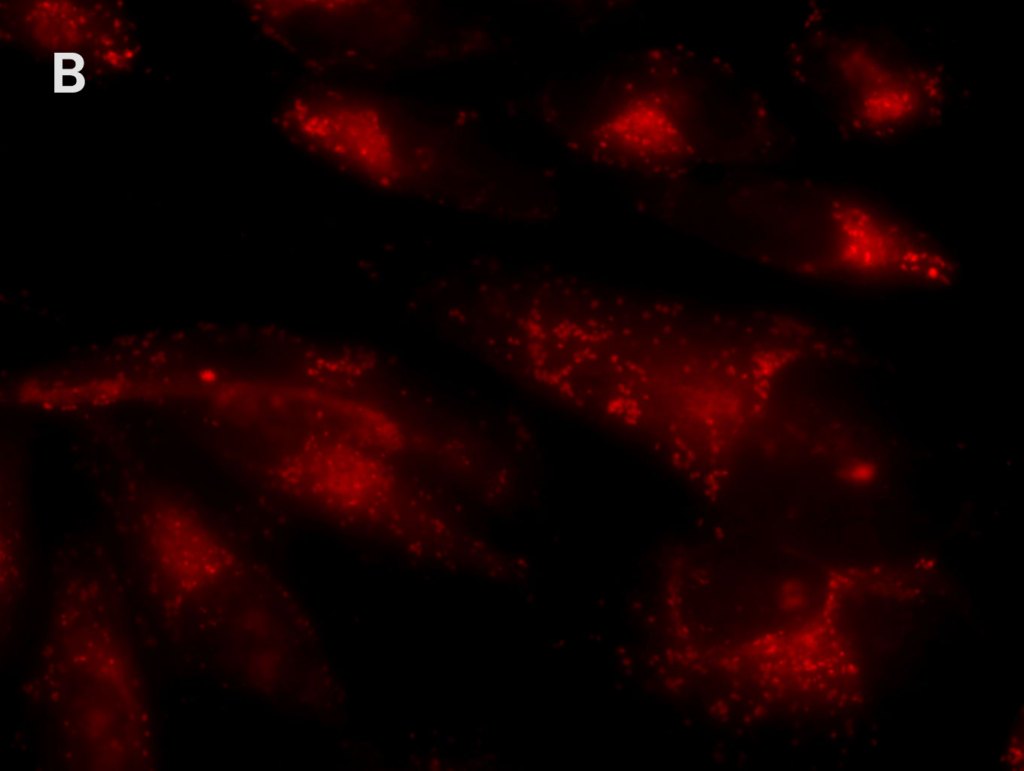
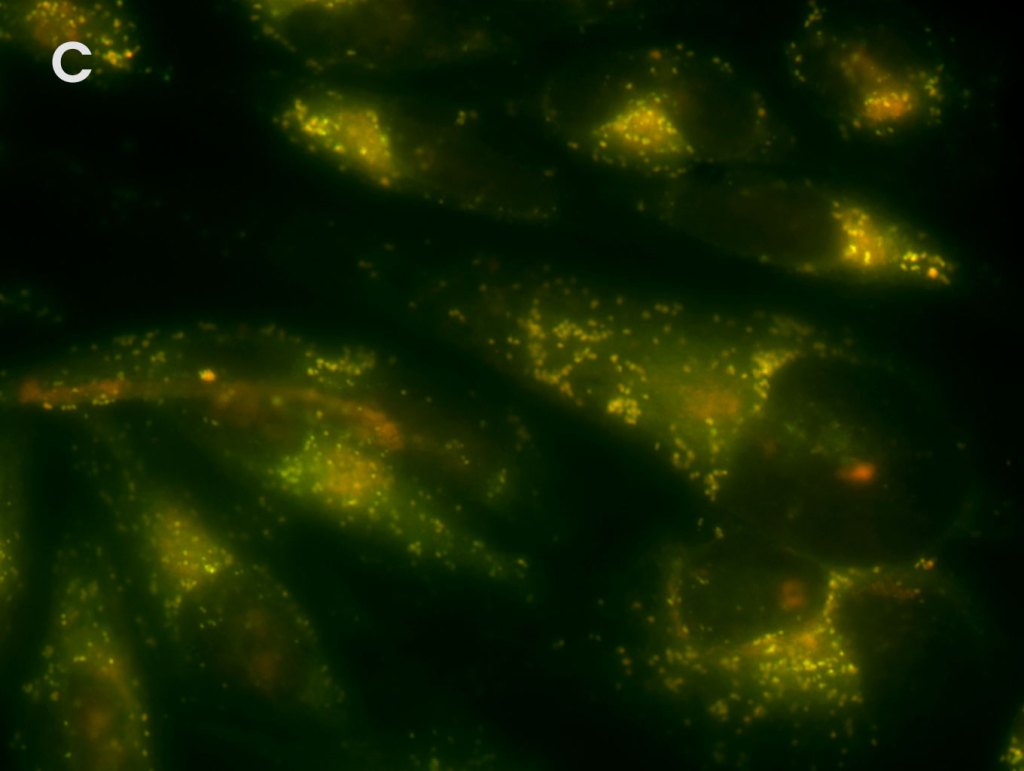
Detection of aggresomes in HeLa cells, treated with proteosome inhibitor MG-132 for 12 hours with (A) PROTEOSTAT® Aggresome Detection Kit (ENZ-51035) (red), (B) aggresome marker p62 antibody conjugated with fluorescein (green). (C) Composite image shows co-localization of aggresomes and p62 (yellow).
