Karine Durand1, Rosaria Esposito2, Morgan Mathieu2, Sylvie Bourthoumieu1
1University Hospital of Limoges, France;
2Enzo Life Sciences, Lausen, Switzerland
INTRODUCTION
Microarray-based comparative genomic hybridization (array CGH) is a fast genome-wide screening tool for the high resolution detection of chromosomal anomalies in the form of copy number variations (CNVs).
In the oncology field, aCGH represents a valuable prognostic tool. It allows the identification of the genetic alterations characterizing the tumor of a specific patient, giving precious information on its evolution, and facilitating the choice of the best treatment. However, biopsies are usually preserved in a formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) form. Both the quantity and the quality of the DNA extracted from FFPE tissues are variable, making the analysis by CGH of these specimens challenging.
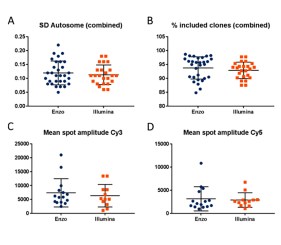
The cytogenetic service at the University Hospital of Limoges carries out hundreds of prenatal, postnatal, and oncological CGH tests per year on a variety of specimens, including amniotic fluid, blood, and FFPE tissues. The objective of this study was to test Enzo’s CYTAG® SuperCGH Labeling Kit with DNA extracted from oncological FFPE tissues, identifying the best labeling protocol to optimize the results
Download this Application Note
Latest Articles



 Lab Essentials
Lab Essentials AMPIVIEW® RNA probes
AMPIVIEW® RNA probes Enabling Your Projects
Enabling Your Projects  GMP Services
GMP Services Bulk Solutions
Bulk Solutions Research Travel Grant
Research Travel Grant Have You Published Using an Enzo Product?
Have You Published Using an Enzo Product?