Olivier Pichon1, Morgan Mathieu2
1Service de Génétique Médicale, CHU Nantes, France
2Enzo Life Sciences, Lausen, Switzerland
INTRODUCTION
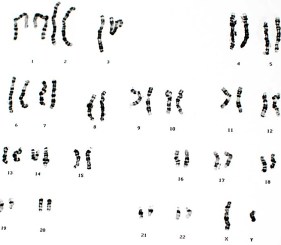
Microarray-based comparative genomic hybridization (array CGH) is a fast genome-wide screening tool for the detection of a large number of chromosomal aberrations in the form of copy number variations. This technology has been used extensively in clinical settings including postnatal diagnostics and oncological prognostics. It is based on the fluorescent labeling of genomic DNA and the co-hybridization with normal reference DNA to probes spotted onto a glass slide or a chip. The combination of high resolution and robustness offers major advantages in choosing array CGH over traditional molecular biology techniques. Recent studies have, for example, demonstrated the ability of array CGH to detect submicroscopic chromosomal imbalances in the range of a few kilobases in 10-15% of patients with mental retardation and/or congenital defects. Since a simple DNA sample is required, an increasing number of cytogenetic facilities have implemented this technique not only for postnatal and oncological testing but also for prenatal testing.
Derivative log ratio (DLR) scores are a measurement of point-to-point consistency or noisiness in log ratio data. Low DLR scores reduce the need for experimental repeats and are key to the interpretation of CGH data. Low DLR scores are difficult to achieve, especially when dealing with challenging samples and small DNA quantities but can be directly correlated to the quality of the labeling. There is therefore a need for labeling tools allowing enhanced labeling efficiency, better dye incorporation, and superior DLR scores. Enzo Life Sciences’ CYTAG® SuperCGH Labeling Kit has been optimized to label as low as 50 ng of genomic DNA for dual sample CGH assays and was chosen for this study.
The cytogenetics laboratory of the CHU de Nantes (France) performs the cytogenetics analyses of prenatal, postnatal, and oncological samples. Karyotyping, fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH), and array CGH are techniques used on a regular basis to deliver cytogenetic diagnostics. Scientists working on the CGH platform have to rely on small amounts of genomic material, which are extracted and purified from a variety of samples such as amniotic fluid. The main objective of this study was to look at the compatibility of CYTAG® SuperCGH Labeling Kit from Enzo Life Sciences with DNA extracted from amniotic fluid. Chromosomal abnormalities were successfully identified in prenatal samples while demonstrating superior DLR scores (0.11-0.15).
Download this Application Note
Latest Articles



 Lab Essentials
Lab Essentials AMPIVIEW® RNA probes
AMPIVIEW® RNA probes Enabling Your Projects
Enabling Your Projects  GMP Services
GMP Services Bulk Solutions
Bulk Solutions Research Travel Grant
Research Travel Grant Have You Published Using an Enzo Product?
Have You Published Using an Enzo Product?