High-Fidelity Detection of Organelle Integrity with ORGANELLE-ID-RGB® III Assay Kit
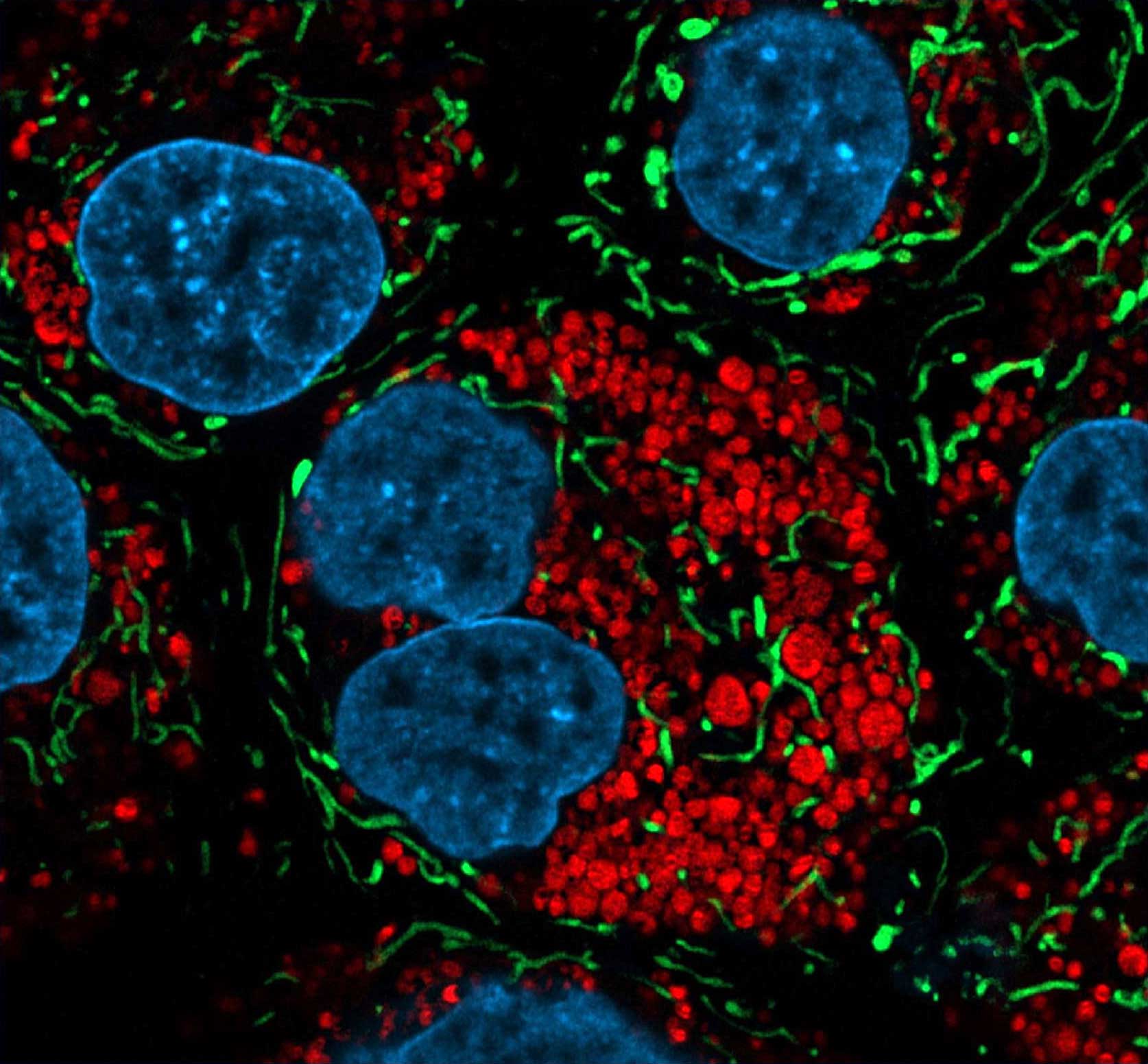
Mitochondria (green), lysosomes (red), and nucleus (blue) stained in MDCK cells with MITO-ID(R) Green (ENZ-51022), LYSO-ID Red (ENZ-51005), and DAPI. Courtesy of Dr. Randy Stout from New York Institute of Technology.
 Lab Essentials
Lab Essentials AMPIVIEW® RNA probes
AMPIVIEW® RNA probes Enabling Your Projects
Enabling Your Projects  GMP Services
GMP Services Bulk Solutions
Bulk Solutions Research Travel Grant
Research Travel Grant Have You Published Using an Enzo Product?
Have You Published Using an Enzo Product?