The eukaryotic nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) plays an important role in inflammation, autoimmune response, cell proliferation, and apoptosis by regulating the expression of genes involved in these processes. Misregulation of the NF-κB signal transduction pathway is observed in a variety of human cancers, especially those of lymphoid cell origin. The prototypical inducible NF-κB is a heterodimeric complex consisting of p50 and p65, which normally exists in the cytoplasm of the cell as an inactive form due to association with its major inhibitory protein, IκBα. IκBα prevents the transport of NF-κB into the nucleus by masking its nuclear localization signal. Activation of NF-κB by extracellular inducers depends on the phosphorylation and subsequent degradation of IκBα by the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway.
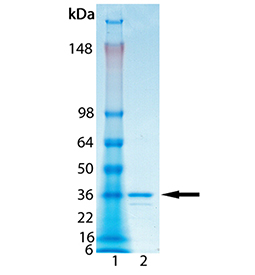
p65 subunit
The NF-κB p65 subunit is usually thought of as conferring the activation function of the NF-κB complex, though its capacity to associate with κB DNA in the absence of p50 and its potential utility as an independent transcription factor have also been demonstrated.
Shipping: Available products typically ship within 24/48h, via priority shipping.
Do you need support? Contact Customer Service or Technical Support.
Online Account
Access or Create Your Account
| Regulatory Status |
RUO – Research Use Only |
|---|
 AMPIVIEW® RNA probes
AMPIVIEW® RNA probes Enabling Your Projects
Enabling Your Projects  GMP Services
GMP Services Bulk Solutions
Bulk Solutions Research Travel Grant
Research Travel Grant Have You Published Using an Enzo Product?
Have You Published Using an Enzo Product?